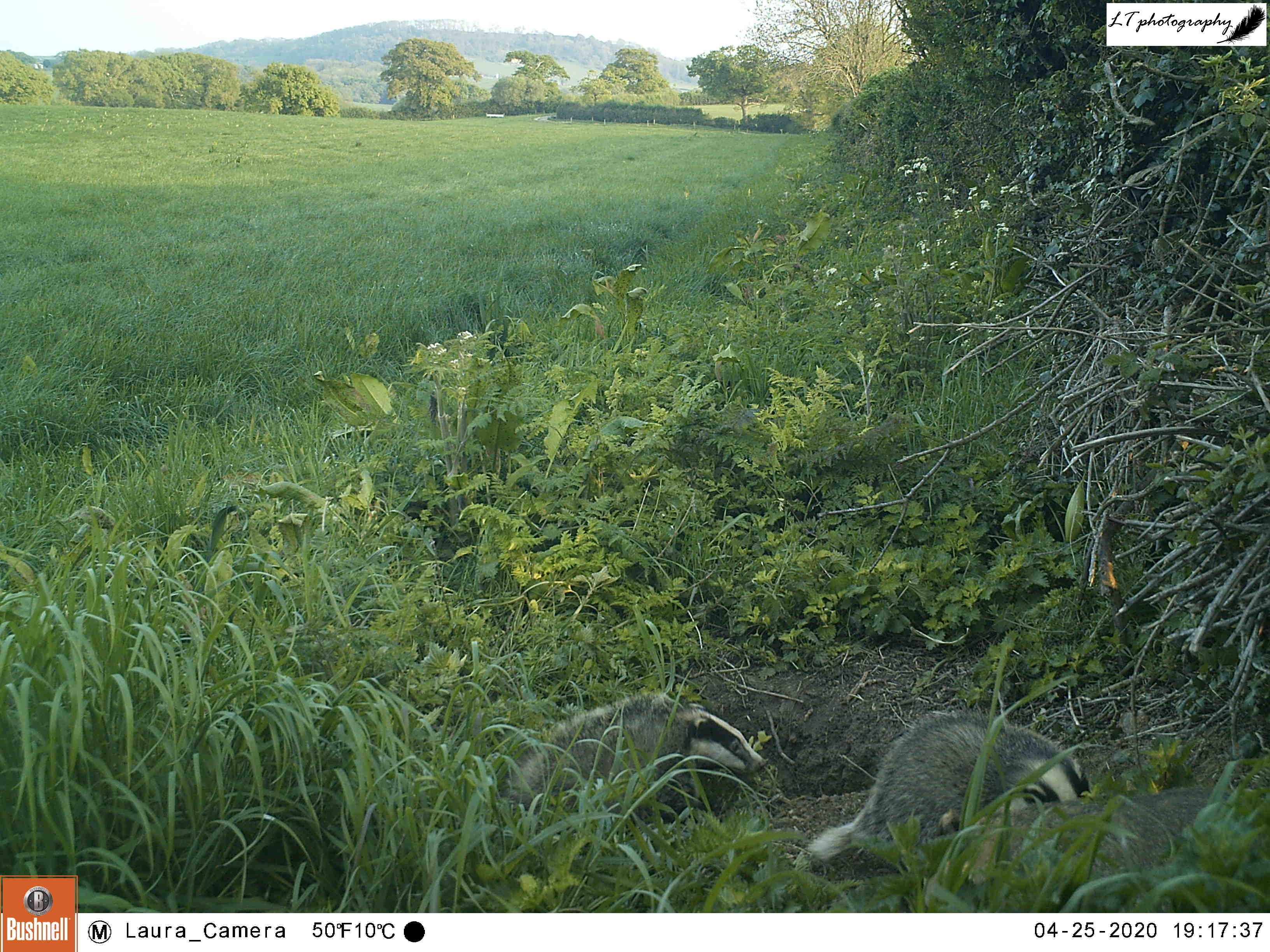
Over the last few years, it has been noticeable that weather patterns and average temperatures have been changing and highly unpredictable, leading to the seasons, such as spring, varying from month-to-month and year-to-year, especially here in Dorset. For example, last year spring began a wash out, moving to cold and stormy spells, before ending with heat waves. This year was an equally odd series of spring weather events with a cold start to the season, followed by wet weather with northerly winds, and finishing with drier spells. It was on average warmer and wetter, but cold nights continued for a long time, and had a noticeable effect on plant growth patterns being seen.


Spring 2023 encountered trends for later spring events and a slow start to spring, which helped to create a mismatch between species and spring events. With a warmer, wetter winter before spring this year, and often above average spring temperatures, it is likely the trends this year may differ to those of 2023. It will be interesting to see if this has had an effect though, by looking at trends for some tree, shrub, flower, insect and bird species. How will spring 2024 have shaped up? Read on to see how my favourite season unfurled this year!


Trees
During 2023, spring emergence dates for trees showed a trend for on average later dates, ranging from 1 to 28 days later. In 2024 though, the majority of spring tree dates were earlier, as seen with field maple, horse chestnut, english oak, and wild cherry, ranging from 1 to 22 days earlier from March through to May. Alder dates though were fractionally later, as were ash and sycamore flowering, and silver birch and norway maple budburst, but the other events for these species occurred earlier. The on average warmer and wetter weather will most likely be the reason for these trends, allowing trees to get a head start this year.


