Photographs will be updated in the future
In the UK, 633 wild bird species have been recorded up to 2024, from eagles and owls to kingfishers and thrushes. Between 2015 and 2020 though, almost half of all bird species in the UK were seen to have experienced a decline in number, adding to a steady decline over 50 years. Some of the biggest factors have been increased development, agricultural intensification, habitat loss, lack of woodland management, disease, and climate change, amongst others.


As bird species continue to lose access to habitat and food sources across the UK, our gardens, however big or small, are becoming an important lifeline for populations. ‘Garden birds’ refer to any species that visit and utilise a garden, and species will depend on what food, water, and habitat is available, and also the habitats that can be found around a garden. This often leads to variation in what people may see from garden-to-garden.
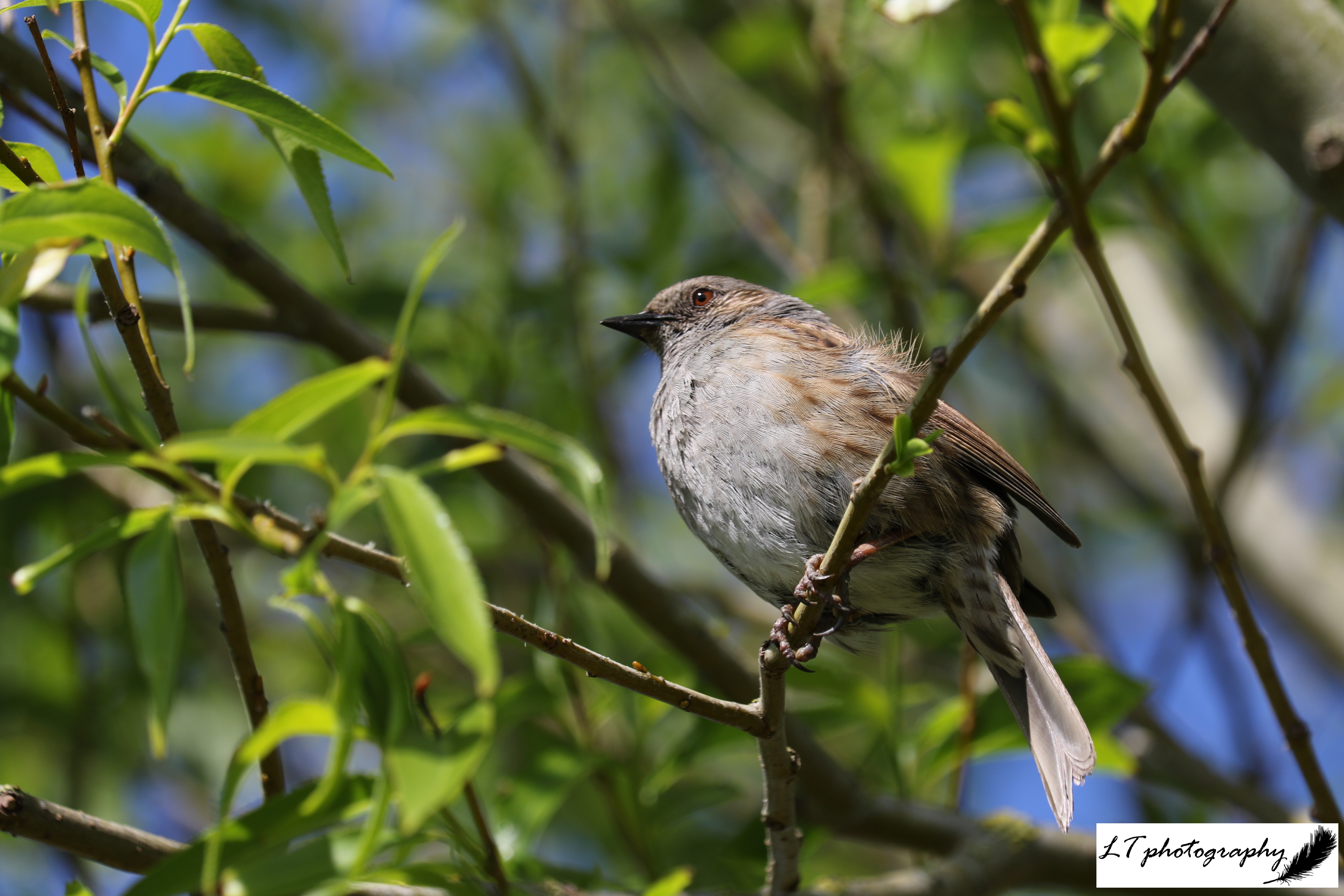


Despite differences, there are a number of birds that are more likely to be seen in gardens, and it is great to know what you may be seeing to help easily tailor your garden for their use, such as what bird food to offer. To help identify species, here you can find a helpful guide to 10 birds that can often be seen in gardens across the UK, even when their populations are decreasing in number. Take a look below!


