June has been one of those months that has passed by in the blink of an eye. Rainy days quickly moved into scorching heat and then back to rain, framing the last of spring’s events. Every day I have tried to be outside as much as possible, with my happy place being out in nature. From work to down time, my life and hobbies revolve around the wild and the natural world around me. This is why I love to share my experiences with others, to excite, inspire, and instill, and to help motivate people to protect and conserve what is left of our natural world.


It is not surprising then that I am always up for a wild challenge. Last year this took the form of the Wildlife Trusts’ 30 Days Wild, an annual nature challenge that has now run for 6 years, with more than a million people taking part last year. This challenge aims to bring people closer to nature whilst making a positive difference for wildlife and its conservation. All you have to do is complete one ‘Random Act of Wildness’ each day for the whole of June. It is that simple!



Last year I really enjoyed participating in 30 Days Wild, with the challenge enriching my days, helping me to relax, and allowing me to develop a deeper connection with the natural world around me. It also gave me an added focus on days that were busy and stressful, keeping me centred and moving forward. My Random Acts of Wildness ranged from making bird food and picking fruit, to dissecting barn owl pellets and learning my chalkland wildflower species. So it was an easy decision this year to take part once again.



Here’s what I got up to during 30 Days Wild 2021:
Day 1: Tuesday 1st (Work)
For the start of my 30 Days Wild, I began strong.
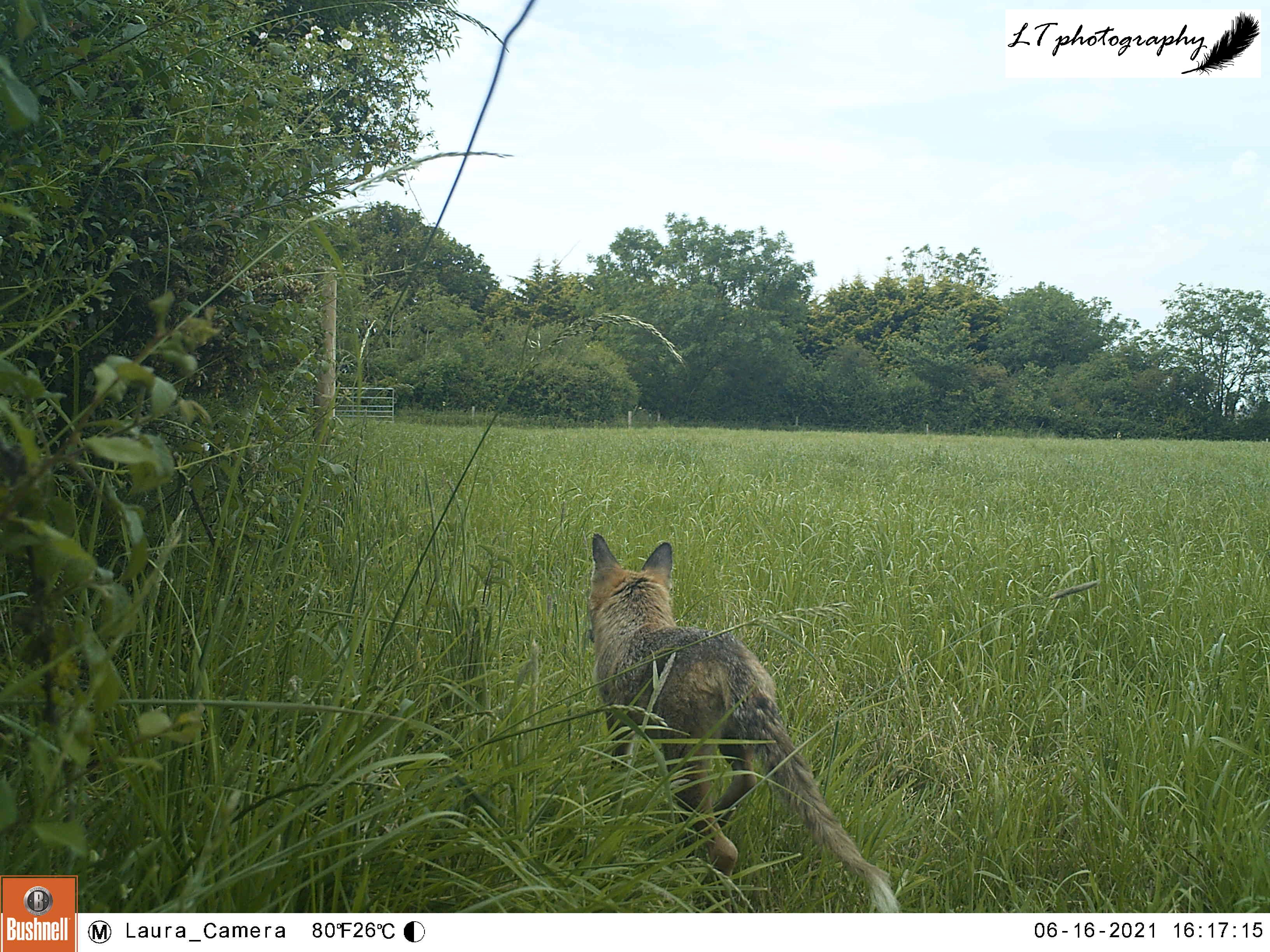
After failing to find an active kestrel nest last year, I finally found the natural nest I had been hoping for! I also checked and moved my camera trap after a week out at a badger sett, discovering my second family of foxes of this year, with it being by far my best camera trapping season yet!
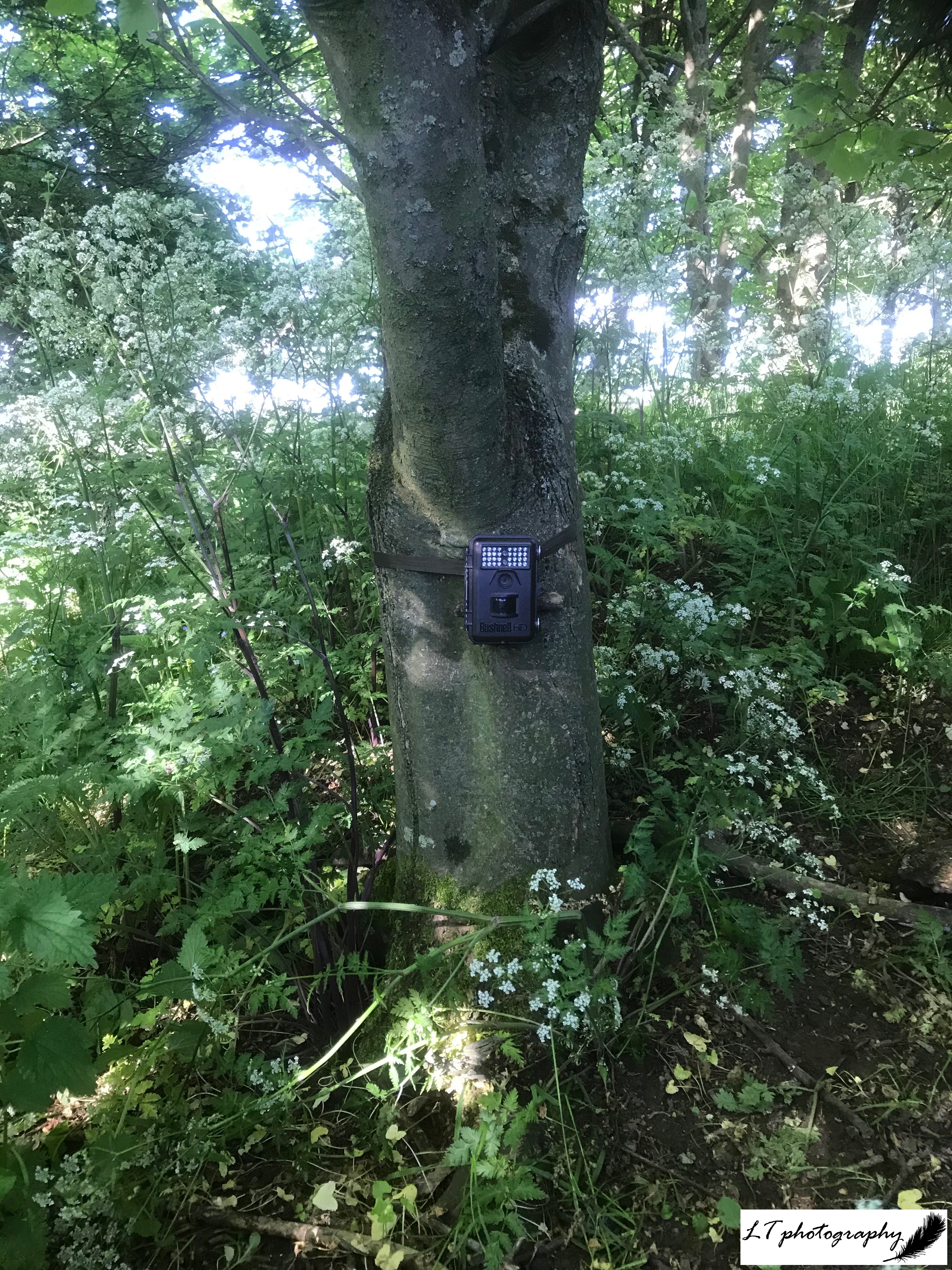


