Last year spring was my lifeline, as we experienced the world around us being thrown into disarray. This year spring was instead turned on its head, with changing weather patterns making it unpredictable and different from what we would usually expect at this time of year. A hot and stormy March, cold April, and wet May made nature emerge later, with spring events taking longer to arrive, and being anywhere up to 60 days late.
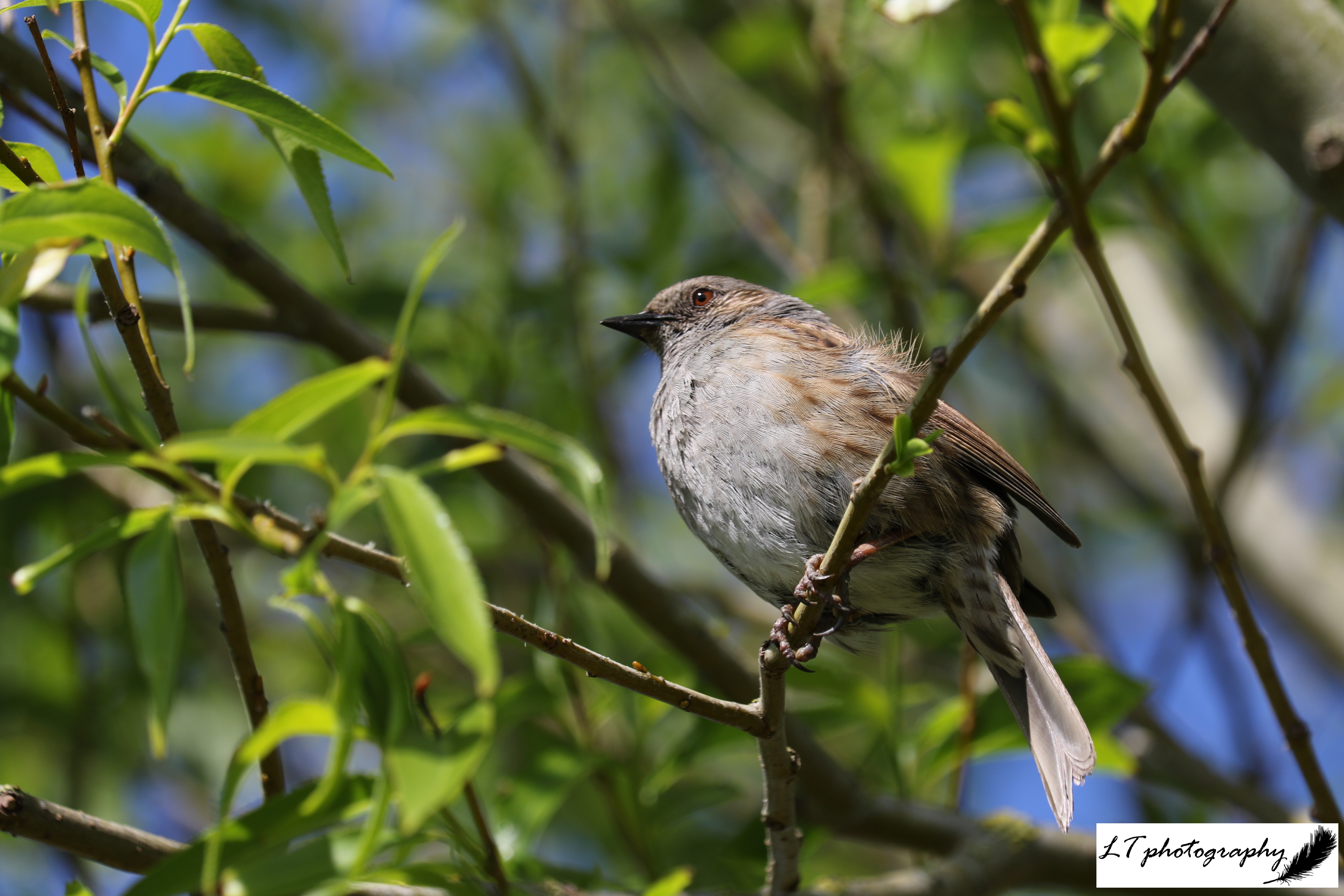
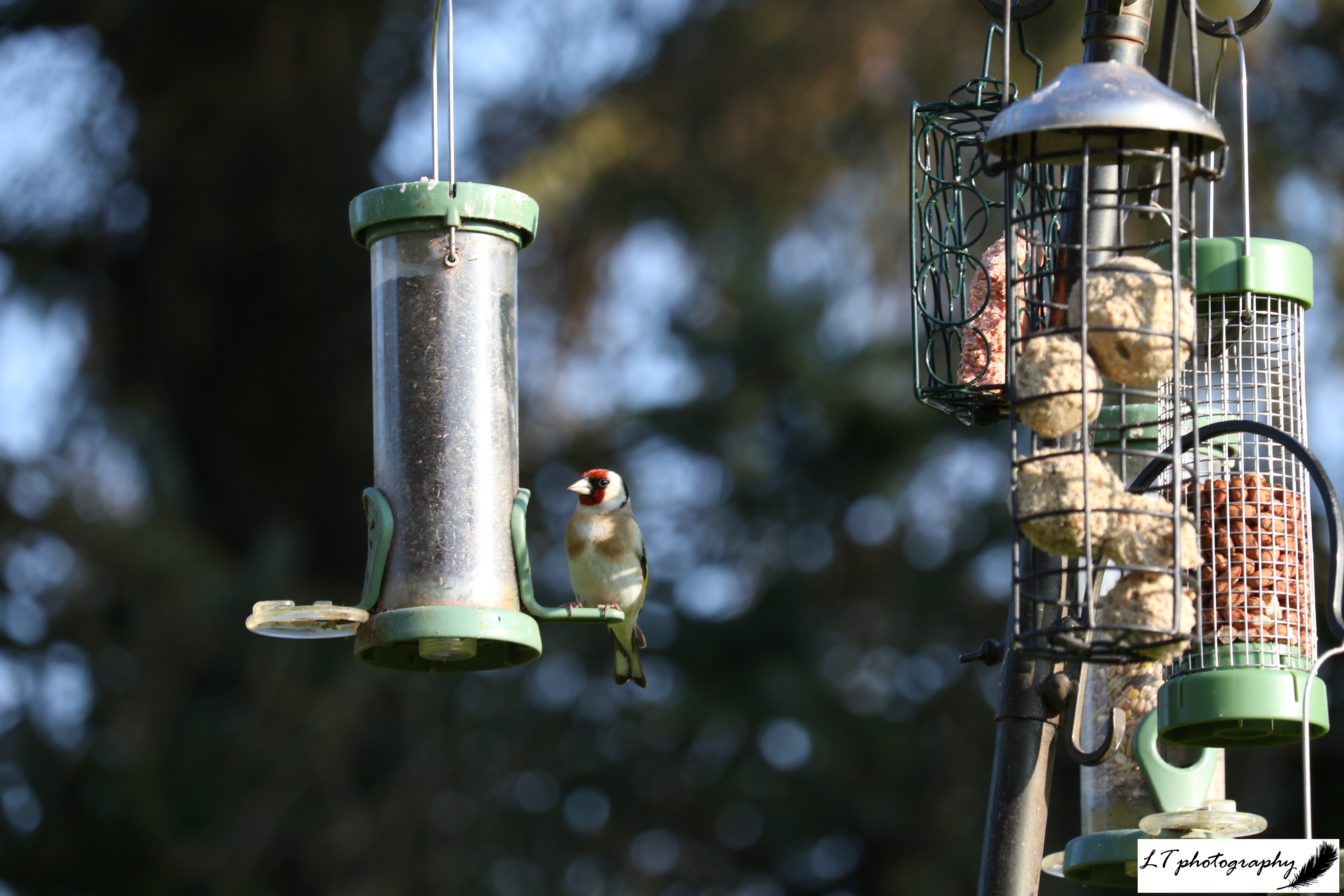
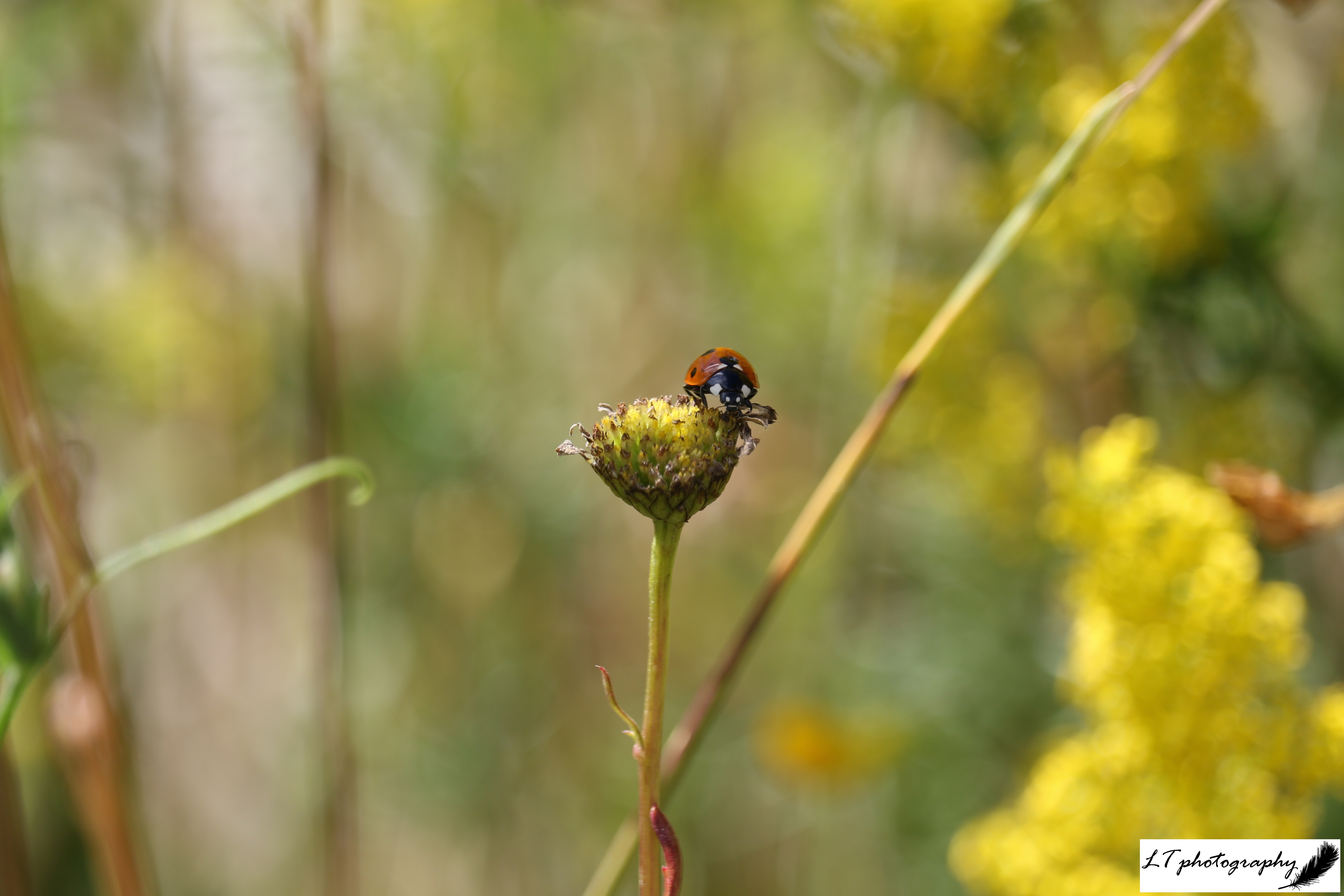
Still this year’s spring has been magnificent. Vibrant and colourful, it had much to be celebrated. My family’s farm in Dorset became full of new life, from blossoming trees and flowers, to fox cubs and leverets. Spring is unsurprisingly my favourite time of year, so this year I again made a point of getting out as much as possible to experience it, with my camera by my side. Here’s a look at some of my favourite photos from this spring, either for their aesthetic appeal, meaning to me, or overall joy factor.