Species:
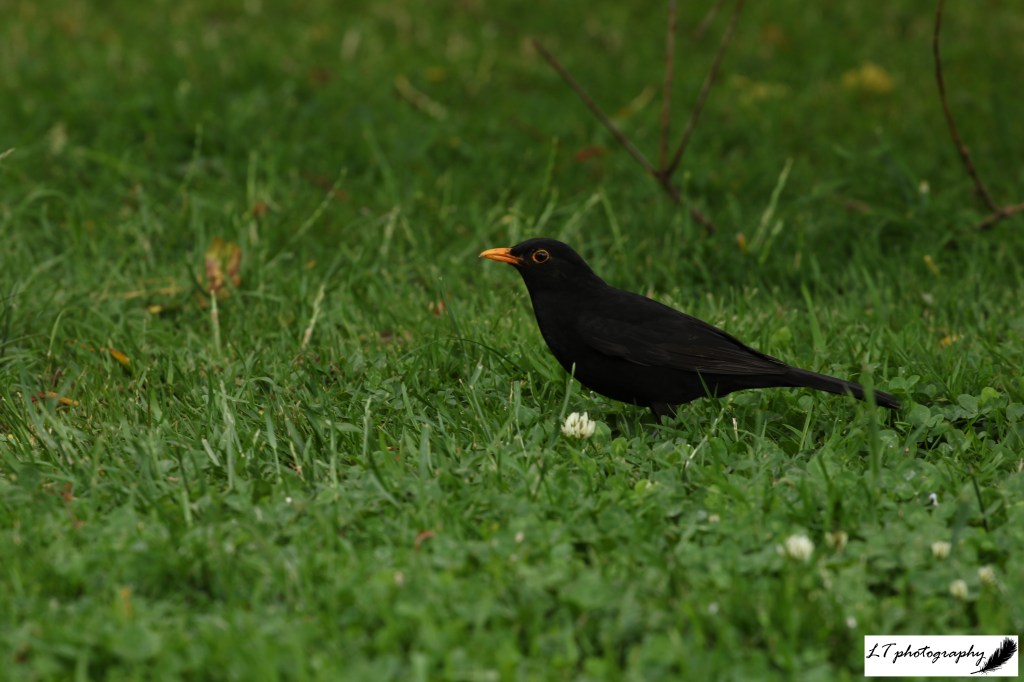
Common Blackbird (Turdus merula)
- Length: 23.5 – 29cm
- Weight: 80 – 125g
- Colour: Adult males are all black with a yellow beak, whilst adult females are dark brown with a more dull beak. Young start as a speckled version of the female and change to adult feathers through moulting their feathers
- What To Feed: Mealworms, fat balls, or sunflower hearts on the floor or in a ground feeder
- Breeding Season: March to Late July
- Nest: A round cup made of twigs, grass and other plant materials, close to the ground in adequate cover
- UK Conservation status: Green



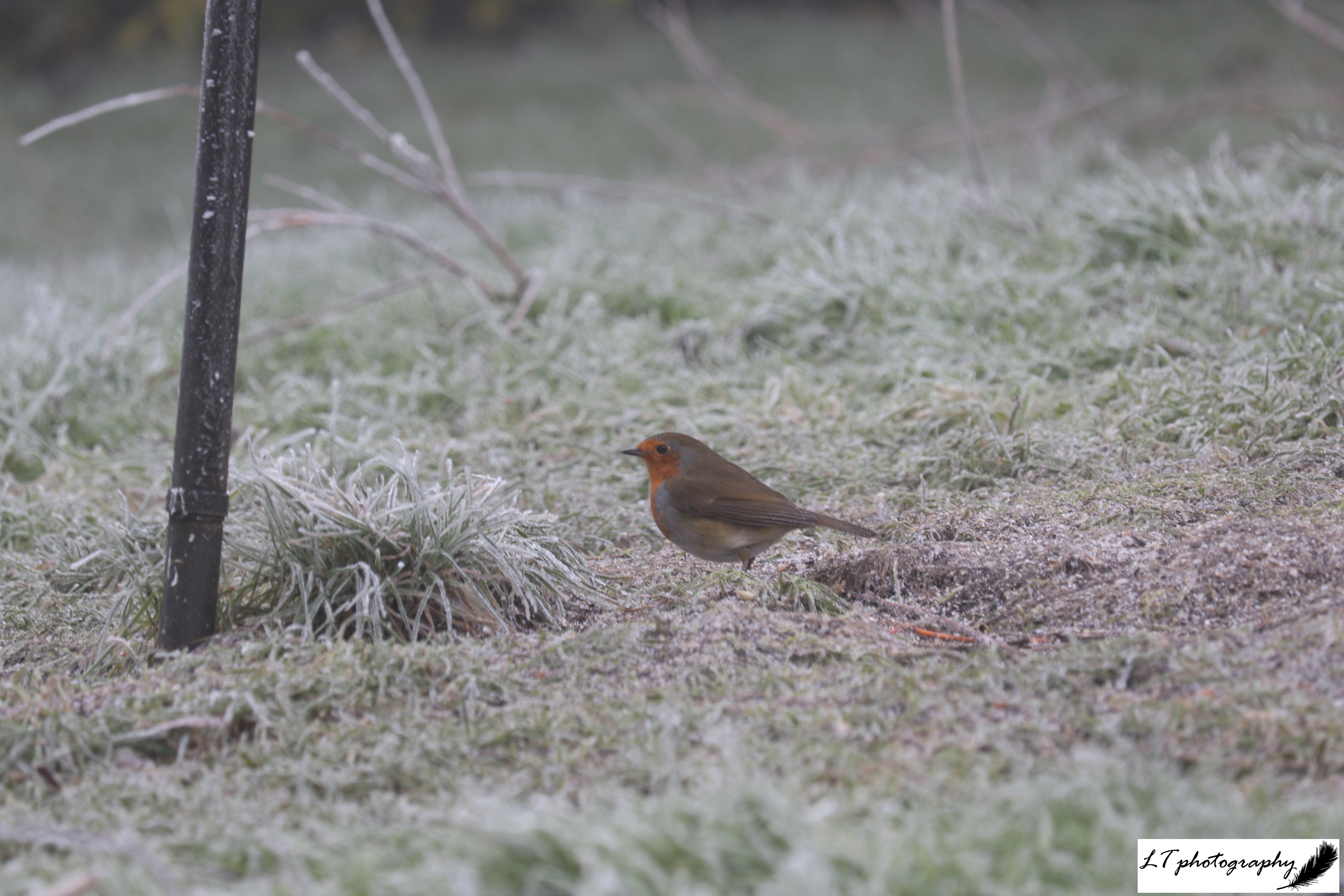
European Robin (Erithacus rubecula)
- Length: 12.5 – 14cm
- Weight: 13 – 21g
- Colour: Adult males and females look the same, both brown with an orange-red breast and white underside. The young start a speckled brown