Day 2: Wednesday 2nd (Day Off)
I love an adventure, and so today I ventured out into my local area in the rain to take in as many different habitats and species as possible, with the highlight being 4 red kites sitting in a tree on my family’s land. After drying off and allowing the rain to pass, that afternoon I headed back outside, this time to test my brand new macro lens and get stuck in to the world of the small.


Day 3: Thursday 3rd (Day Off)
For my second day off, I made the most of free time and went for a long ride with a friend, the highlight being riding through chalk grasslands, embellished with colourful flowers and melodious birds. Being on horseback in this way allows me to take in a range of wildlife in a short period of time and also give me great up-close views.

Day 4: Friday 4th (Work)
For spring, my wildlife blog has been back up and running, and every Friday has been a Wild Friday. For this week, my new post was all about the spring bluebells, which are one of my favourite parts of spring each year. Check it out on my blog now!


Day 5: Saturday 5th (Work)
After a long day at work, I still had energy to work on some of my nature projects. This included putting my dad together a list of all the bird species seen on my family’s land in the last year (65!), and learning how to fill in nest records for the BTO’s Nest Record Scheme, beginning with a blackbird’s, kestrel’s, and barn owl’s nest.


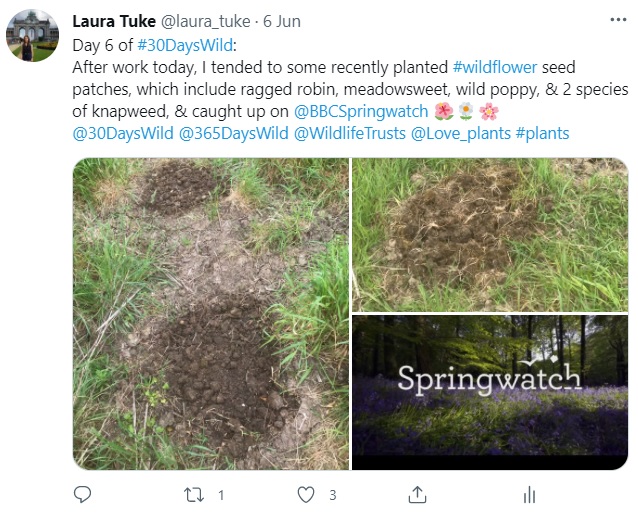
Day 6: Sunday 6th (Work)
A week ago I cleared a small wildlife area of docks and sowed some homemade wildlife mixes, so this evening after work I headed over to the area to do some management and to water the seeds. I then headed home to finish off my day with Thursday’s and Friday’s missed episodes of Springwatch.


Day 7: Monday 7th (Work)
After catching my neice’s cold, today I felt particularly under the weather. It was a perfect way then to spend my evening curled up in an armchair reading some lovely nature blogs to cheer myself up before an early night.
Day 8: Tuesday 8th (Work)
My happy place is out in nature, and so I have been enjoying working at the moment on my family’s farm in Dorset, and keeping an open mind to what I might discover during day-to-day life. Today I had everything from peacock butterflies and Lackey moth caterpillars, to yellowhammers singing and brown hares grazing within 10 metres of me!