Spring in Photos 2021
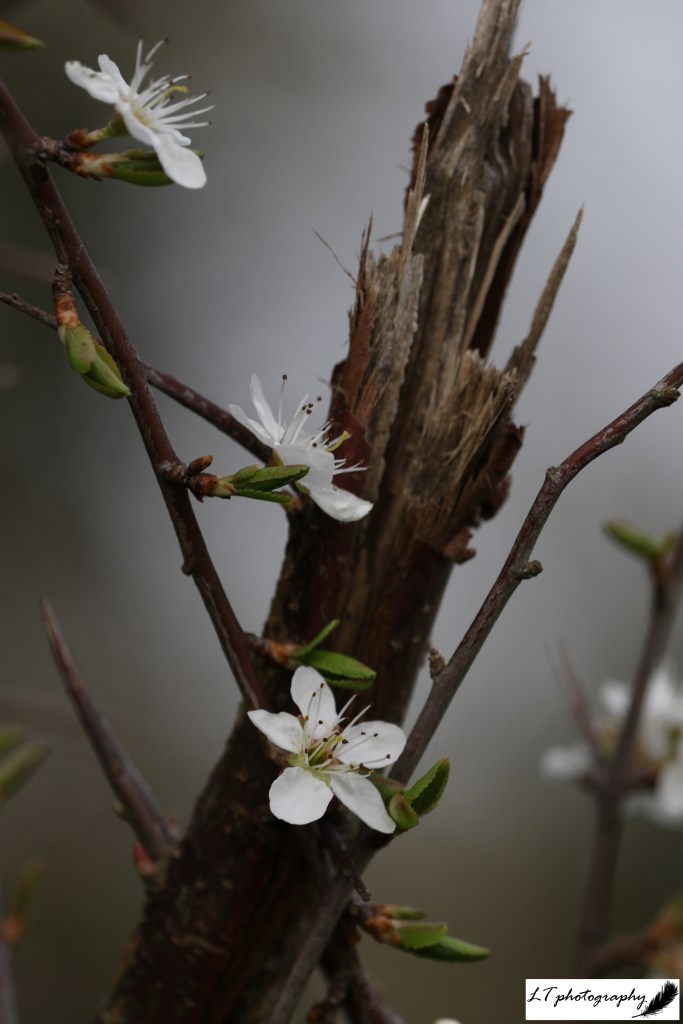
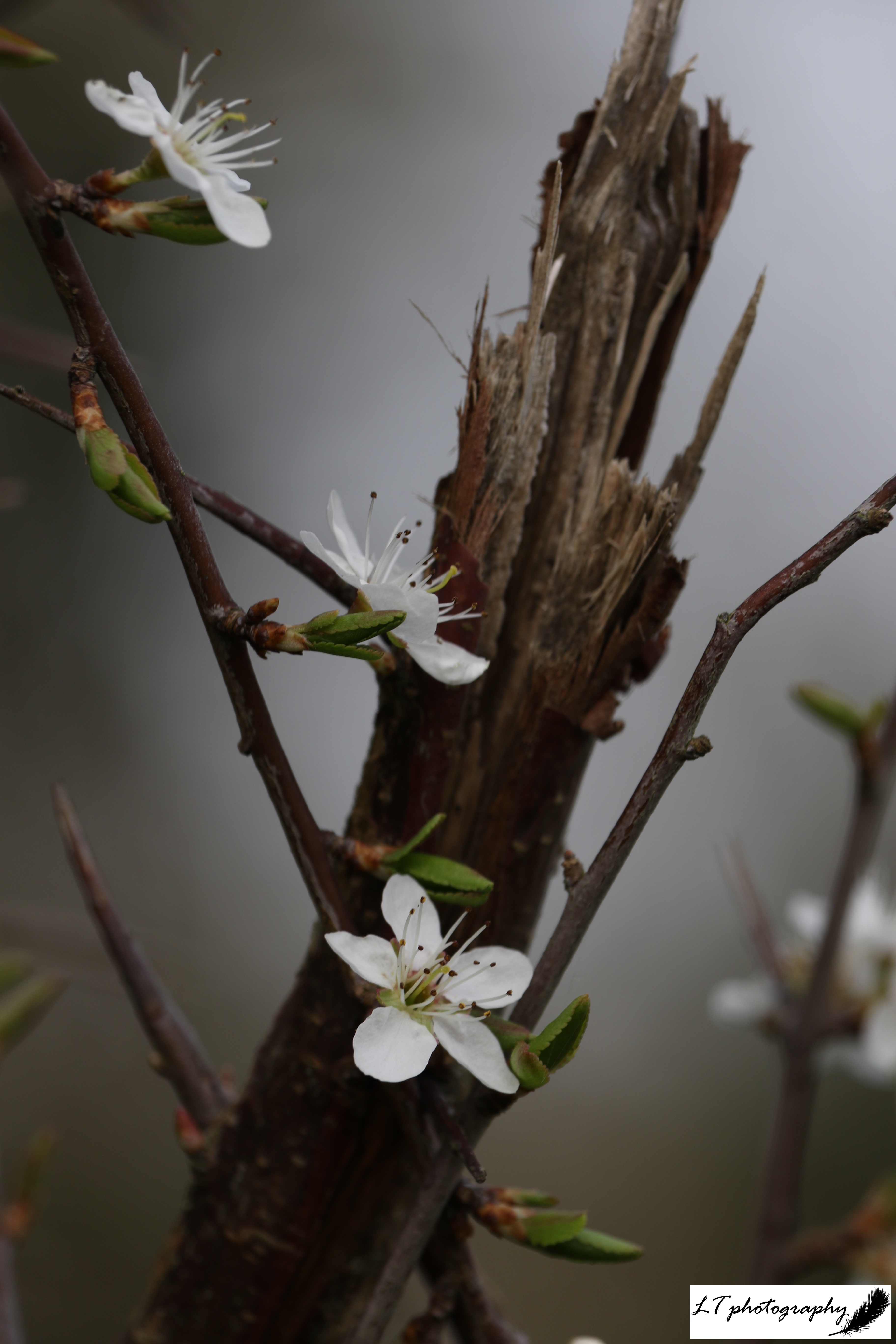
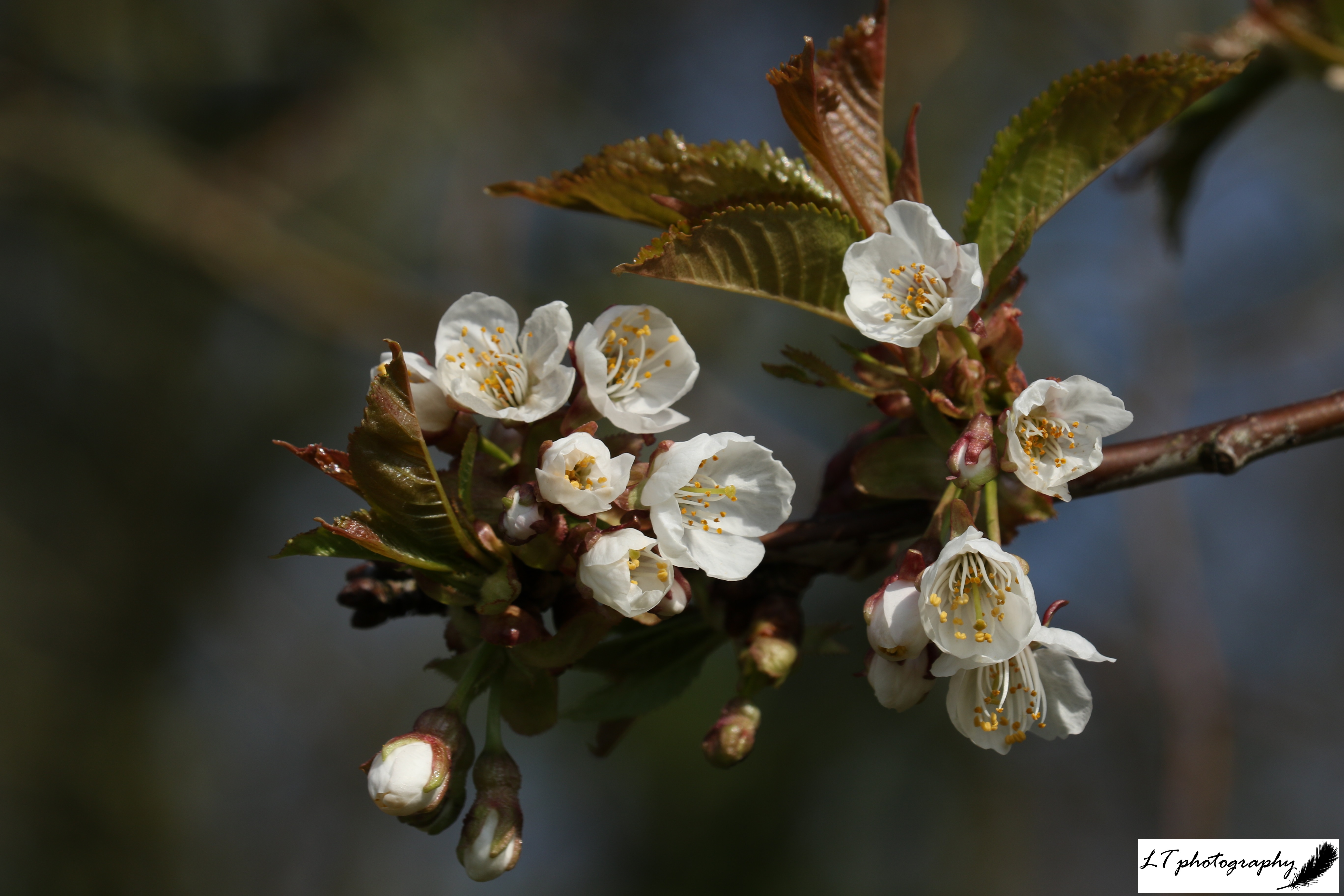
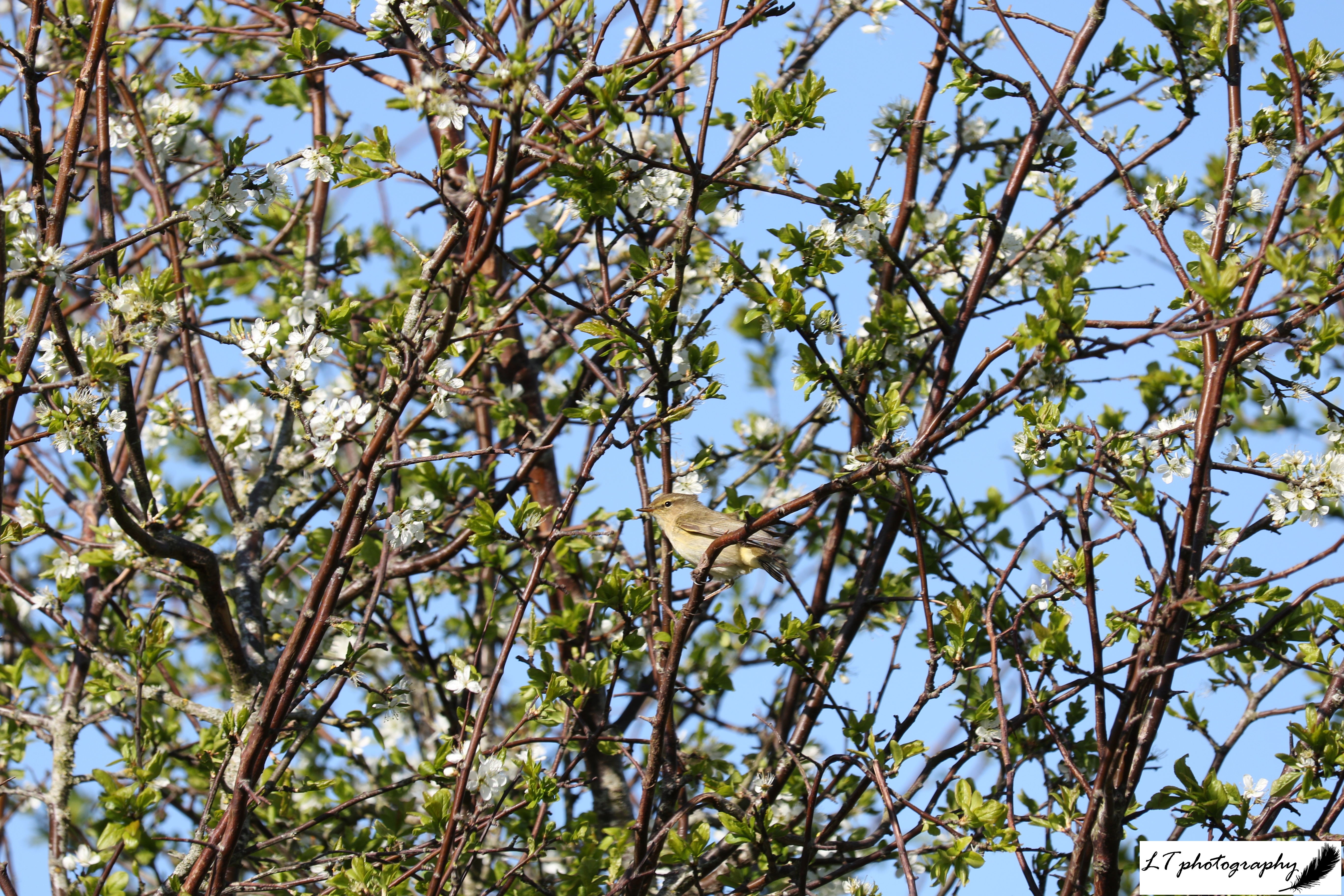
1. Blackthorn – This photo was taken at the beginning of April on a misty morning. It was a beautiful way to see delicate white blackthorn flowers in a different light, framed in front of a splintered stem.