Flowers
Plants flowering during spring 2023 occurred on average later, varying from 1 to 16 days. During spring 2024 though, flowering has occurred earlier, as was the trend with tree species. For snowdrops, lesser celandines, primroses, greater stitchwort, wood anemones, early purple orchids, wild garlic, yellow archangel, cuckooflowers, oxeye daisies, and bluebells flowering occurred 1 to 32 days earlier between January and May. The exceptions were found with daffodils, flowering 6 days later during February, and cowslips, 4 days later during April. It would be understandable thus to think that the warmer, wetter weather of the start of spring will have had a heavy influence on these events, just like with trees.


Insects
Of 12 species that had the emergence date recorded during spring 2023, the majority emerged later than the year before, ranging from 2 to 46 days later. This year though, spring 2024 saw the occurrence of a 50:50 split for the 10 species that had their emergence date recorded, with some species from 2023 yet to be seen at all, such as painted lady butterflies.


Buff-tailed bumblebees, 7-spotted ladybirds, and orange tip, red admiral, and speckled wood butterflies all emerged earlier this year, ranging from 2 to 46 days earlier. Conversely, queen wasps, and brimstone, peacock, gatekeeper, and small tortoiseshell butterflies all emerged later than 2023, ranging from 8 to 47 days later. Though not complete for all, the split does tend to be due to March to April species emerging earlier this year whereas April to June species emerged later this year. This may be due to April being a cooler, wetter month this year, impacting insect species more greatly than plant species that were already making their advance and were less impacted.


Shrubs
Spring 2023 mainly showed a trend for later shrub budburst, leaf unfurling and flowering, ranging from 3-27 days from March to May. In contrast, for spring 2024, the majority of events for shrubs occurred earlier, ranging from 1 to 53 days earlier from December through to May. These included for blackthorn, dog rose, elder, hawthorn and hazel, with the only later event being for red female hazel flowers being observed. This trend shows similarities to those of trees and spring flowering plants, and would be similarly due to a warmer, wetter winter and start of spring, allowing events to occur earlier and shrubs to get a head start on the season.


Birds
Following on from the last two years (2022 and 2023), the dates of bird events during spring 2024 showed no clear trend, with a split between different species and events. Rooks began building their nests earlier, chiffchaffs and swallows arrived earlier, song thrushes and yellowhammers first sang earlier, and the first wrens fledged earlier. Conversely, blackbirds first sang later, the first blackbirds fledged later, blackcaps, cuckoos and house martins arrived later, and great-spotted woodpeckers drummed later.


Some of these event timing changes will be due to spring temperatures and weather conditions on short term and long term scales. Other reasons are less obvious currently, but the hope is that bird events will still have been timed right with other species to make the most of resources this year.


Conclusion
Spring 2024 was a thoroughly odd season, varying from month-to-month, but feeling like wet weather prevailed more than the normal. In the end it was vibrant and colourful, though missing the traditional spring feeling. This year spring was heavily effected by climatic changes and changes to weather patterns, and this may become typical during the springs to come. It is really hard to predict then how each season will play out, and it will be interesting to see now how all British species cope with such unpredictability as time goes on. Only time will tell!


Species List
- Alder (Tree) Alnus glutinosa
- Ash (Tree) Fraxinus excelsior
- Blackbird (Bird) Turdus merula
- Blackcap (Bird) Sylvia atricapilla
- Blackthorn (Shrub) Prunus spinosa
- Bluebell (Flowering Plant) Hyacinthoides non-scripta
- Brimstone butterfly (Insect) Gonepteryx rhamni
- Buff-tailed bumblebee (Insect) Bombus terrestris
- Chiffchaff (Bird) Phylloscopus collybita
- Common wasp (Insect) Vespula vulgaris
- Cowslip (Flowering Plant) Primula veris
- Cuckoo (Bird) Cuculus canorus
- Cuckooflower (Flowering Plant) Cardamine pratensis
- Daffodil (Flowering Plant) Narcissus spp.
- Dog rose (Shrub) Rosa canina
- Early purple orchid (Flowering Plant) Orchis mascula
- Elder (Shrub) Sambucus nigra
- English oak (Tree) Quercus robur
- Field maple (Tree) Acer campestre
- Gatekeeper butterfly (Insect) Pyronia tithonus
- Greater stitchwort (Flowering Plant) Stellaria holostea
- Great-spotted woodpecker (Bird) Dendrocopos major
- Hawthorn (Shrub) Crataegus monogyna
- Hazel (Shrub) Crataegus monogyna
- Horse chestnut (Tree) Aesculus hippocastanum
- House martin (Bird) Delichon urbicum
- Lesser celandine (Flowering Plant) Ficaria verna
- Norway maple (Tree) Acer platanoides
- Orange-tip butterfly (Insect) Anthocharis cardamines
- Oxeye daisy (Flowering Plant) Leucanthemum vulgare
- Peacock butterfly (Insect) Aglais io
- Primrose (Flowering Plant) Primula vulgaris
- Red admiral butterfly (Insect) Vanessa atalanta
- Rook (Bird) Corvus frugilegus
- Seven-spot ladybird (Insect) Coccinella septempunctata)
- Silver birch (Tree) Betula pendula
- Small tortoiseshell butterfly (Insect) Aglais urticae
- Snowdrop (Flowering Plant) Galanthus spp.
- Song thrush (Bird) Turdus philomelos
- Speckled wood butterfly (Insect) Pararge aegeria
- Swallow (Bird) Hirundo rustica
- Sycamore (Tree) Acer pseudoplatanus
- Wild cherry (Tree) Prunus avium
- Wild garlic (Flowering Plant) Allium ursinum
- Wood anemone (Flowering Plant) Anemone nemorosa
- Wren (Bird) Troglodytes troglodytes
- Yellow archangel (Flowering Plant) Lamium galeobdolon
- Yellowhammer (Bird) Emberiza citrinella