Day 9: Wednesday 9th (Day Off)
I began my first of two days by heading to my bird ringing trainer’s private nature reserve to help with summer maintenance work, before returning home to check the kestrel nest and to head round to my next door neighbour’s to look for active swallow nests (4 so far!).
Day 10: Thursday 10th (Day Off)
For my second day off, I had a lovely relaxing hack with Marsha exploring a new route near my home, and spent time watching and counting the birds visiting the feeders in my garden. From pheasants and house sparrows to goldfinches and greenfinches, all species and their abundance are recorded in my garden and sent off at the end of the week to the BTO’s Garden BirdWatch scheme.
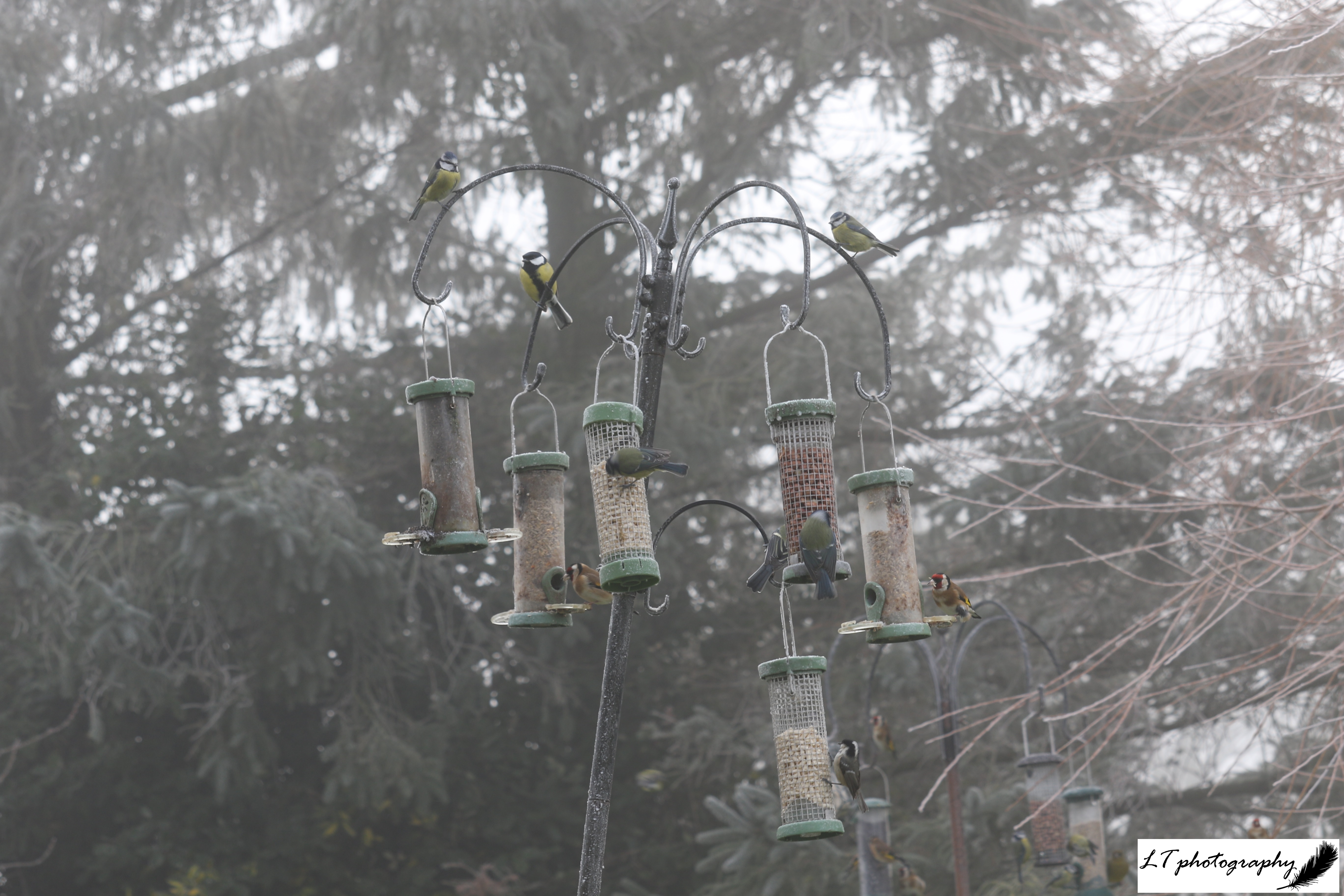