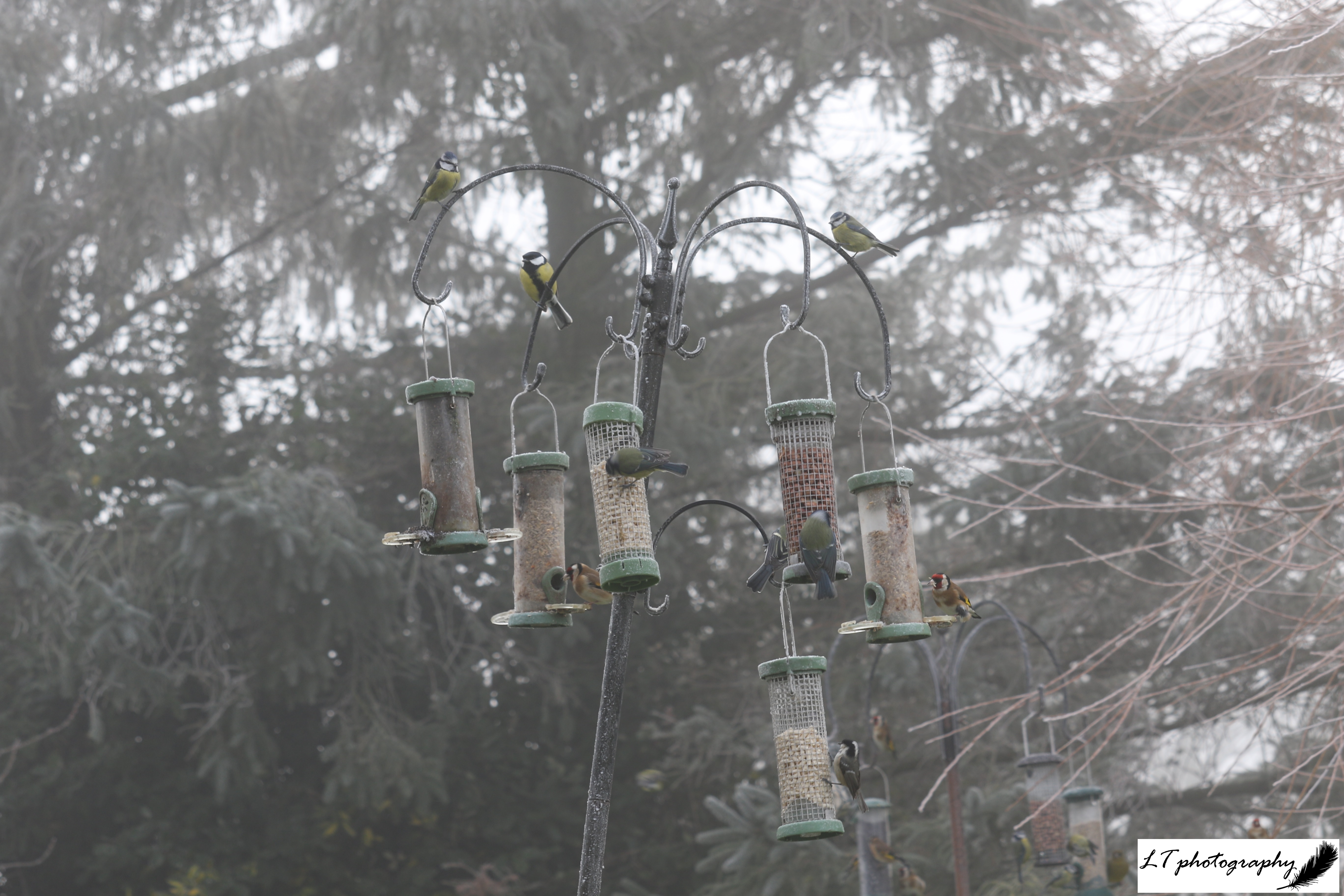
2. Male blackbird – Blackbirds are an iconic sound of spring for me and also so many others. Their beautiful song often symbolises the beginnings of longer, lighter evenings, or for me fresh spring mornings. This male would sit in this willow tree every morning throughout spring to sing his song, defending his territory and mate. In particular, this male and his female nested in our shed, successfully fledging 5 chicks at the start of June.
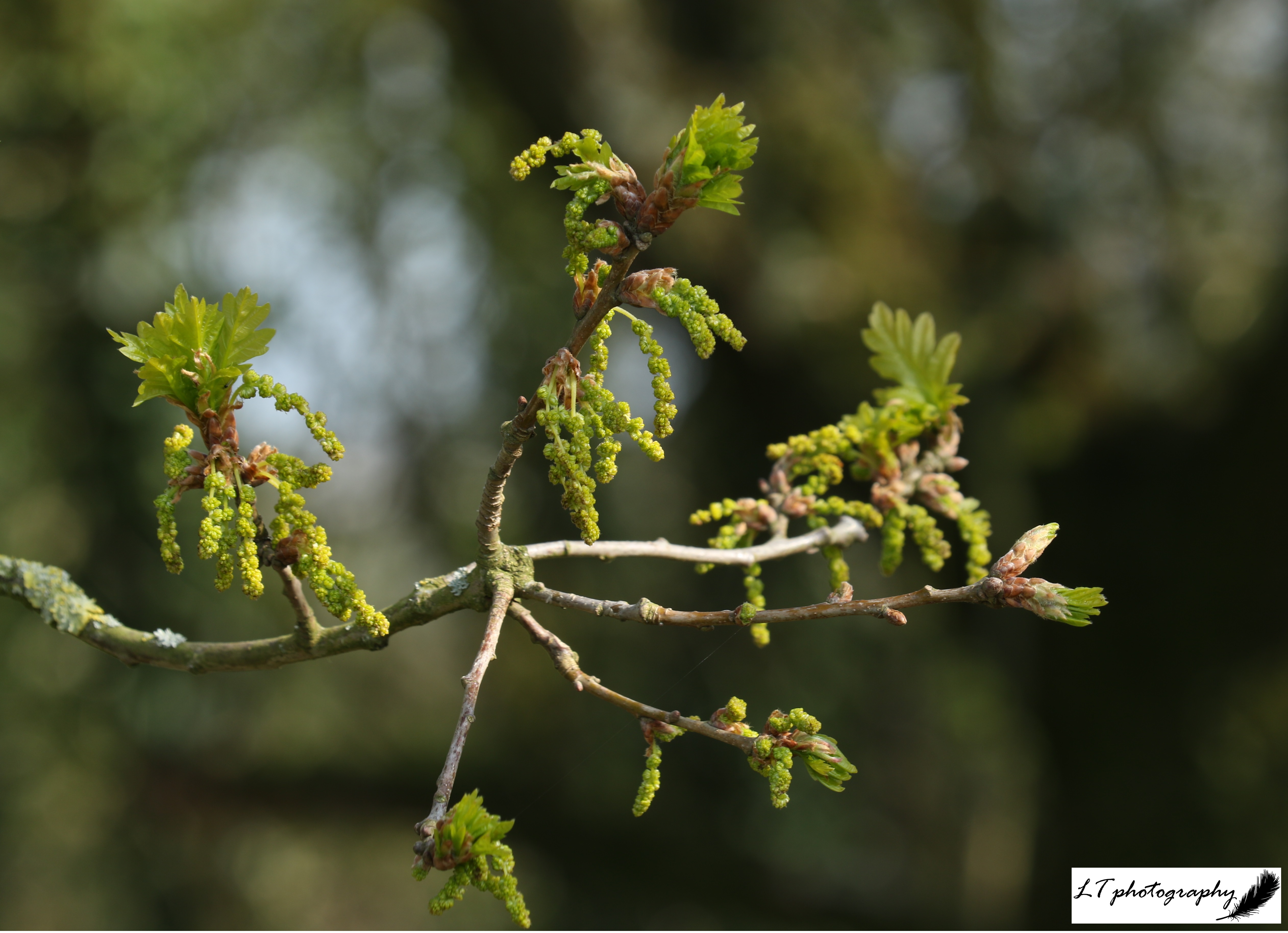
3. Oak trees of a farming landscape – What hits me first in this photo is how bare this landscape seems for late April. The oak trees have barely begun their bud burst, looking skeletal behind a farm field that is being worked. This almost autumnal scene is refreshing though, showing the new beginnings of another year in nature.