- What To Feed: Mealworms, suet, or seeds on a ground feeder, bird table or bird feeder with platform
- Breeding Season: March to mid-August
- Nest: A round cup made of grass, moss and leaves and lined with hair and maybe feathers, usually tucked in a hole, crevice or behind something
- UK Conservation Status: Green



House Sparrow (Passer domesticus)
- Length: 14 – 16cm
- Weight: 23 – 35g
- Colour: Adult males have a grey crown and cheeks, chestnut sides to head, black bib, grey underparts, rufous-brown back, and white wing-bar. Adult females and young (until body moult) have buff-brown upperparts, underparts grey, brown cap and cream supercilium behind eye
- What To Feed: Will eat a range food, including seeds and grains from feeders
- Breeding Season: March to August
- Nest: In cavities, where dried plant material is stuffed in to make an untidy sphere which is then lined with softer materials, such as feathers
- UK Conservation Status: Red


Blue Tit (Cyanistes caeruleus)
- Length: 13.5 – 15cm
- Weight: 9 – 13.5g
- Colour: Blue crown, wings and tail, white cheeks, black eye-stripe, underparts yellow, and greyish-black central belly stripe. Their young begin with more dull feathers and yellowish cheeks
- What To Feed: Fat balls, suet, peanuts, or sunflower seeds from hanging feeders
- Breeding Season: March to June
- Nest: Built inside cavities and formed of a cup of plant material, such as moss, lined with soft materials, such as feathers, wool and fur
- UK Conservation Status: Green



Great Tit (Parus major)
- Length: 13.5 – 15cm
- Weight: 14 – 22g