Day 11: Friday 11th (Work)
Today after work I spent time expanding my wildlife knowledge through reading the BTO’s Lifecycle magazine and BBC Wildlife magazine, and watching the very last episode of 2021’s Springwatch.
Day 12: Saturday 12th (Work)
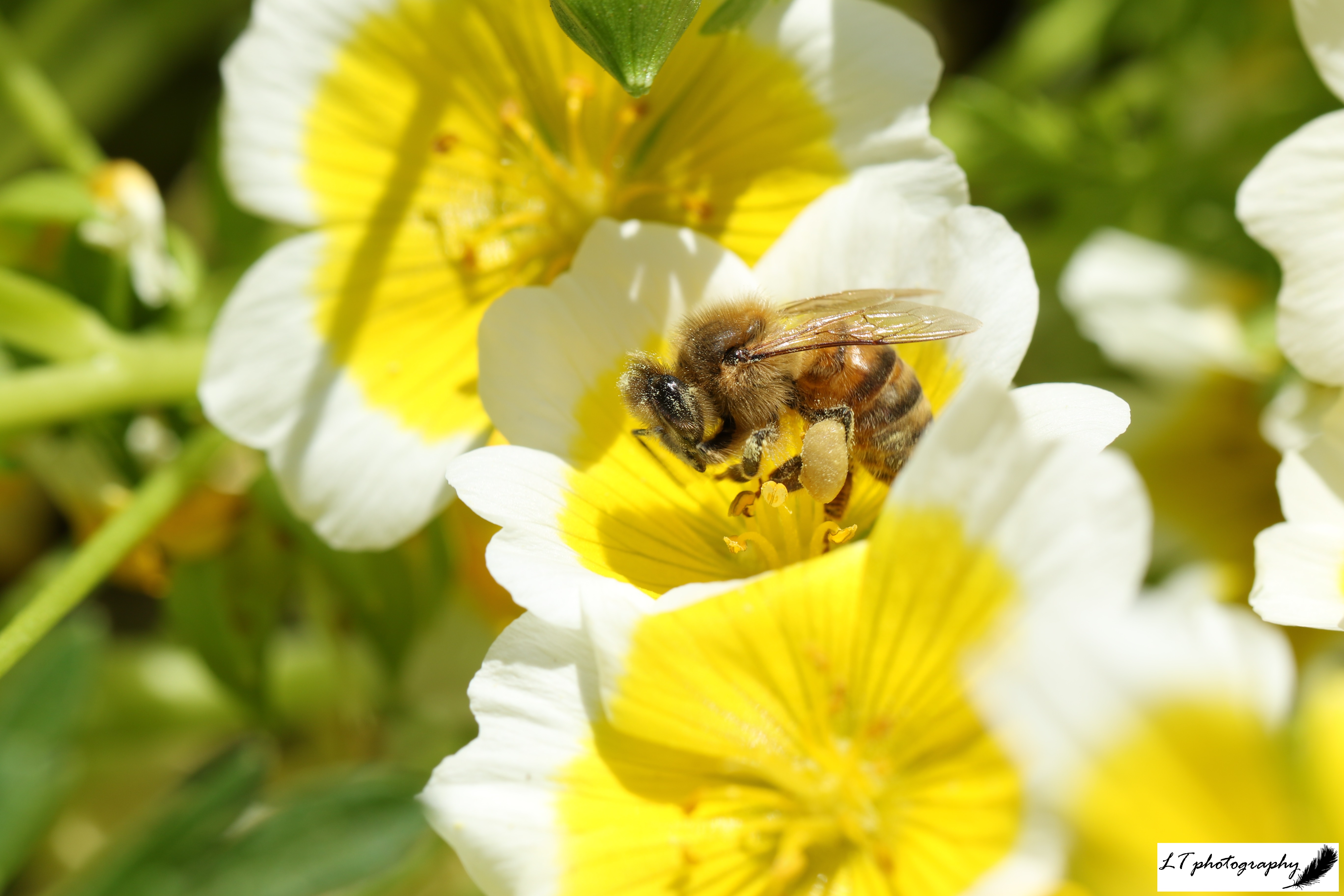
Today I used my lunch break to take photos of the bees buzzing around the poached egg flowers in my family’s garden using my brand new macro lens (very exciting!). My evening was then spent relaxing with my family in my brother and sister-in-law’s garden for a lovely family bbq in the setting sun.


Day 13: Sunday 13th (Work)
Last year I completed a self-set challenge to find an example of wildlife for every letter of the alphabet during just 1 day. Today I decided to have a go once again, but with the added challenge of finding different examples compared to last year. It was tough, but I did it!



Day 14: Monday 14th (Work)
After a long day at work, I spent some time exploring Twitter’s wildlife community, visiting some of my favourite and some new pages. Why not check them out yourself to find out what they have been getting up to?
Day 15: Tuesday 15th (Work)
After work, I had a really lovely evening checking my family’s barn owl nest box and kestrel tree nest with fully licensed members of my ringing group. We were excited to find the adult female barn owl brooding 4 young and the adult female kestrel feeding 3 two week old chicks!


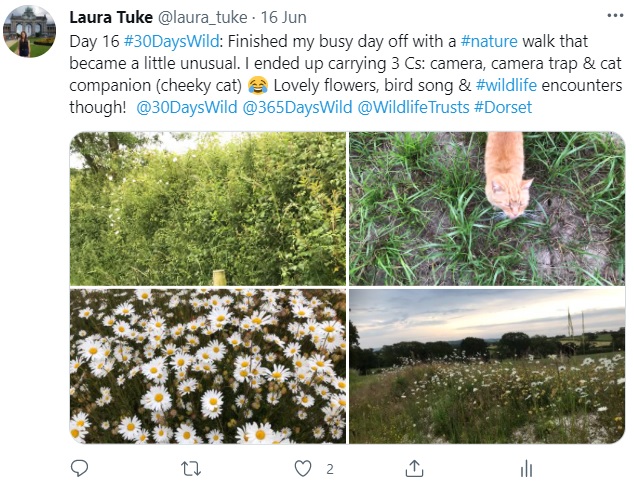
Day 16: Wednesday 16th (Day Off)
To finish off a jam packed day off, I went for a lovely evening walk that began with just me and my camera and ended with me also carrying my camera trap and family’s farm cat. He likes to have a walk, but he gets tired too easily!
Day 17: Thursday 17th (Day Off)
Around my usual horse riding today, I kept myself busy with my wildlife photography, using my camera, taking photos off of memory cards, organising photos, and sorting my camera trap.