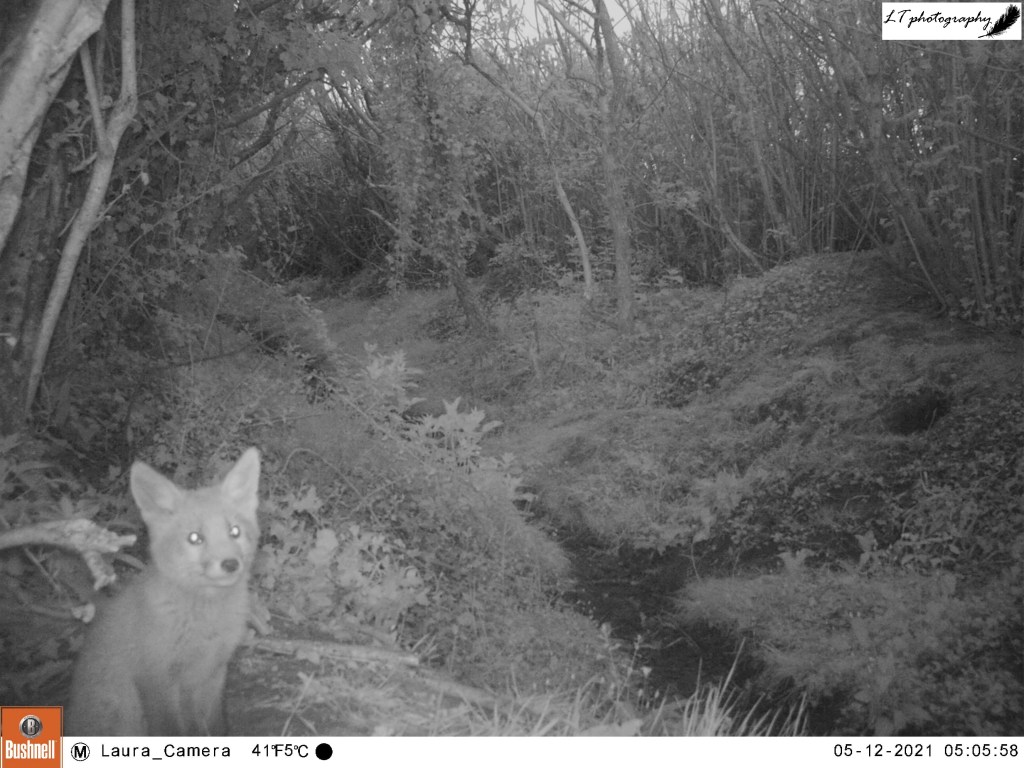
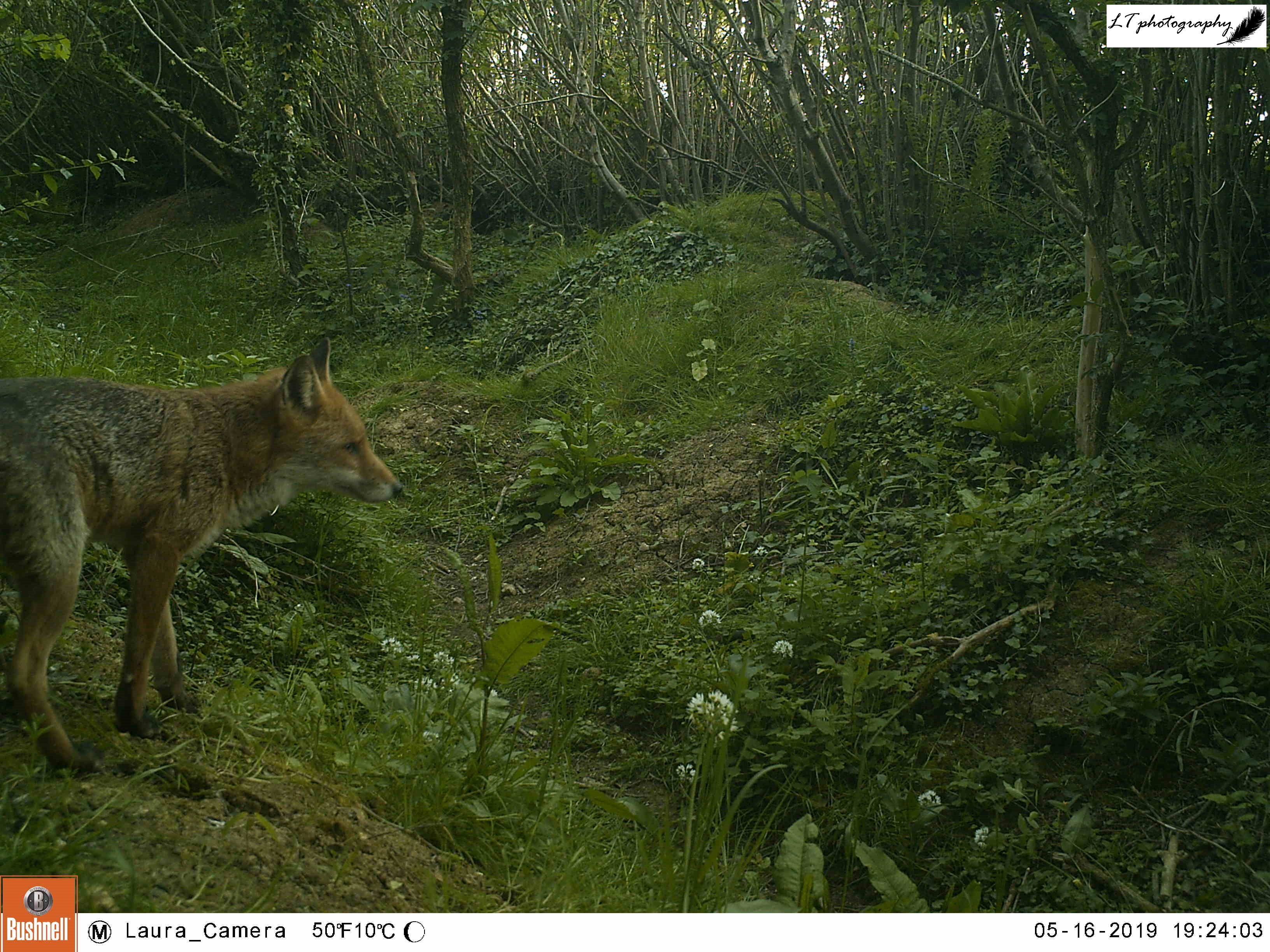
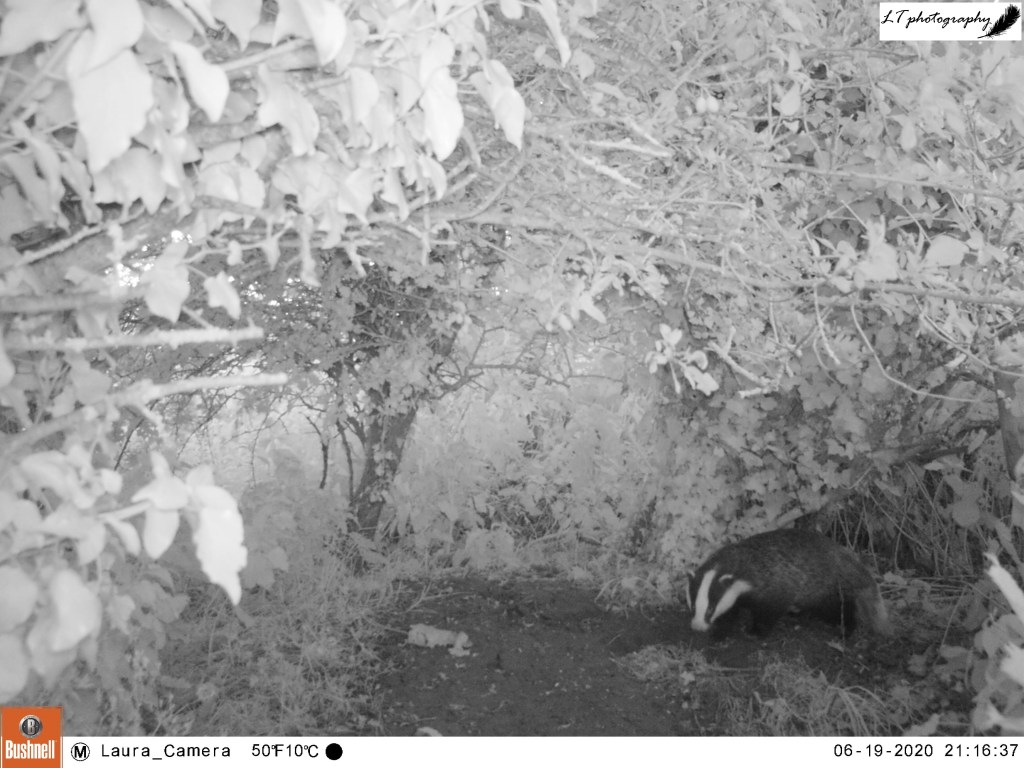
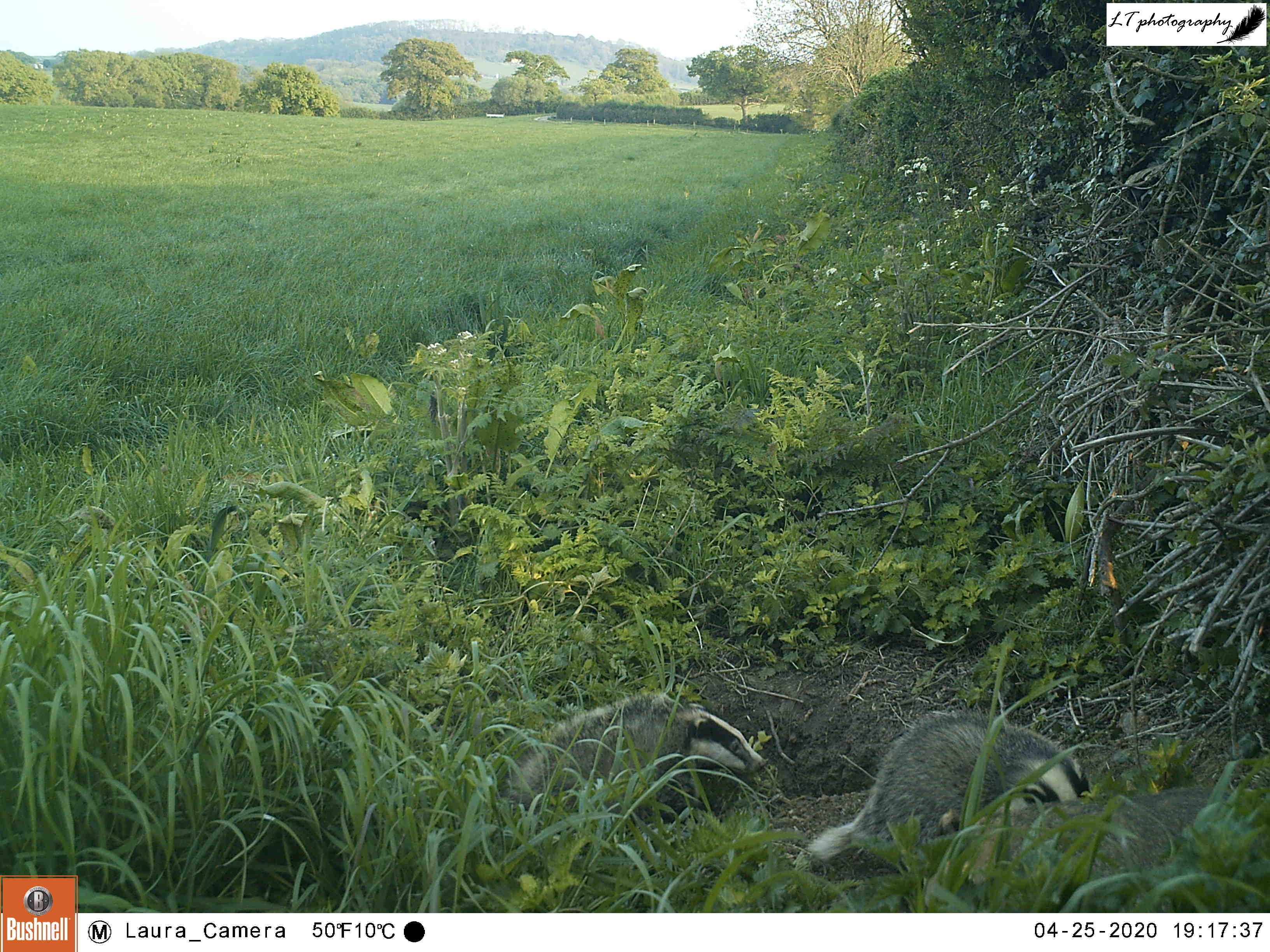
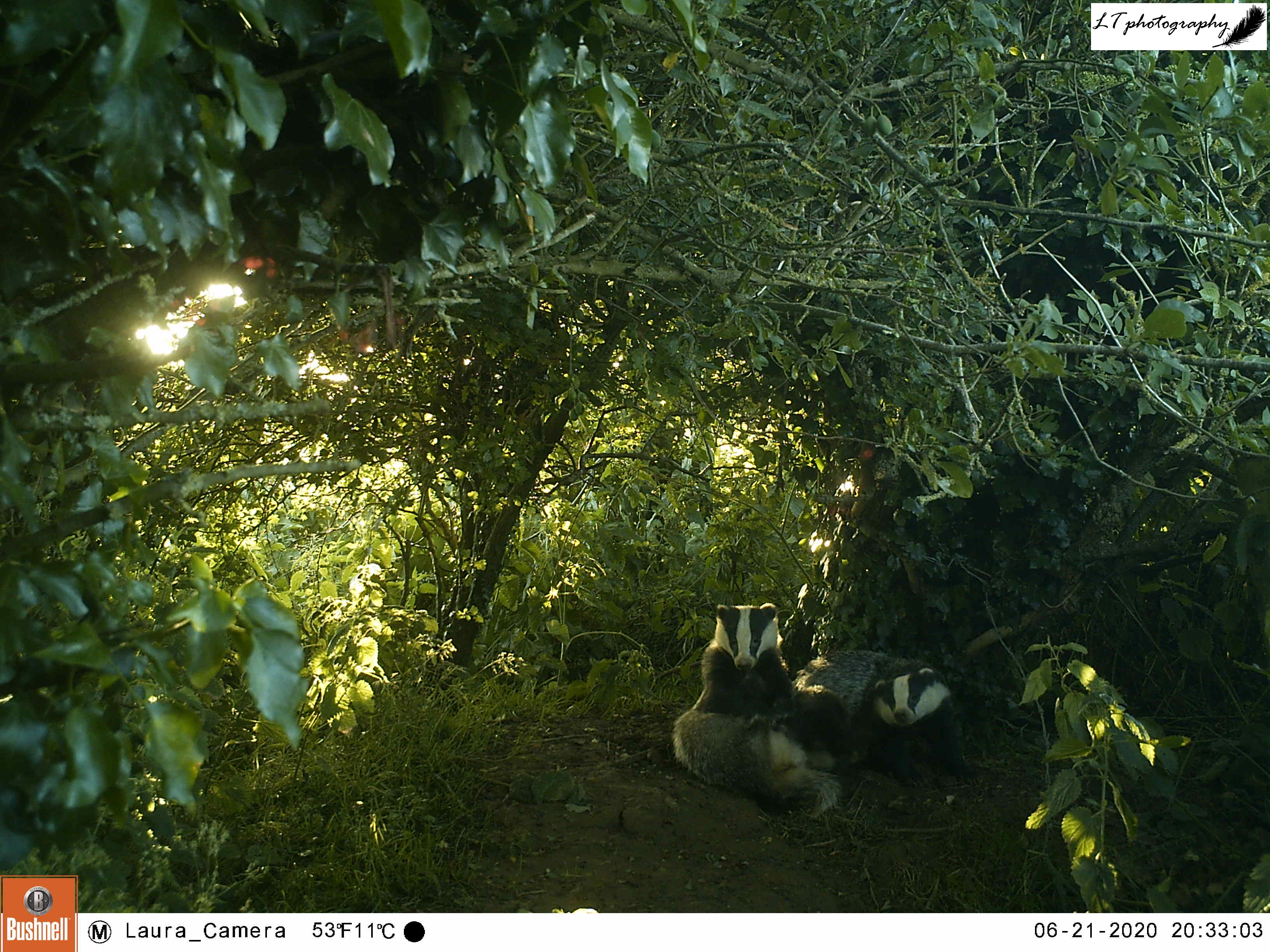
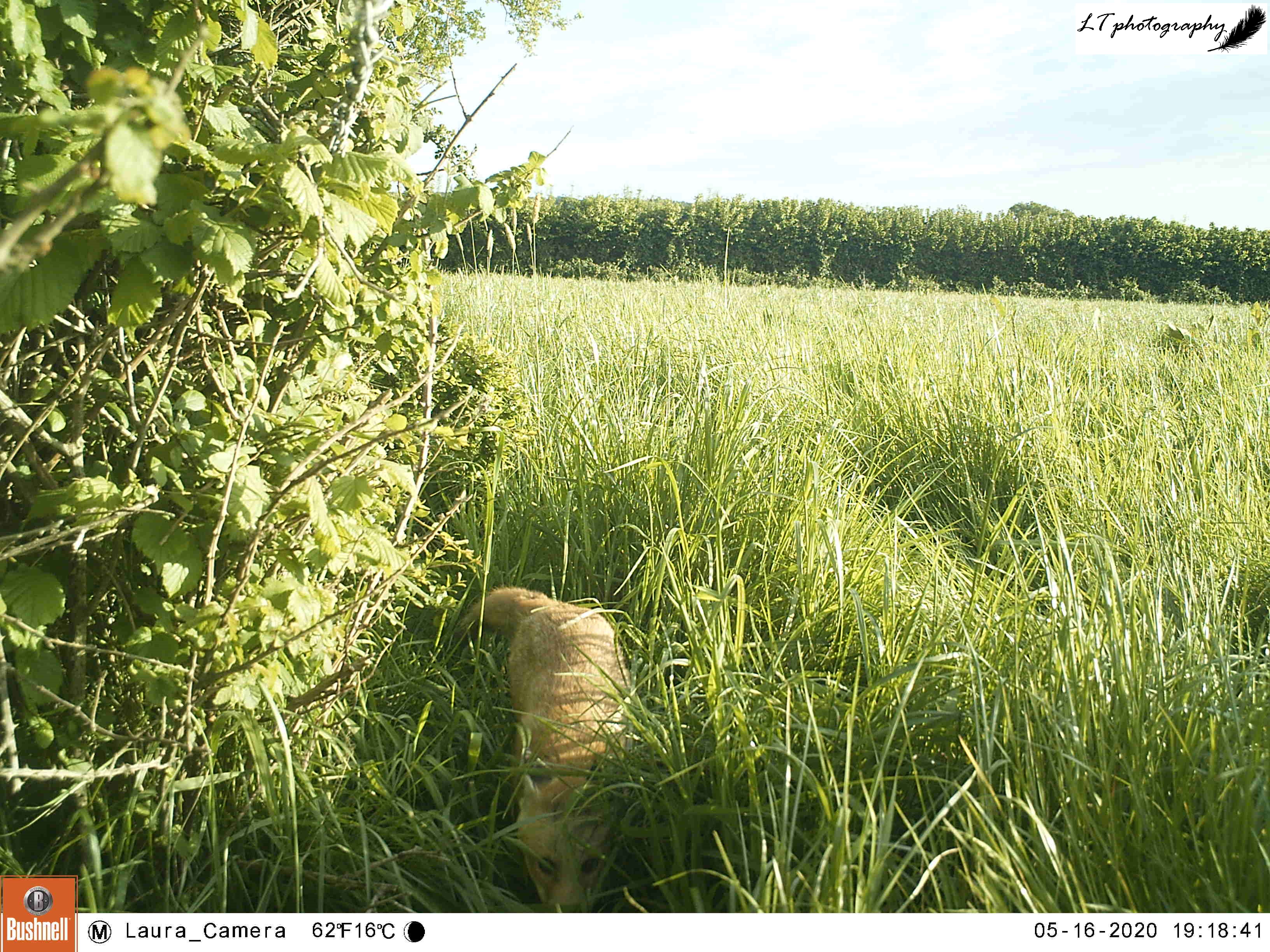
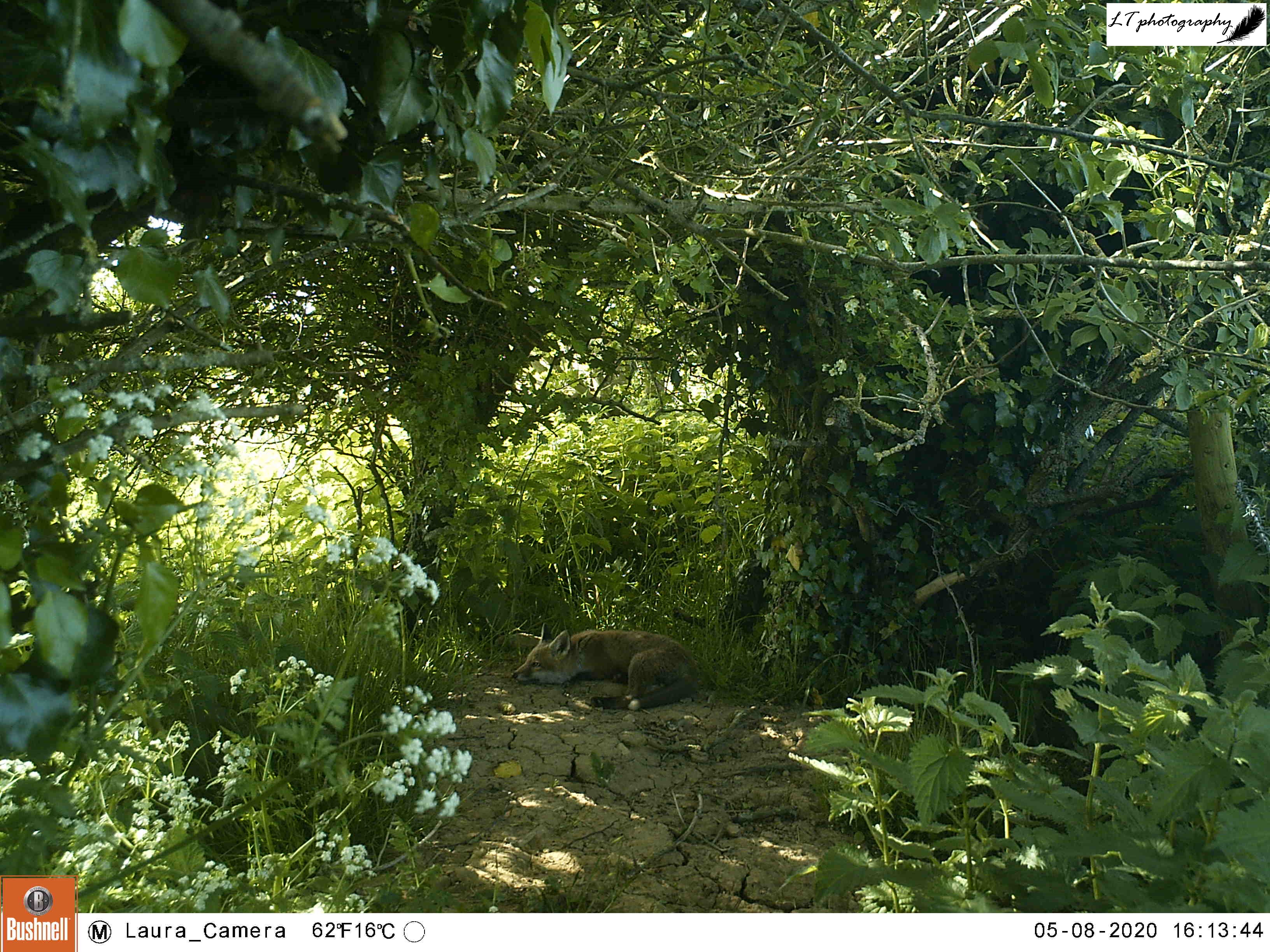
4. Camera trap fox cub – This photo is one of my favourites from this spring, symbolising a successful spring camera trapping season (blog post to come). This was one location, an abandoned badger sett, where I thought that foxes may have been breeding. My camera trap proved my feeling to be right, and treated me to an assortment of photos, day and night, of 2 very active fox cubs. Just one of multiple litters that I found on my family’s farm this year!
5. Wood anemones – Wood anemones have slowly become one of my favourite spring flowers, being one of the first to appear in woodlands