- Colour: Black head with white cheeks, moss-green back, blue-grey wings and tails, yellow underparts and black central belly-band. Males have wider, more defined belly-band. Young begin more dull and with yellowish cheeks
- What To Feed: Suet, fat balls, peanuts, or sunflower seeds in hanging feeders
- Breeding Season: March to July
- Nest: Built inside cavities, formed of a cup of twigs, roots, moss, lichen and/or grasses, and lined with soft materials, such as hair or plant material
- UK Conservation Status: Green



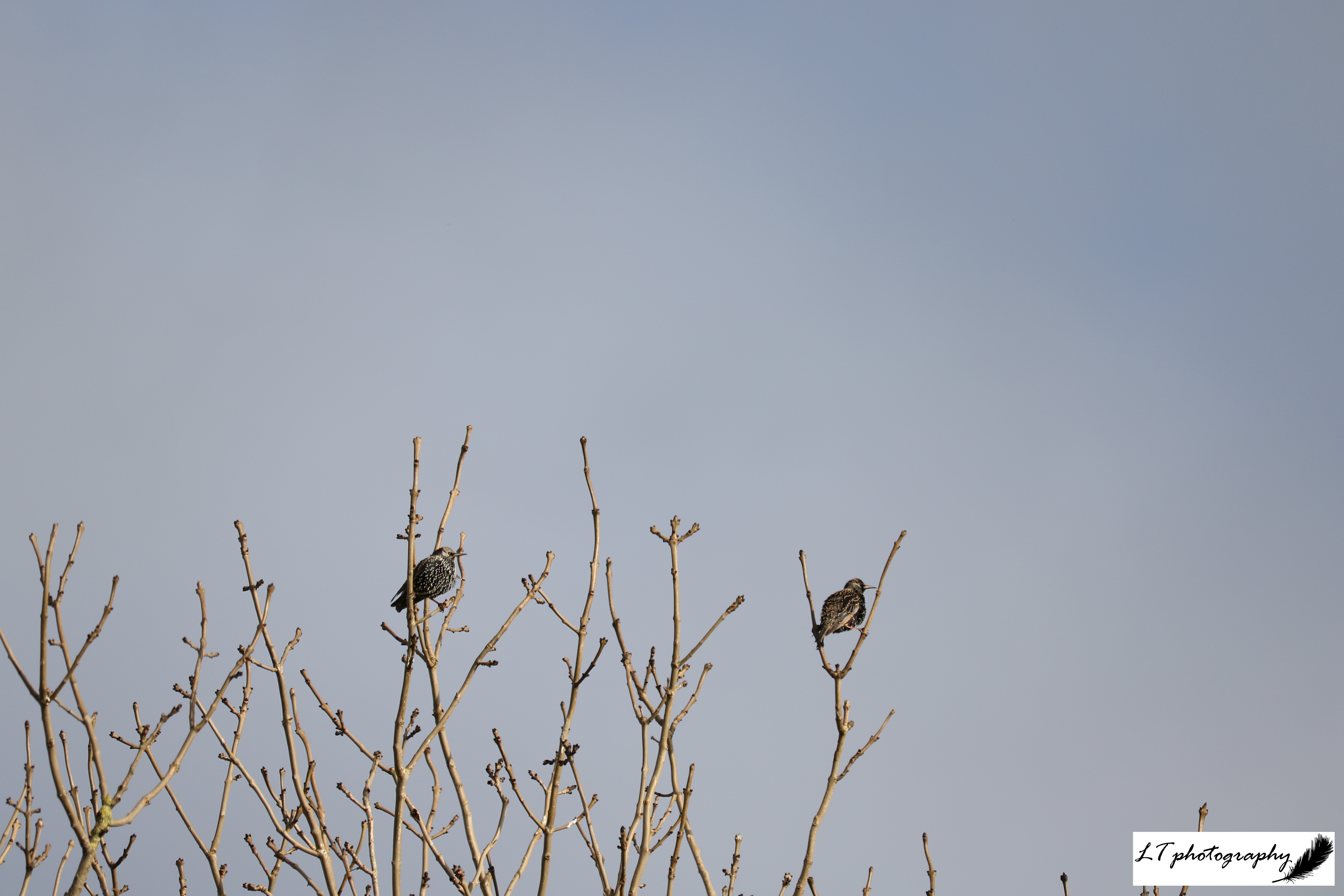
Starling (Sturnus vulgaris)
- Length: 19 – 22cm
- Weight: 60 – 97g
- Colour: Black bird with long-pointed yellow bill, white spots dotted through plumage, a green-purple sheen to the feathers and pale pink legs. The young start with grey-brown feathers and change with body moult