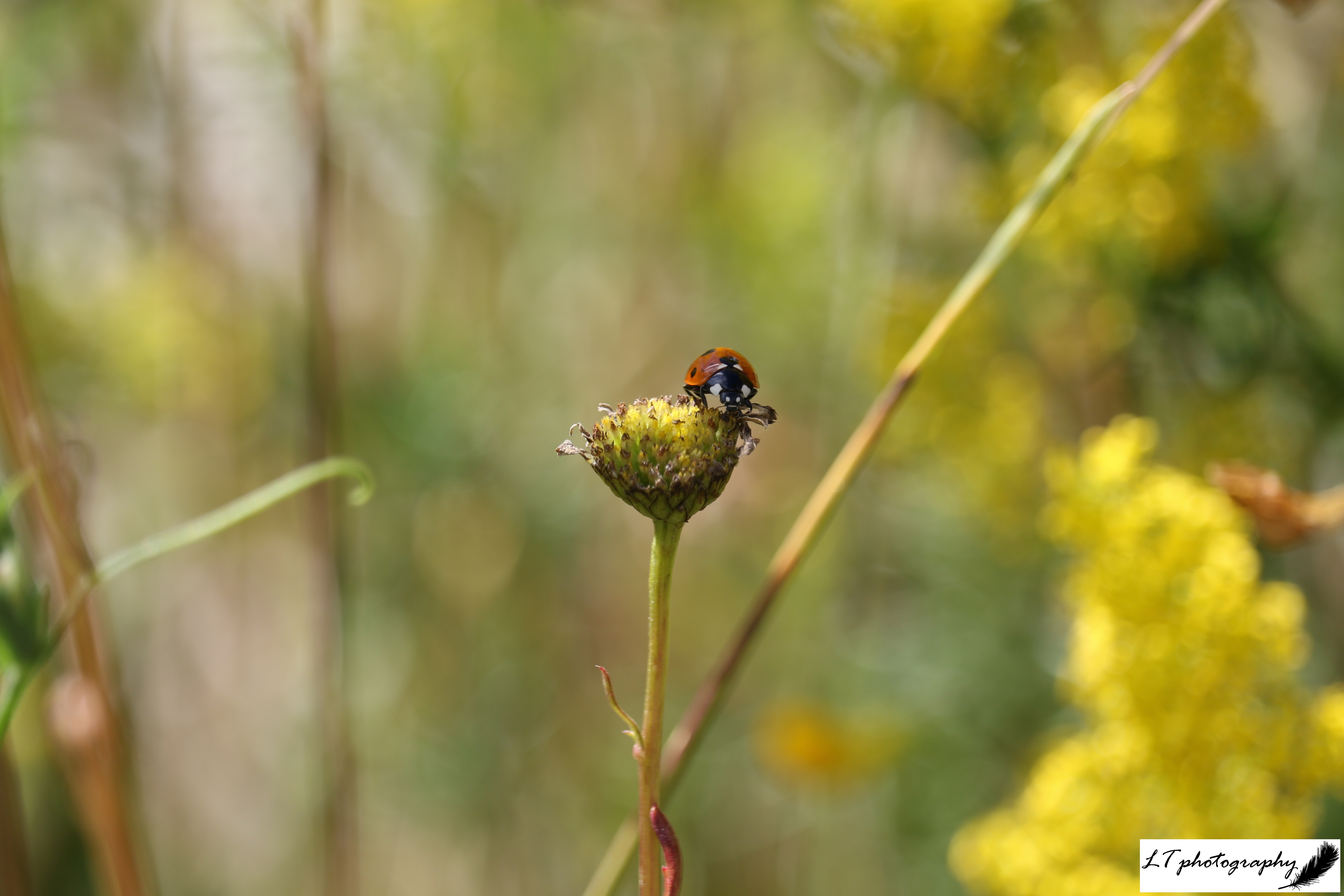
Day 18: Friday 18th (Work)
Today was another ‘Wild Friday‘ on my blog meaning a brand new blog post went up all about how spring 2021 unfurled. A little scientific, a little anecdotal, and a little visual-based, it was an enjoyable piece to write.


Day 19: Saturday 19th (Work)
Today I have been very busy looking after my parents’ farm whilst they are away. It has been a great opportunity to take in all that the farm has to offer and to appreciate all the work my parents have done and are doing for wildlife on the farm, from digging ponds to planting trees.
For more information check out my 2020 blog post called ‘Giving Nature a Home on the Farm’.
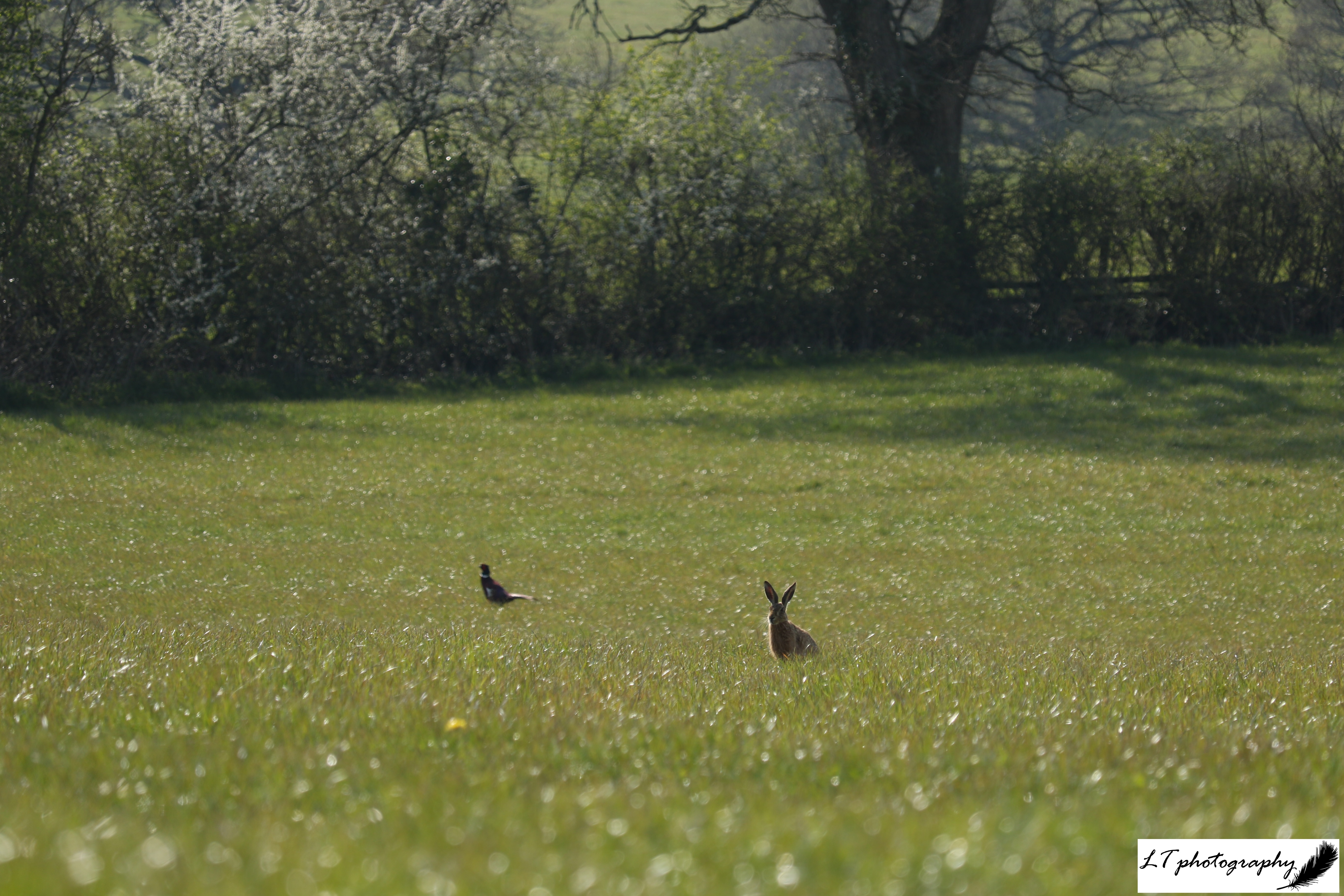