across the UK. They are a great indicator of ancient woodland, and an interesting flower to photograph for their shape and colour. My memory cards are full of all sorts of different types of photos of this species!
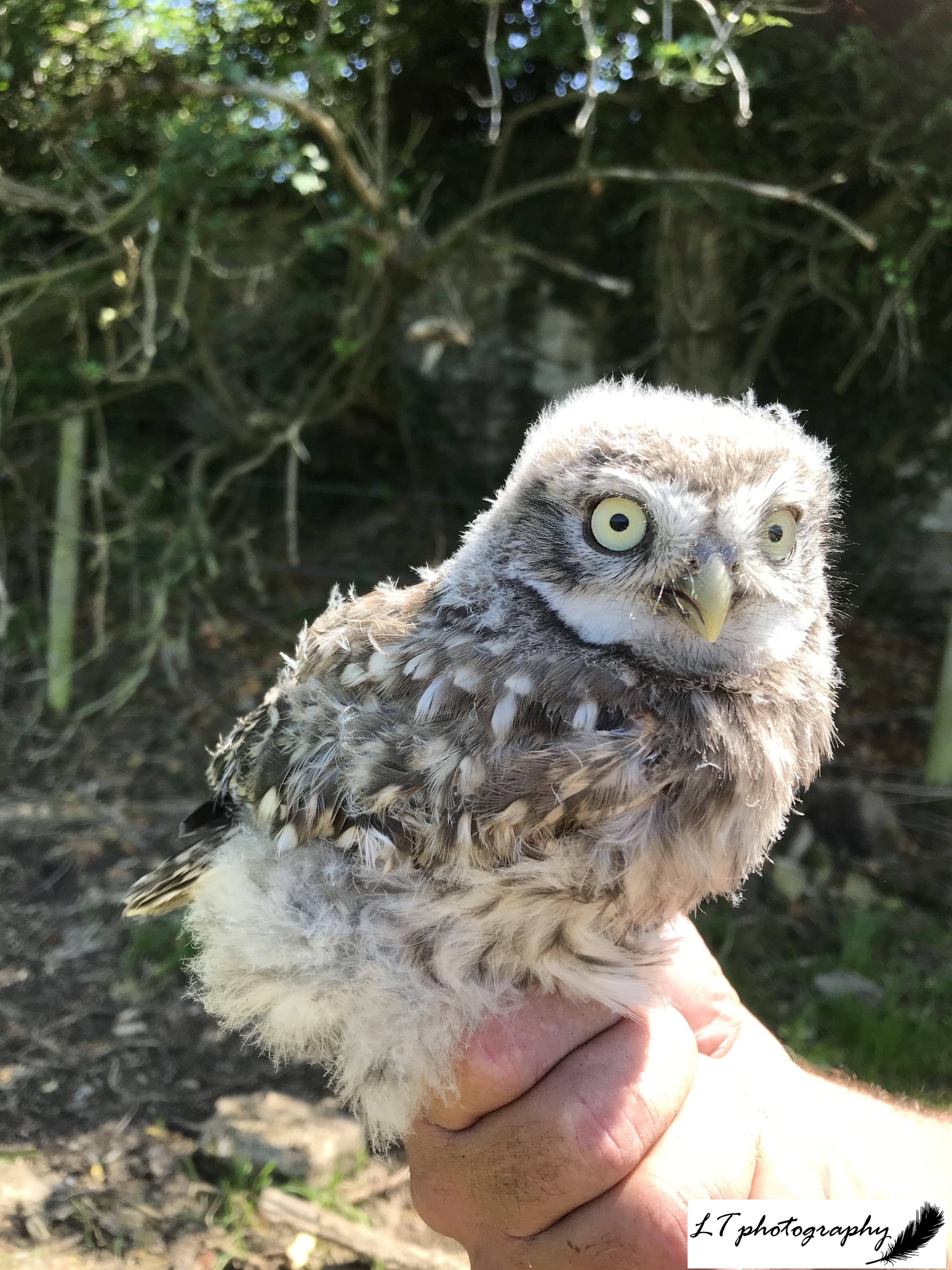
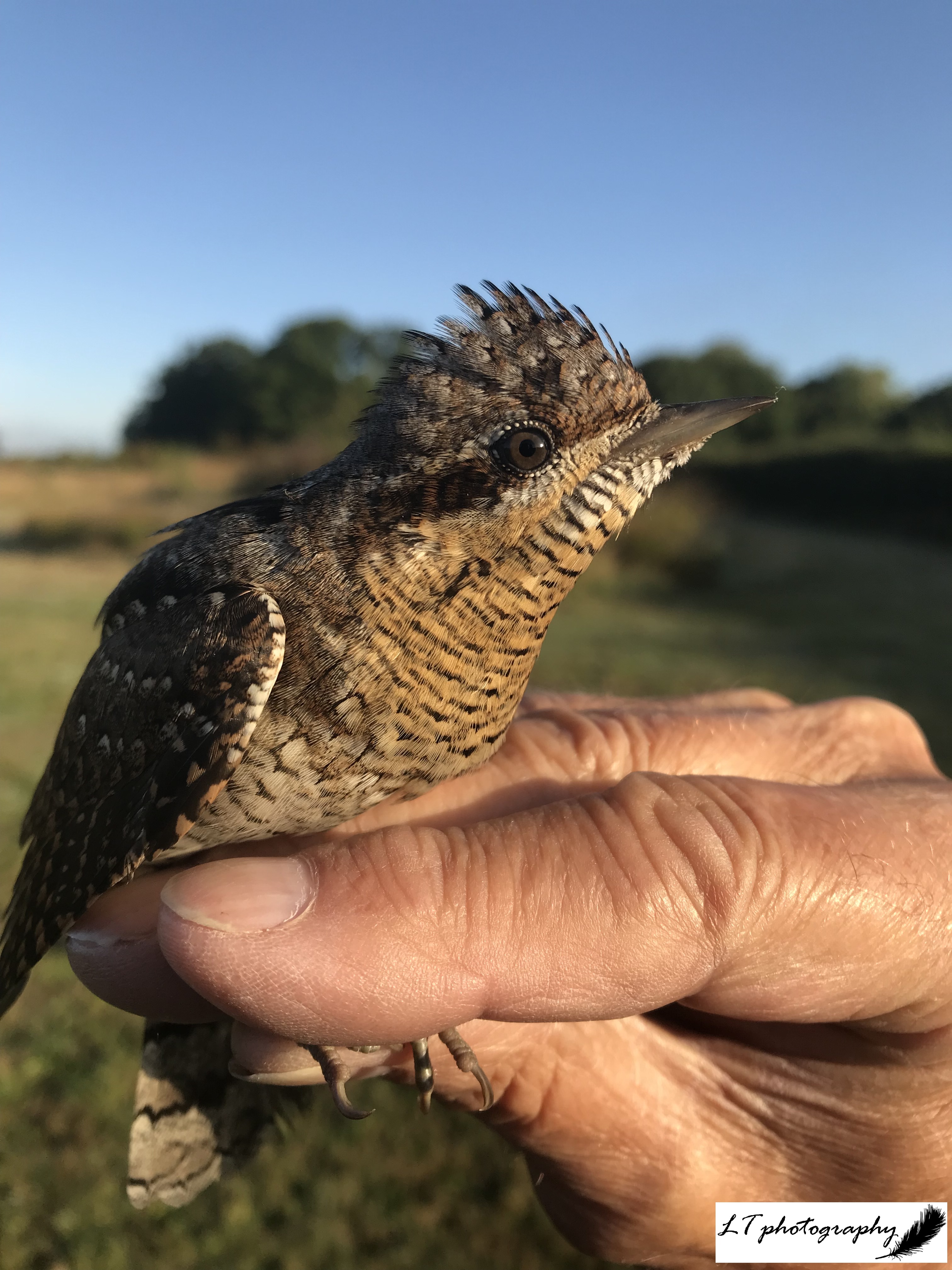
6. Tawny owl chicks – One of my highlights of spring this year has been ringing chicks under license with my bird ringing group (Conservation Action). In particular, I had a great day in early May at the Woodland Trust’s Duncliffe Woods site in North Dorset checking tawny owl nest boxes. It has been a poor year for tawny owls in general, which was reflected by Duncliffe Woods, but we did get lucky and found 3 active nest boxes. I had the pleasure of ringing these chicks, under permit, which will provide important information to help conserve tawny owls in the future.