- What To Feed: Suet, peanuts or sunflower hearts in hanging and ground feeders
- Breeding Season: March-July
- Nest: In holes and cavities in trees and buildings, made up of a messy depression of plant stems, grass, and moss, and often lined with feathers or wool
- UK Conservation Status: Red



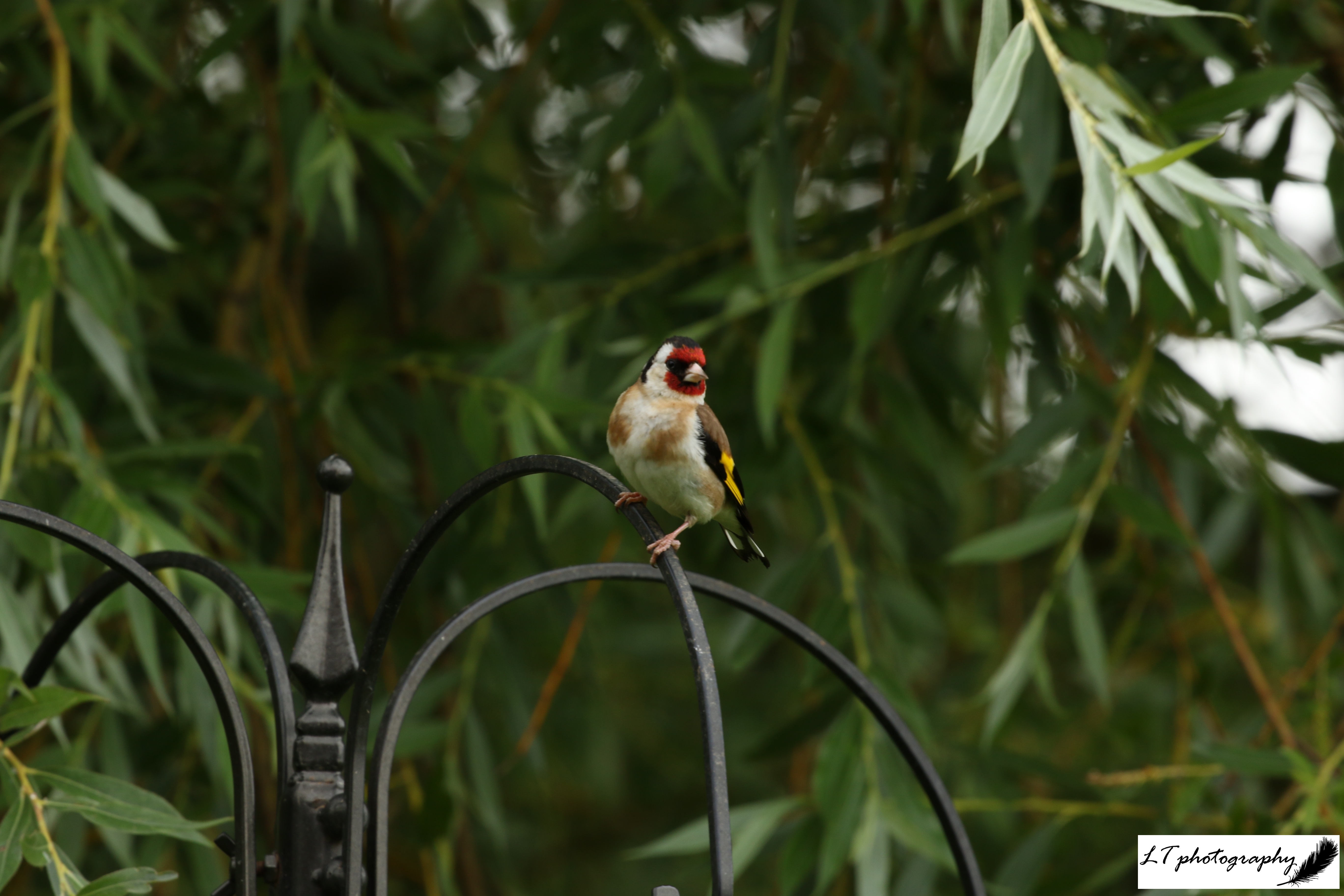
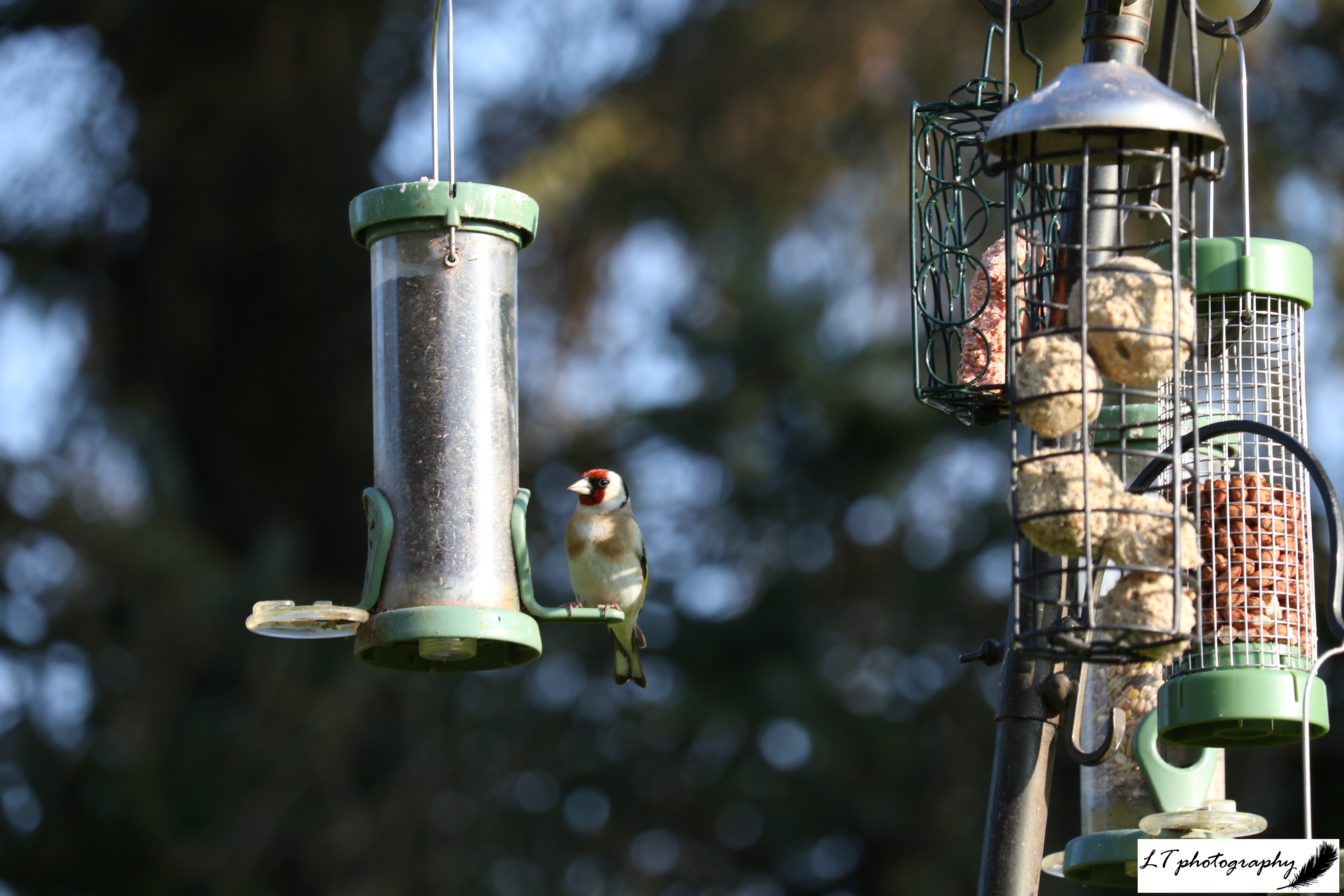
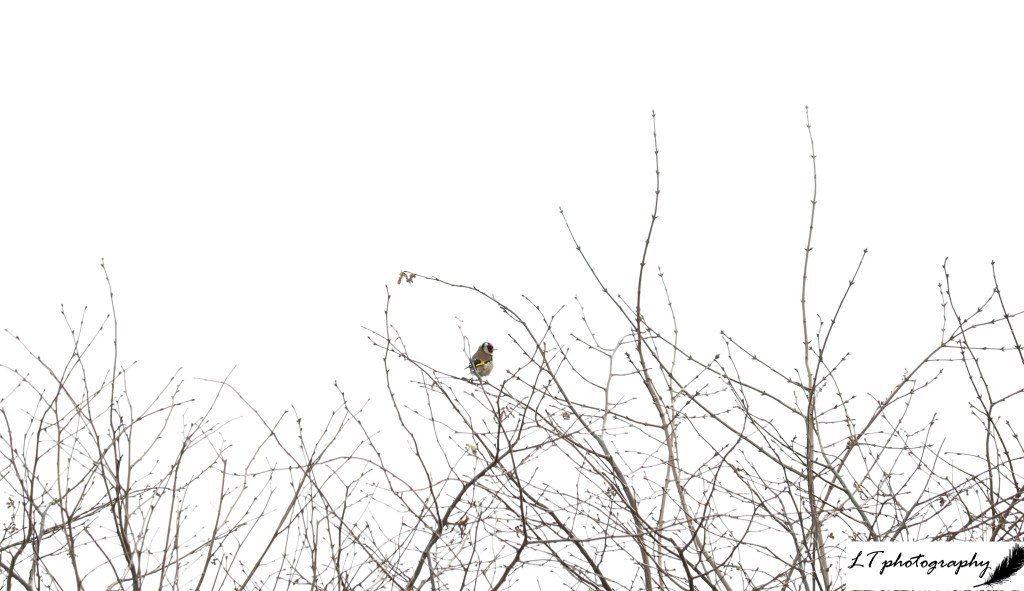
Goldfinch (Carduelis carduelis)
- Length: 12 – 13.5cm
- Weight: 13 – 20g
- Colour: Adults have a black and white head with red face, brown back, black wings with yellow bar, and black tail with white spots. Young lack colourful head until body moult
- What To Feed: Sunflower hearts, niger seeds or mixed seed in hanging feeders
- Breeding Season: April to August
- Nest: A neat cup made of moss, grass, wool, and hair, relatively far off of the ground in tight tree branches, hedges or shrubs