Day 20: Sunday 20th (Work)
After a busy few days looking after the farm, this afternoon I took some time to relax with my family, and be a proud aunt seeing how my very intelligent neice is learning more and more about wildlife. To top off my day, I took part in the Wildlife Trusts Big Wild Quiz, getting a respectable 28 out of 35.
Day 21: Monday 21st (Work)
Nature has a strong influence on british culture, influencing everything from music to art and literature. Nature is also a great inspiration for my own creativity, for example encouraging me to improve my own ability to draw and sketch, and to use my drawings to illustrate my wild ‘How to’ guides.
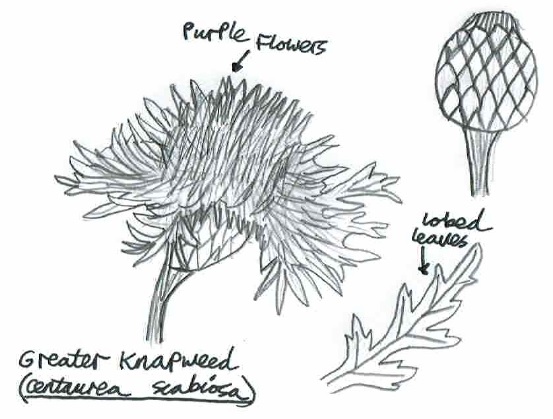
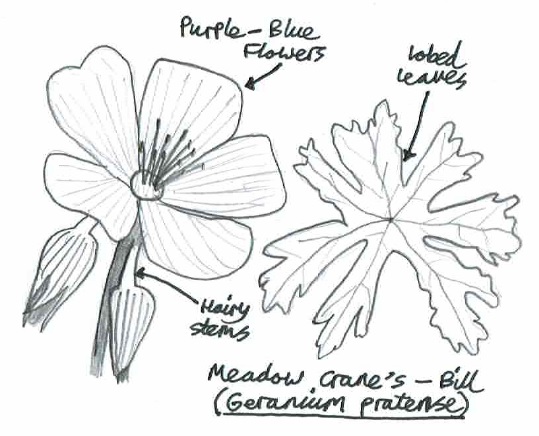
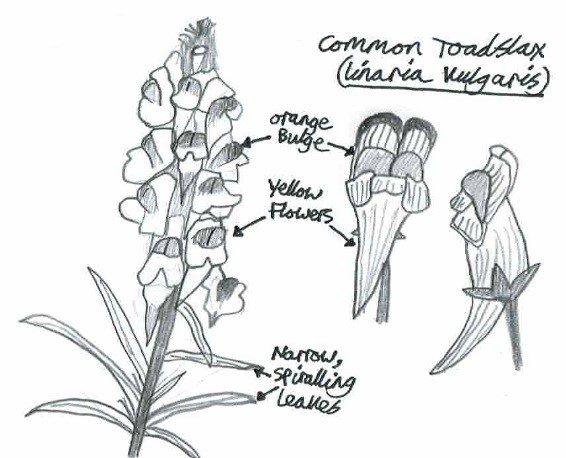
Day 22: Tuesday 22nd (Work)
After a busy day at work, I decided that for today’s Random Act of Wildness I would make a valuable donation to Dorset Wildlife Trust. Any donation that can be made is important for such organisations to be able to do their conservation work, such as rewilding and habitat management.
Day 23: Wednesday 23rd (Day Off)
Around a lovely much needed catch up with and old friend, I spent my day off countryside walking, checking swallow nests, and baking. I followed suit of last year’s baking, and kept it simple with yummy sponge cakes with wild decorations, in the form of flowers, butterflies and leaves. A lot of fun!
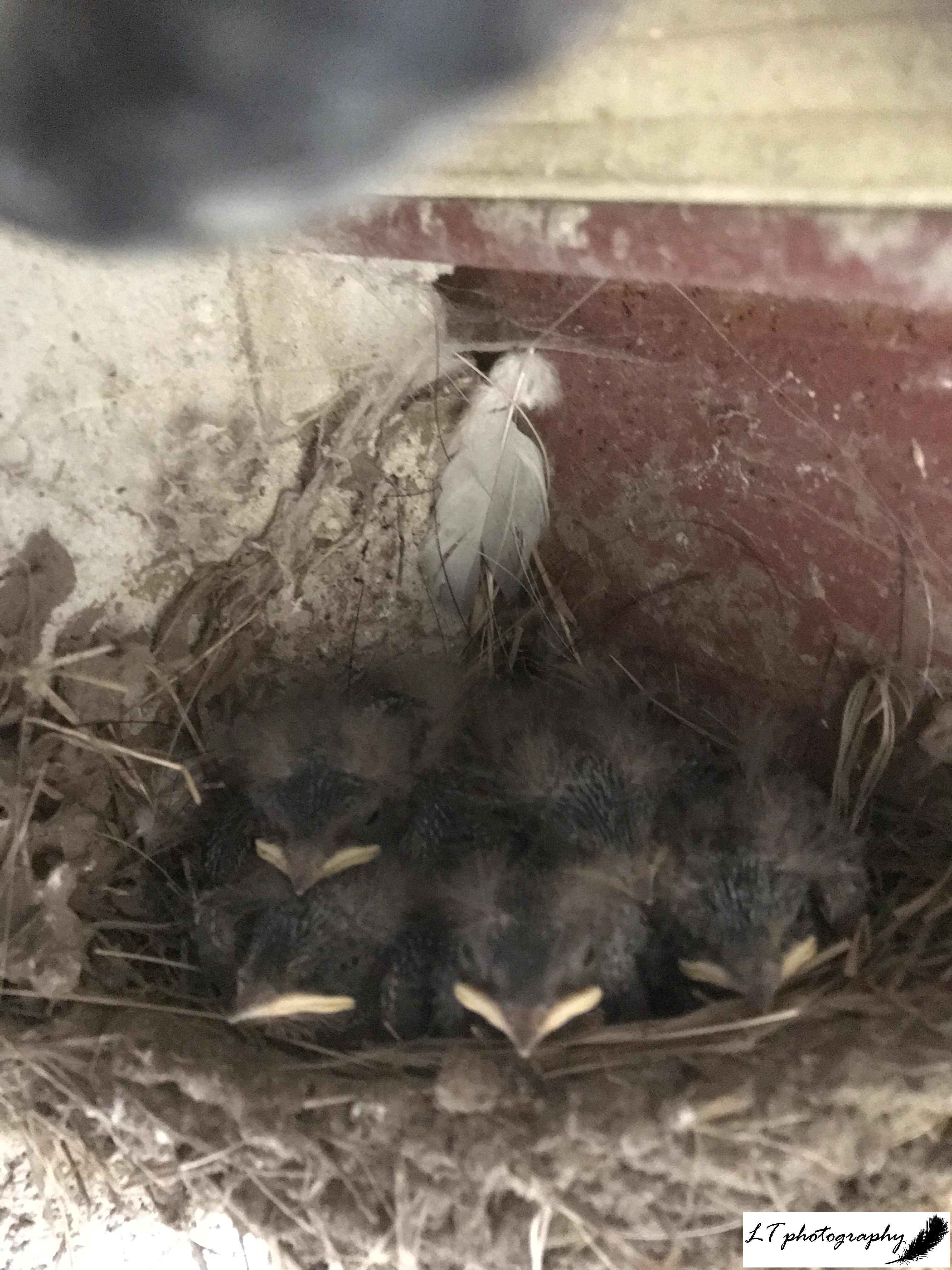