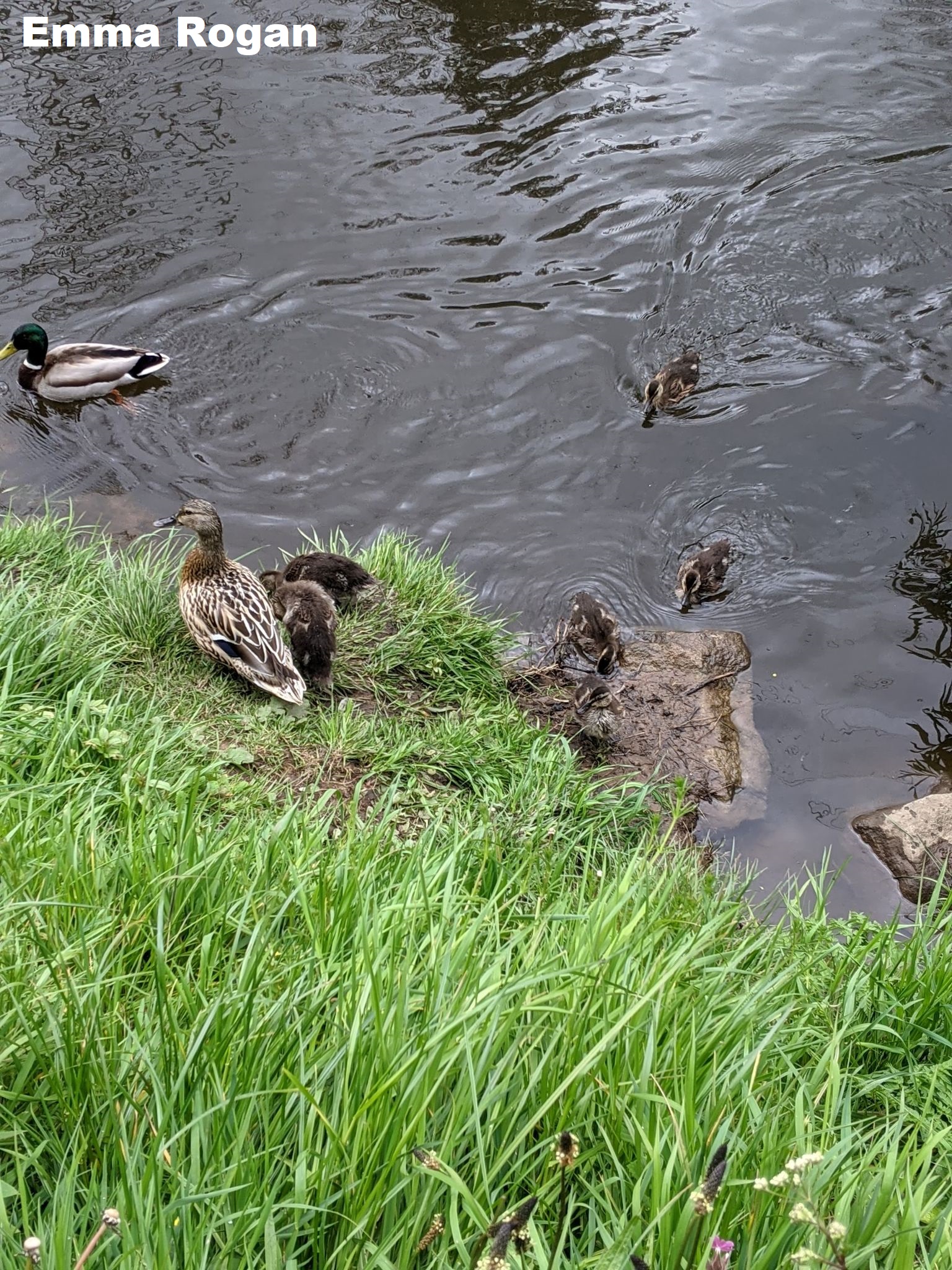
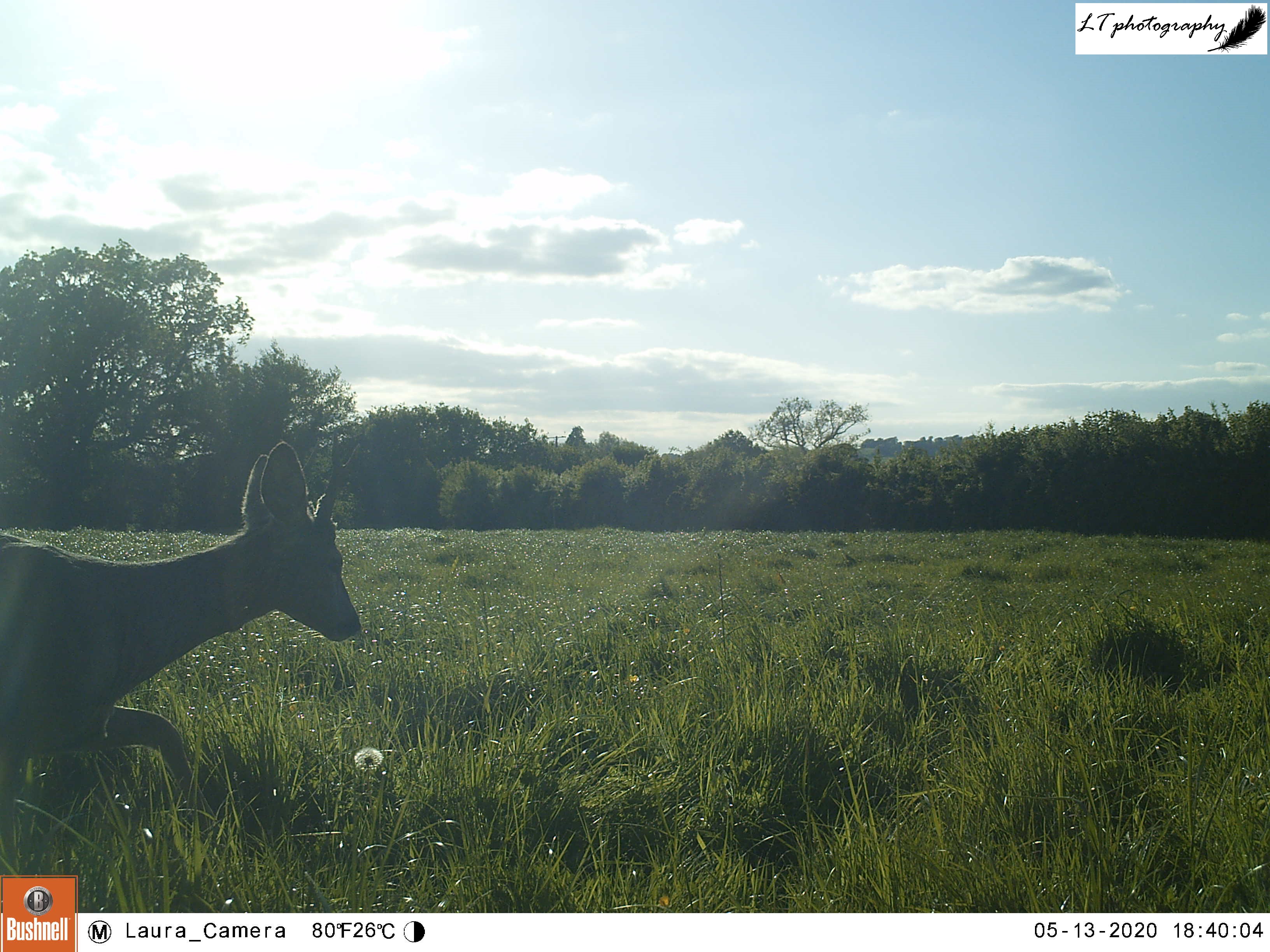
7. Brown hare – This year has been the year of the hare on my family’s farm in Dorset. We have a reputation for being a great site for this species, but this year has been truly astounding. With 1-3 hares to every field, I was humbled to spend my spring out working alongside them everyday, getting to see them up close and experience their behaviour firsthand. Truly magical!
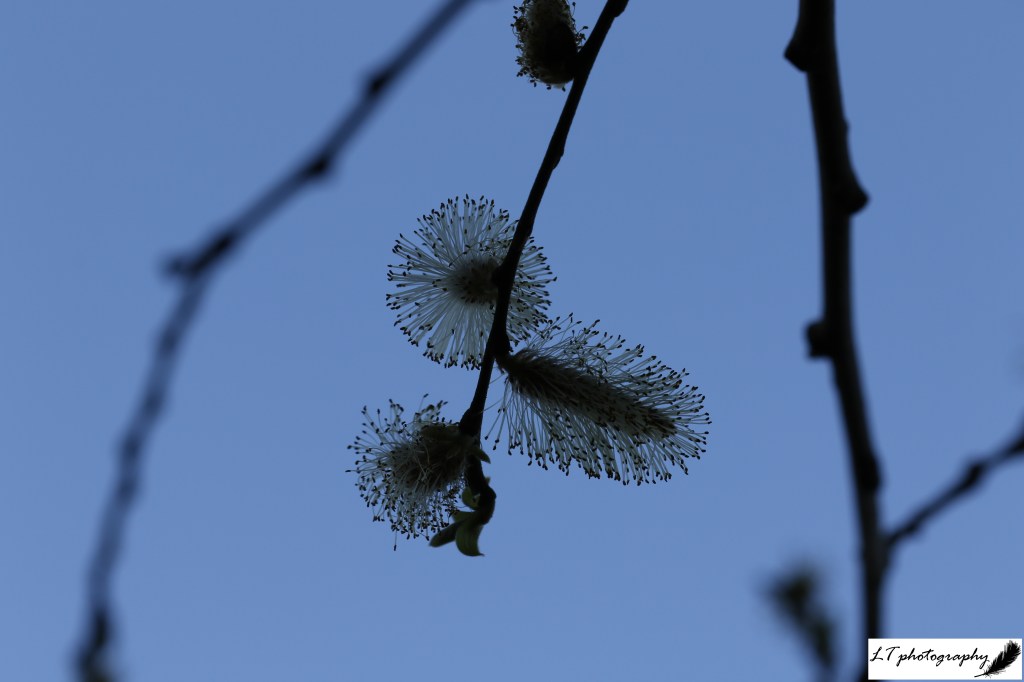
8. Pussy willow flowers – Willow flowers have been a difficult subject for me to photograph this year, with poor results. I was pleased though to find this refreshing photo on my memory card, of willow flowers stood out against a clear blue evening sky. They are beautiful in their own right.