- UK Conservation Status: Green



Chaffinch (Fringilla coelebs)
- Length: 14 – 16cm
- Weight: 17.5 – 29g
- Colour: Adult males have pinky-red cheeks and breast, and blue-grey crown and neck, whereas adult females and young lack the colourful head and instead have a grey-green one. All have a distinct pale rump and double white wing bars
- What To Feed: Peanuts, sunflower seeds, seed mixes, or suet in hanging or ground feeders
- Breeding Season: April to June
- Nest: Deep cup of lichens, grass, roots and feathers, lined with plant down, feathers or wool, usually in the fork of a tree, shrub or hedgerow
- UK Conservation Status: Green


Collared Dove (Streptopelia decaocto)
- Length: 29 – 33cm
- Weight: 168 – 249g
- Colour: Pale pinky-grey-brown feathers, black neck collar, dark eye, grey underparts, and reddish feet
- What To Feed: Small seeds from ground feeders or bird tables
- Breeding Season: March to September
- Nest: Sparse platform of twigs and leaves in trees or high up in buildings
- UK Conservation Status: Green


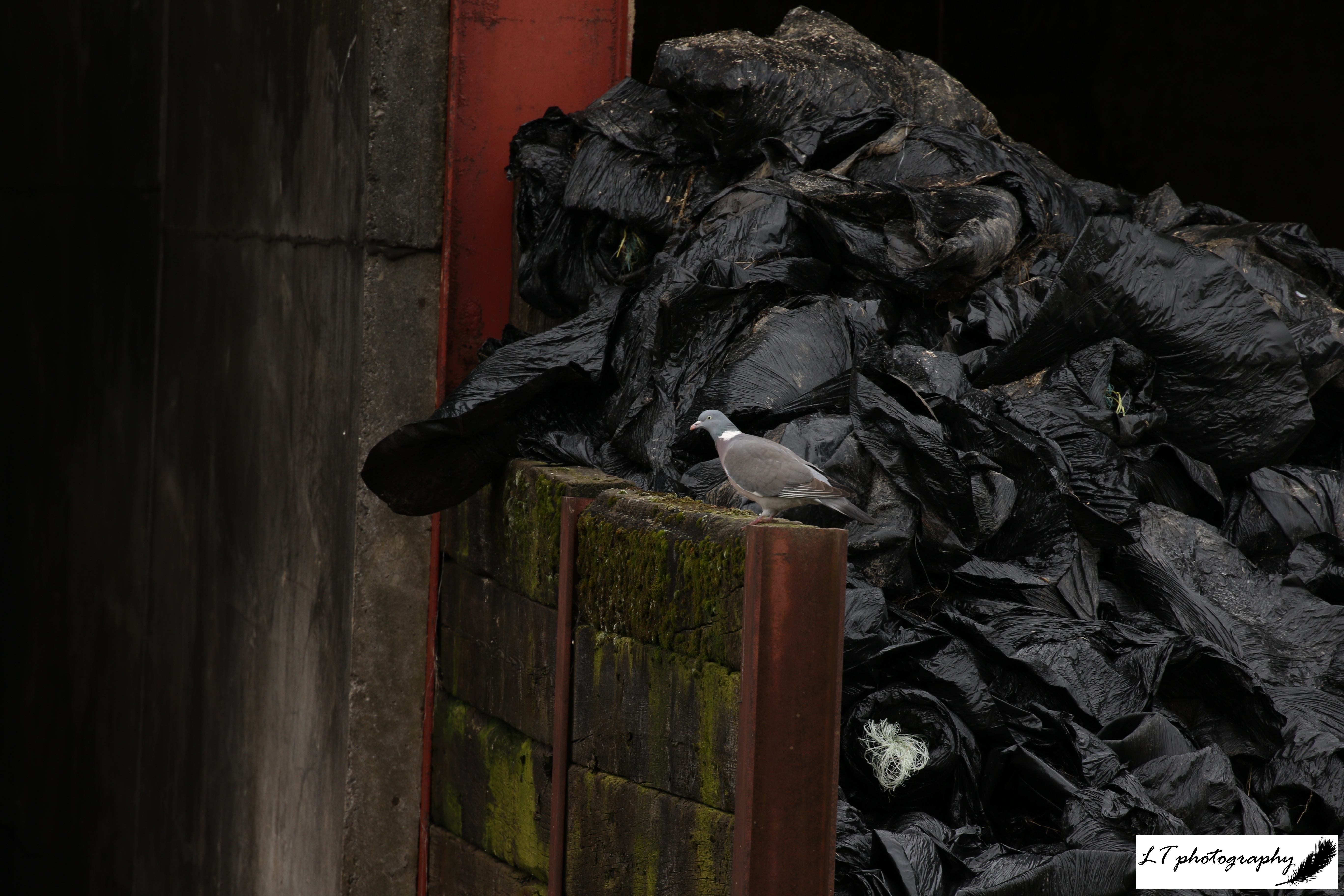
Woodpigeon (Columba palumbus)
- Length: 38 – 43cm
- Weight: 325 – 620g
- Colour: Grey-blue head and back, pinky-red belly, large white patch on neck, sides of neck iridescent purple and green, white wing patches and pink legs. Young are pale with no neck patch.
- What To Feed: Only British herbivorous bird. Feed seeds on a bird table, ground feeder or the ground
- Breeding Season: February to November
- Nest: Simple platform constructed from sticks in trees, shrubs, vegetation or ledges
- UK Conservation Status: Amber