Day 24: Thursday 24th (Day Off)
Today I spent my day checking barn owl nest boxes with Dorset County Council and Alan who I ring with at Conservation Action. Such experiences always feel like a privilege to me and it was a great training experience, topped off with ringing 3 out of 4 of my swallow nests.
Day 25: Friday 25th (Work)
Today was Wild Friday on my blog, with this week’s post being all about my how spring looked for me personally, featuring 16 of my favourite photos from the season. They are either aesthetically pleasing, a great memory, or just bring me joy. Check it out now!


Day 26: Saturday 26th (Work)
Today on a much needed afternoon off, activities included exploring a road verge in my local area to ID plants with my mum (24 wildflower species), and picking elderflower heads to make this year’s elderflower cordial.


Day 27: Sunday 27th (Work)
For the last 2 years I have been enjoying training as a bird ringer, and have become a member of my trainer’s conservation group called Conservation Action. We are based in Dorset and the South West and aim to protect, restore and preserve biodiversity, promote conservation, and to research and monitor the state of nature.
For more information, check out our website at www.conservationactionuk.org or our Twitter and Instagram pages.
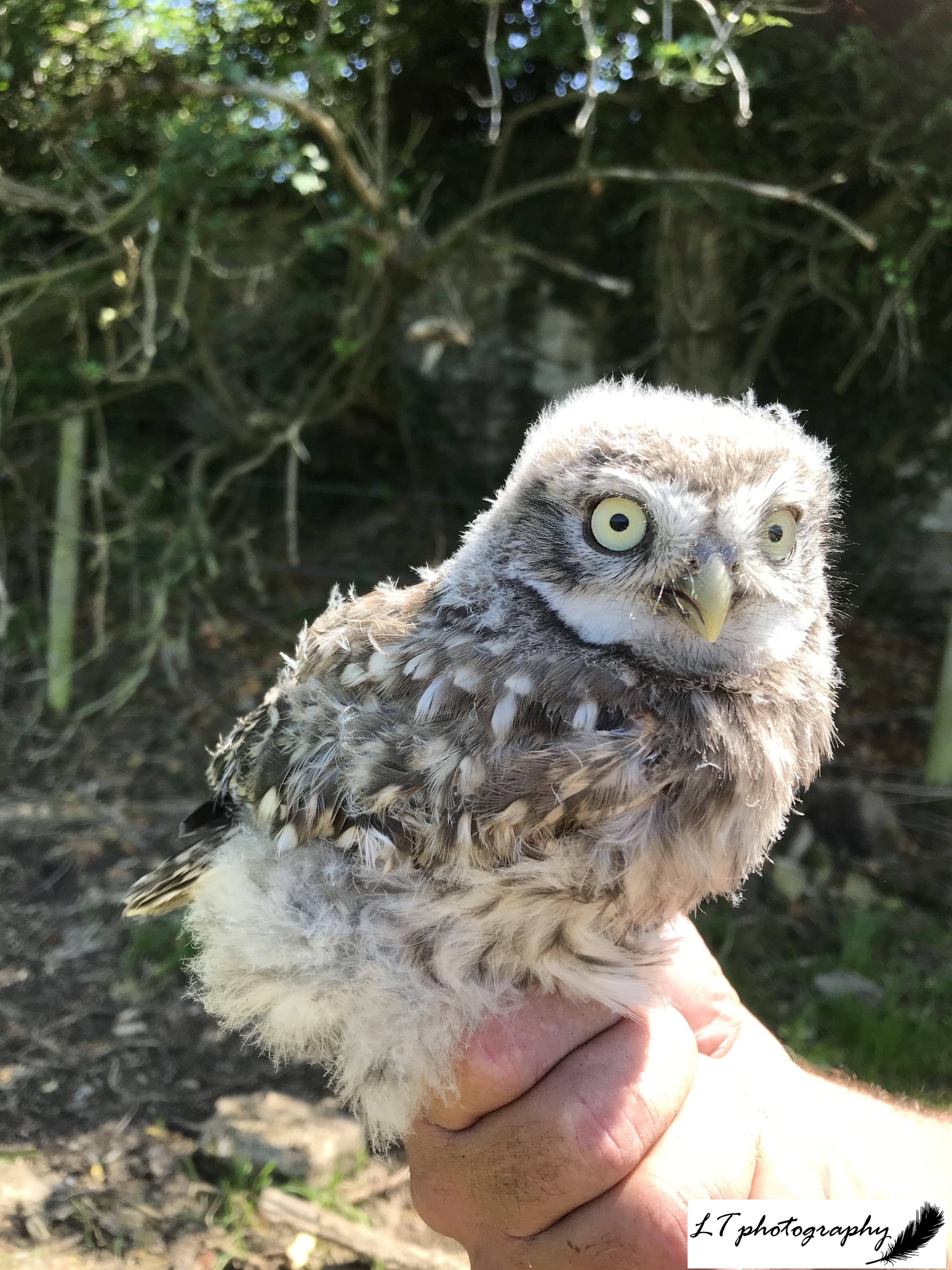
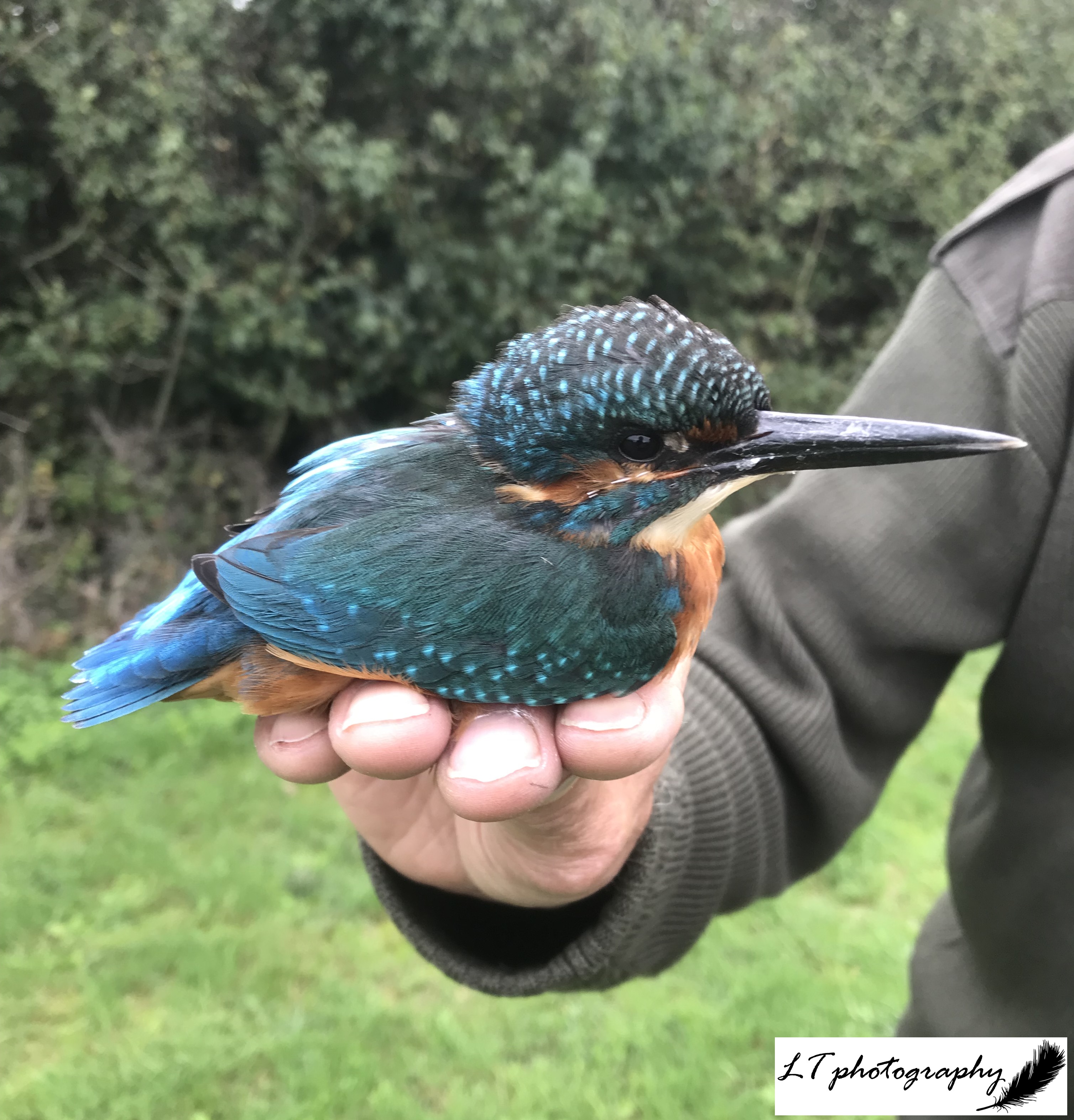


Day 28: Monday 28th (Work)
Though my happy place is being outside in all weathers, today was one of those days when I got a bit too wet and then a bit too sweaty. The day was still very productive, so I felt content at the end of the day to head home and curl up with my current wild book: Gavin Thurston’s ‘Journeys into the Wild: Secret Life of a Cameraman’.
Day 29: Tuesday 29th (Work)
Today I accidentally found a bird’s nest at waist height in a hedge on my family’s farm, spent a lovely half hour out in my garden, the flowers thick with bumblebees, and ringed my final of first brood swallow nest.


Day 30: Wednesday 30th (Day Off)
Today I had a glorious last day of 30 Days Wild. I had a lovely early morning walk with my mum, took photos of the many butterflies on the farm at the moment, and finished the day checking barn owl boxes with my bird ringing training as the sun set


A lovely, active and wild month spent in some of the best ways possible!