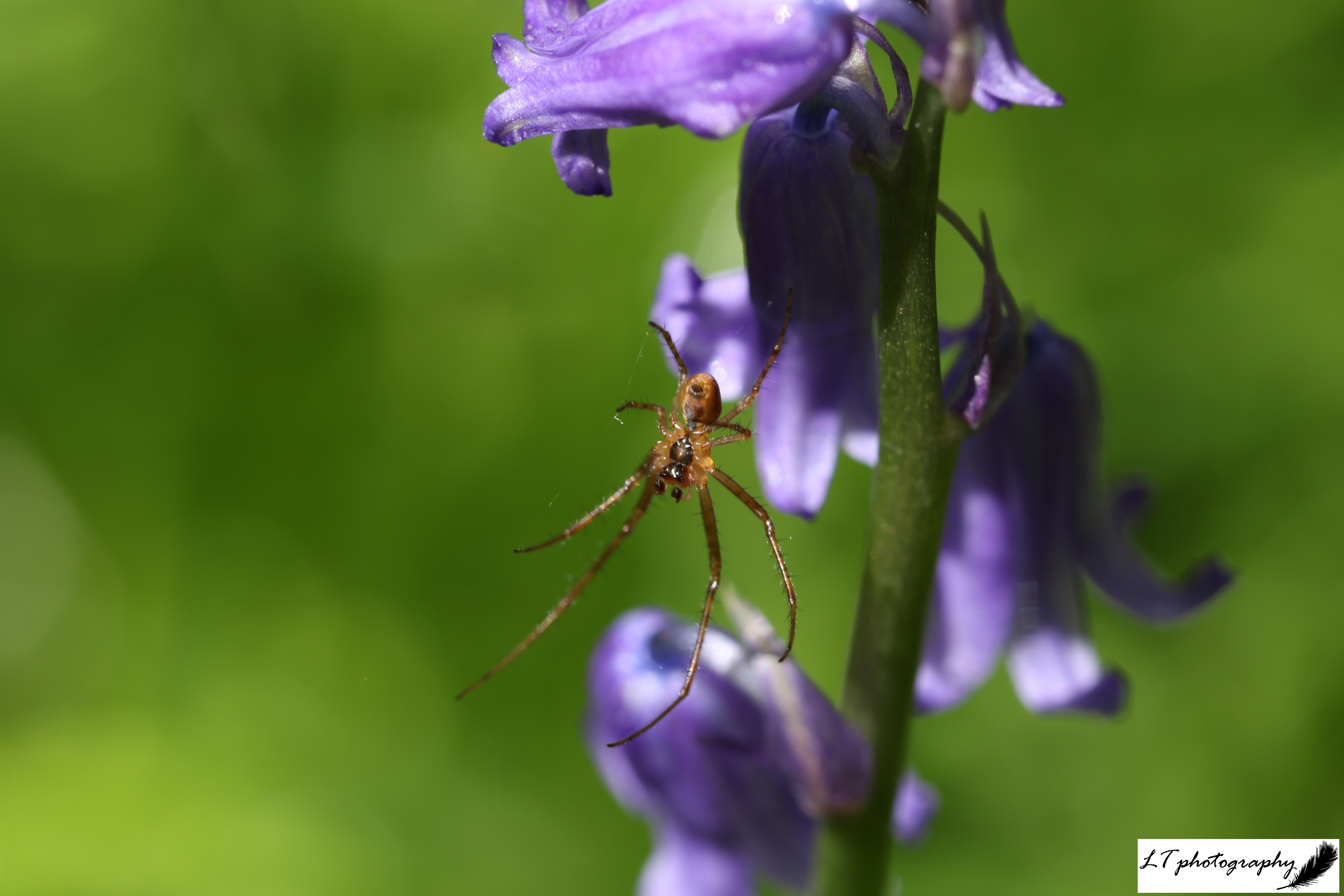
9. Spider in macro – This photo that is not photographically ‘perfect’ is still a favourite of mine from this spring for other reasons. As I invest in my camera equipment, my latest edition has been my first professional macro lens. So this photo was the first photo I even took with my new lens, and it fills me with joy to see the new world I can now start to explore.
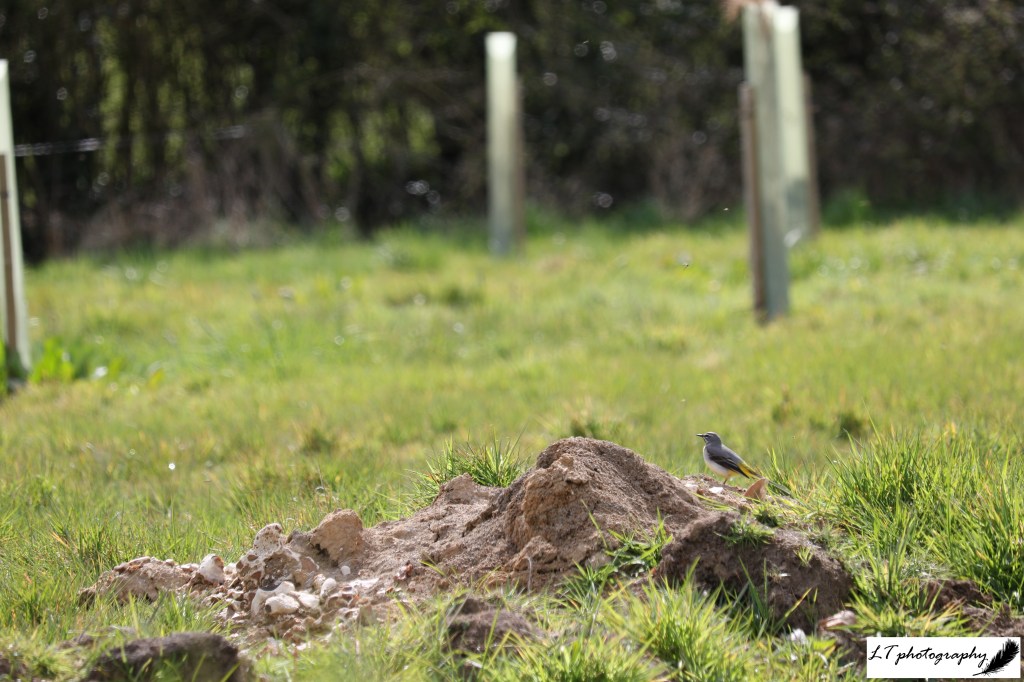
10. Grey wagtail – Last year my Dad began digging a pond in his field that he is currently wilding. Though he was rained off in the autumn before completion, the half-dug pond is already attracting a wealth of species from birds to insects. Majestic grey wagtails that have begun populating this area over the winter have also found the pond this spring.
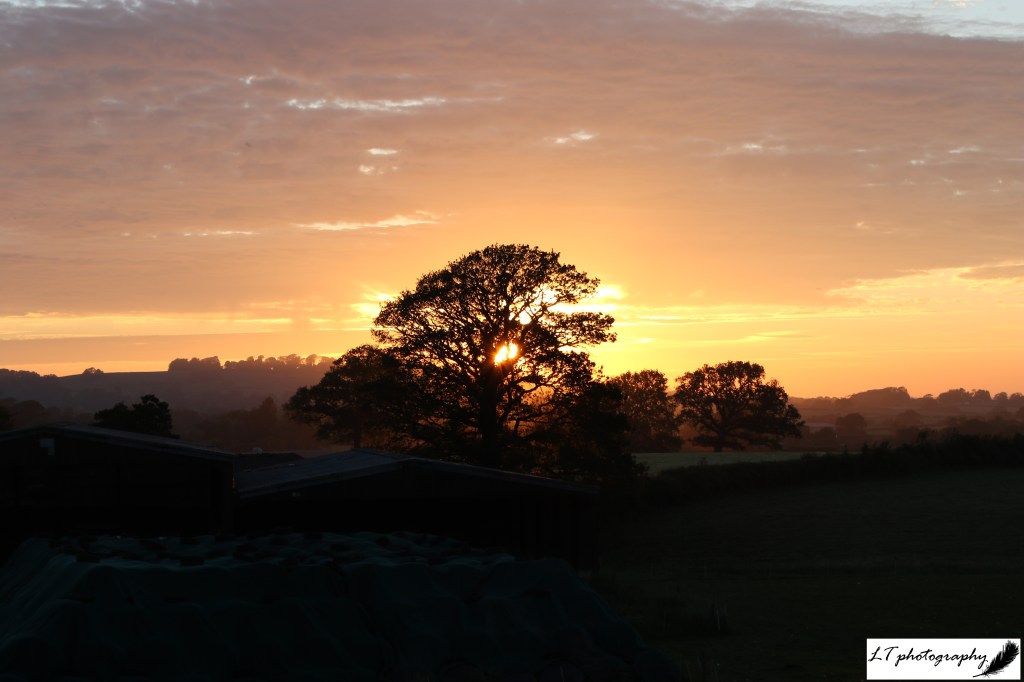
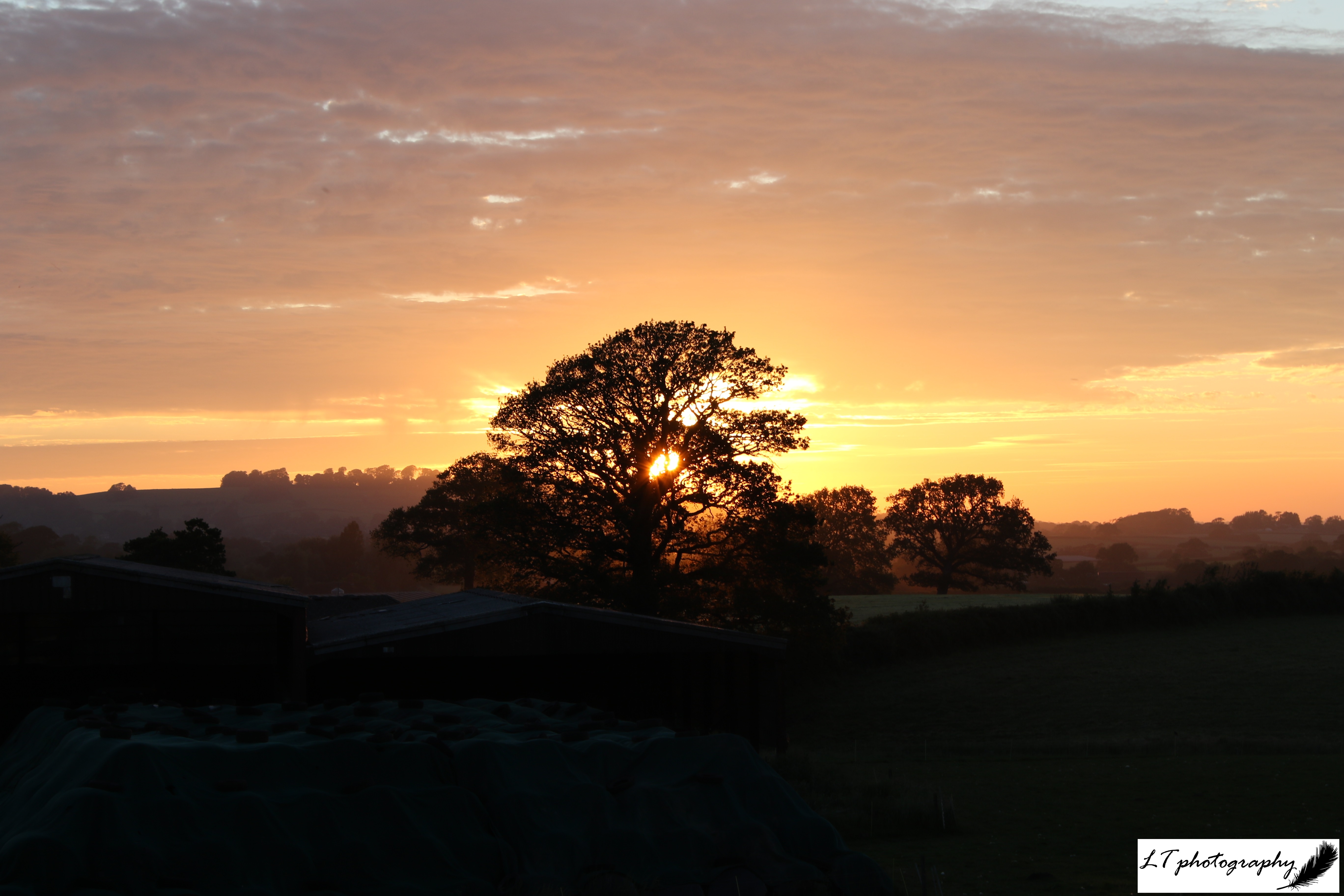
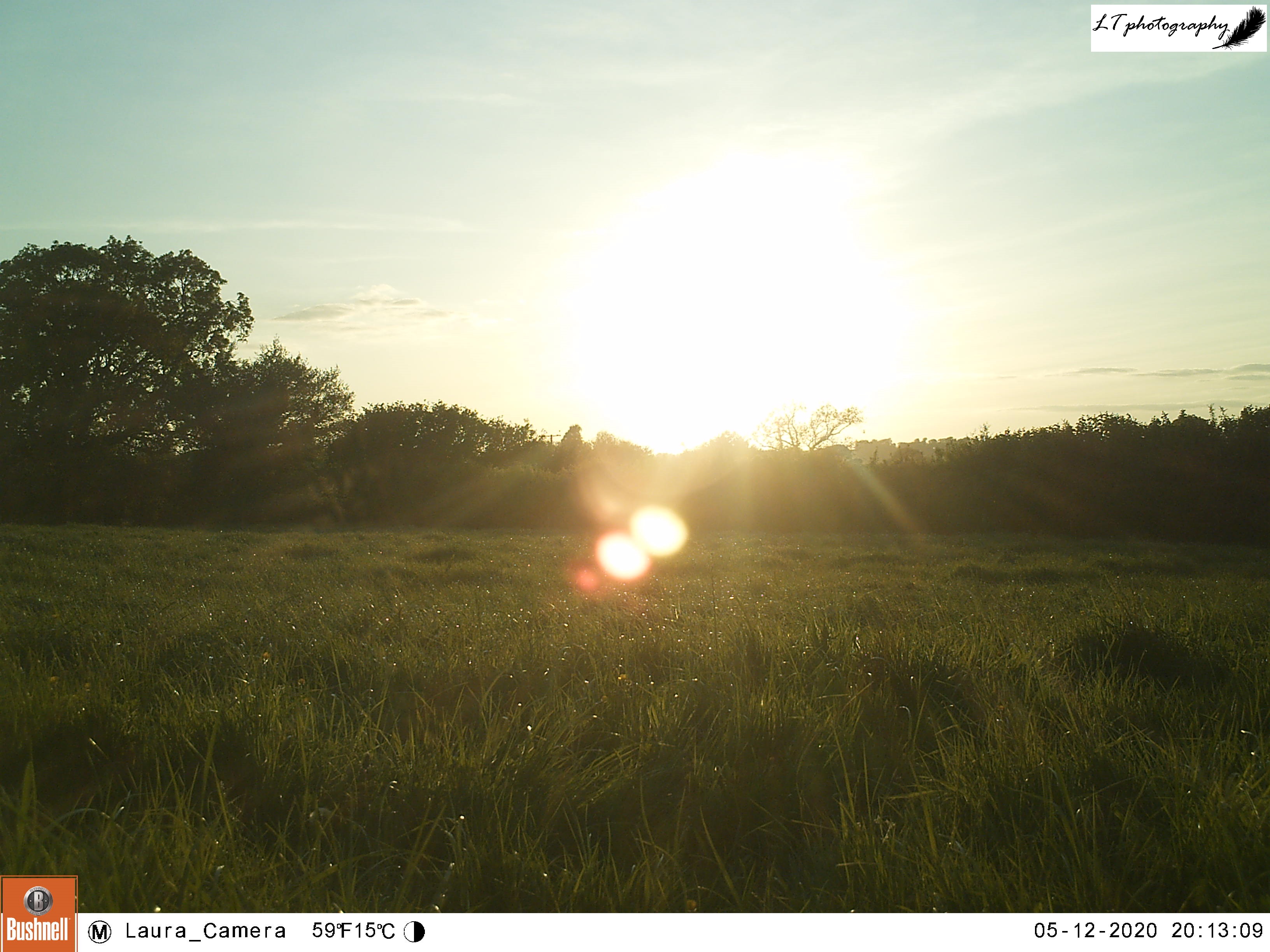
11. Sunset – Though sunrises are magical, sunsets have always been my most favourite time of the day. This is because many of my happiest memories can be linked to beautiful and vibrant sunsets from field research in Canada to evenings at home on my family’s farm. I have seen so many incredible sunsets already so far, but I hope to see many more in the future.
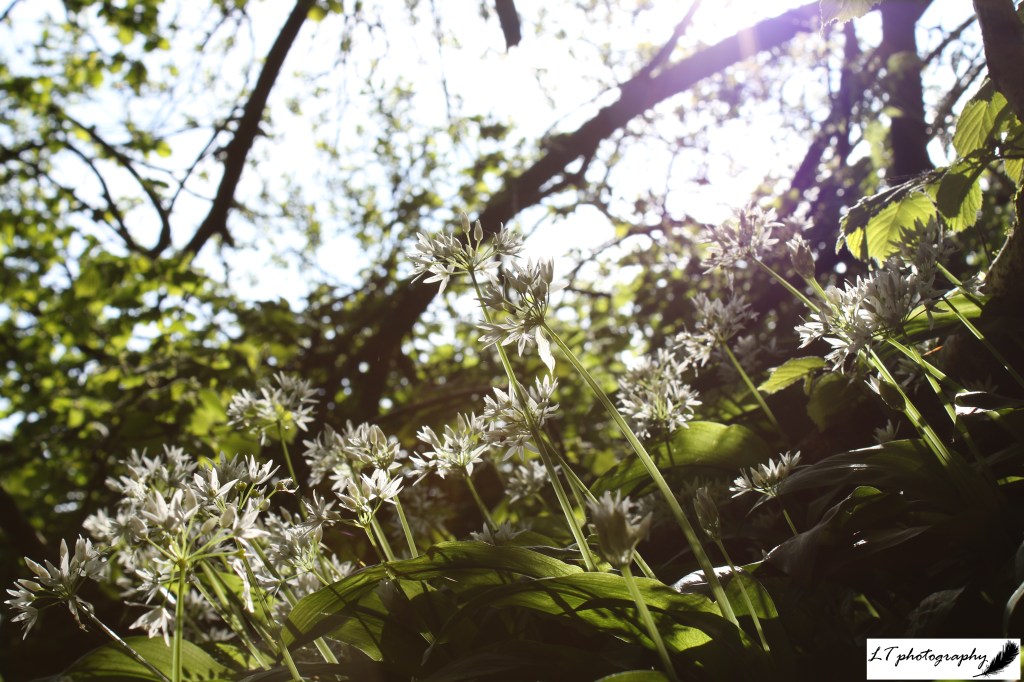
12. Wild garlic – Though my busy spring dissuaded me from mornings waking up before the sunrise, I did spend a couple of glorious mornings waking up and getting out an hour or so after instead. The light is glorious at this time of day and always provides me with inspiration for my photos and life in general. This photo represents this magical time of day and the joys of spring flowers, wild garlic being an iconic example.
13. Feather in the bluebells – Wait, a feather again? Well feathers always sneak into my many files of photos, being a symbol of mine and representing my love of feathered species. They can also tell us useful information about what is living in a habitat, for example this feather is most likely from a collared dove.
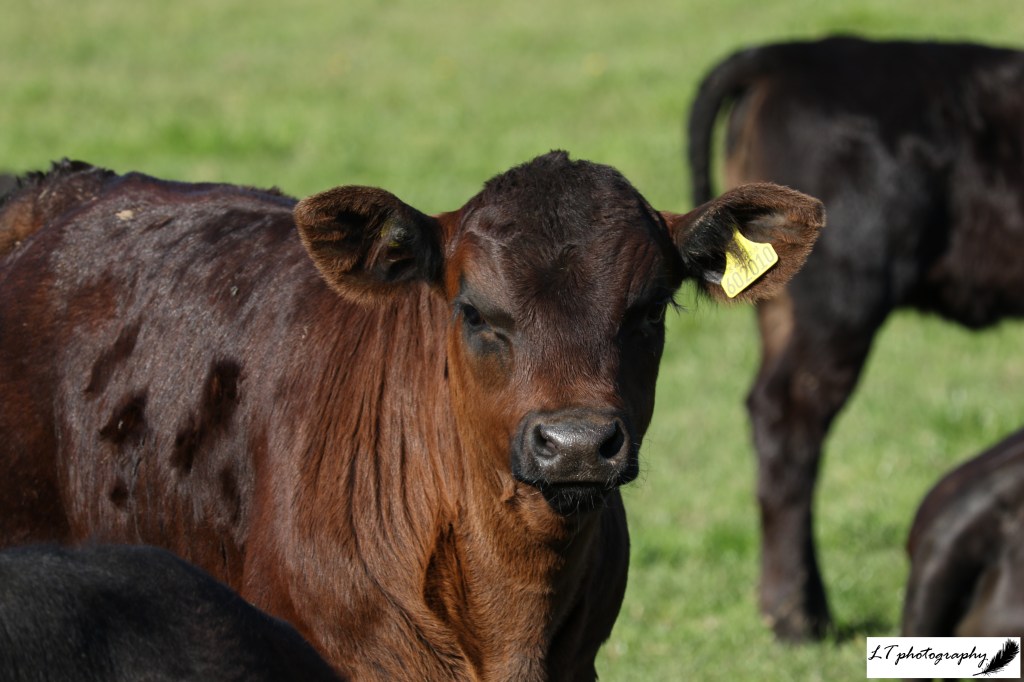
14. Aberdeen angus calf – This photo is one of my favourite photos of one of my mum’s beef suckler calves. Spring is a time of new life in nature and on the farm, with my mum’s small free range beef herd giving birth at this time. This year they have weathered it through some turbulent months, but now are enjoying a bit of sunshine on their backs.
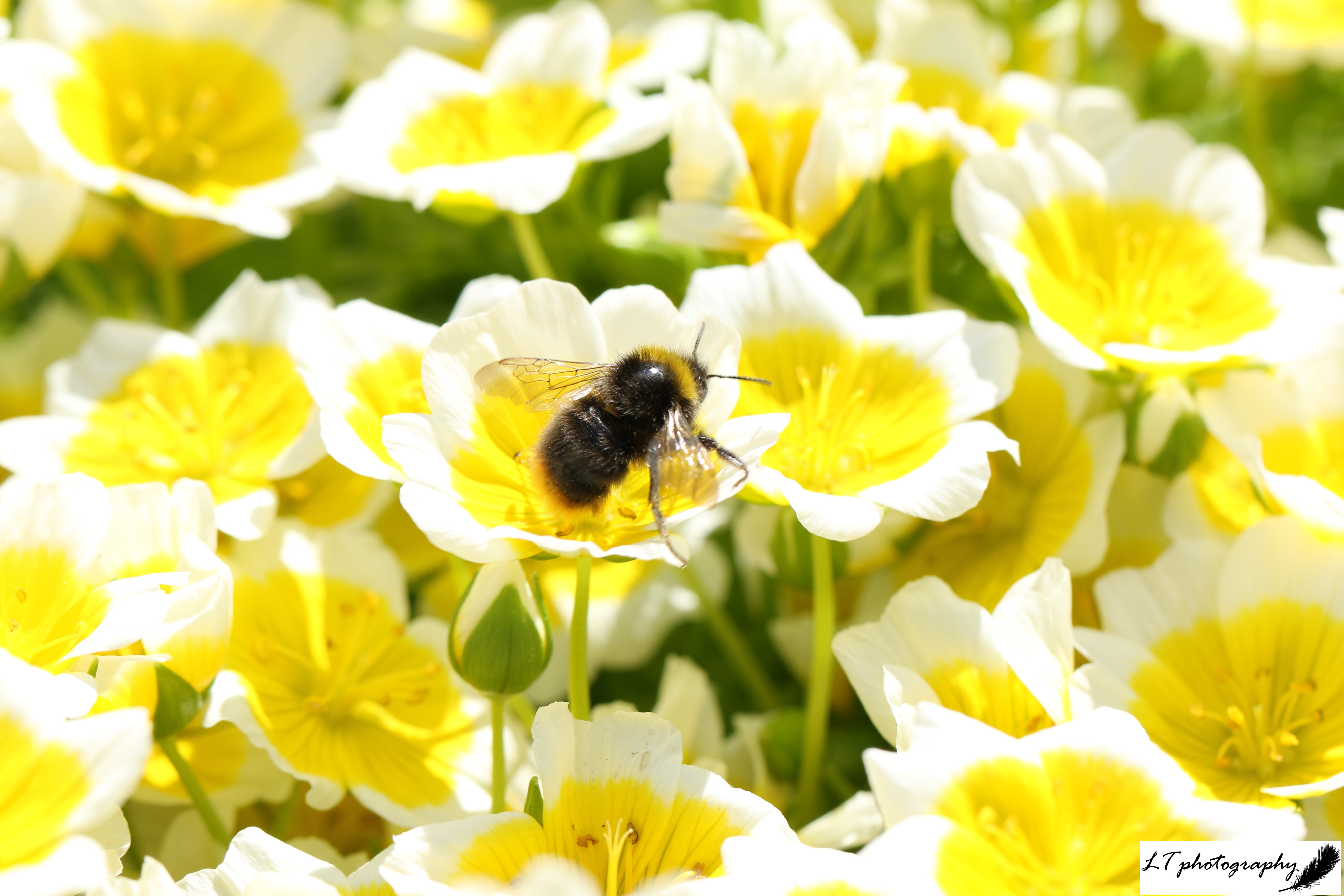
15. Honey bee – As I was intending to buy a macro lens this year, I made sure to time my purchase to be able to use it on the flowering of the poached egg plants in my family’s garden. It arrived well in advance, and, despite some rained off days, I got to spend some happy lunchtimes in the sunshine photographing bees on these flowers. This is one of my favourite macro photos of the flowers this year.
16. Dog roses – Dog roses were the last event of spring that I looked out for this year, and it kept me waiting! They were 22 days later for me than last year, with the first flowers blooming on the 8th June. They came out in force though, covering hedges within the space of a couple of days, adding some more colour to our hedgerows. With their lateness though, I feel like they also marked the end of spring this year.