“The camera is an instrument that teaches people how to see without a camera” – Dorothea Lange
“The two most engaging powers of a photograph are to make new things familiar and familiar things new” – William Thackeray
As each year passes, and spring rolls around once again, I set out with my trusty camera trap to record the wildlife that call my family’s Dorset farm home. Remote cameras are a great way to delve into and explore the hidden worlds of the wildlife that live alongside us, without causing disturbance. You never know what you may discover, and so there is nothing quite like the excitement I feel each time I check my cameras.


For the last few years I have spent an increasing amount of time using my camera traps to explore and survey my area of Dorset, and each year the results have got better and better. Species recorded range from small mammals and birds up to larger more iconic mammal species, such as badgers. These adventures have allowed me to open my eyes to the species that goes unnoticed on the farm each day, and to help my family forge a deeper connection with the wildlife we strive to manage and protect. Check out my blog posts from 2019, 2020, and 2021 for more!


This year I have visited 8 locations on my family’s farm, using both my old camera trap and brand new model to see what I could discover (check out next week’s blog post for the 8th location). Last year 6 locations were used that were all visited this year also. Some of these sites were used with a set purpose and question to answer, whereas others are just great sites to use for exploring wildlife. This year 9 species were recorded, with 1 new one to add to the collection. Read on to find out what my camera traps found!


Camera Trapping 2022
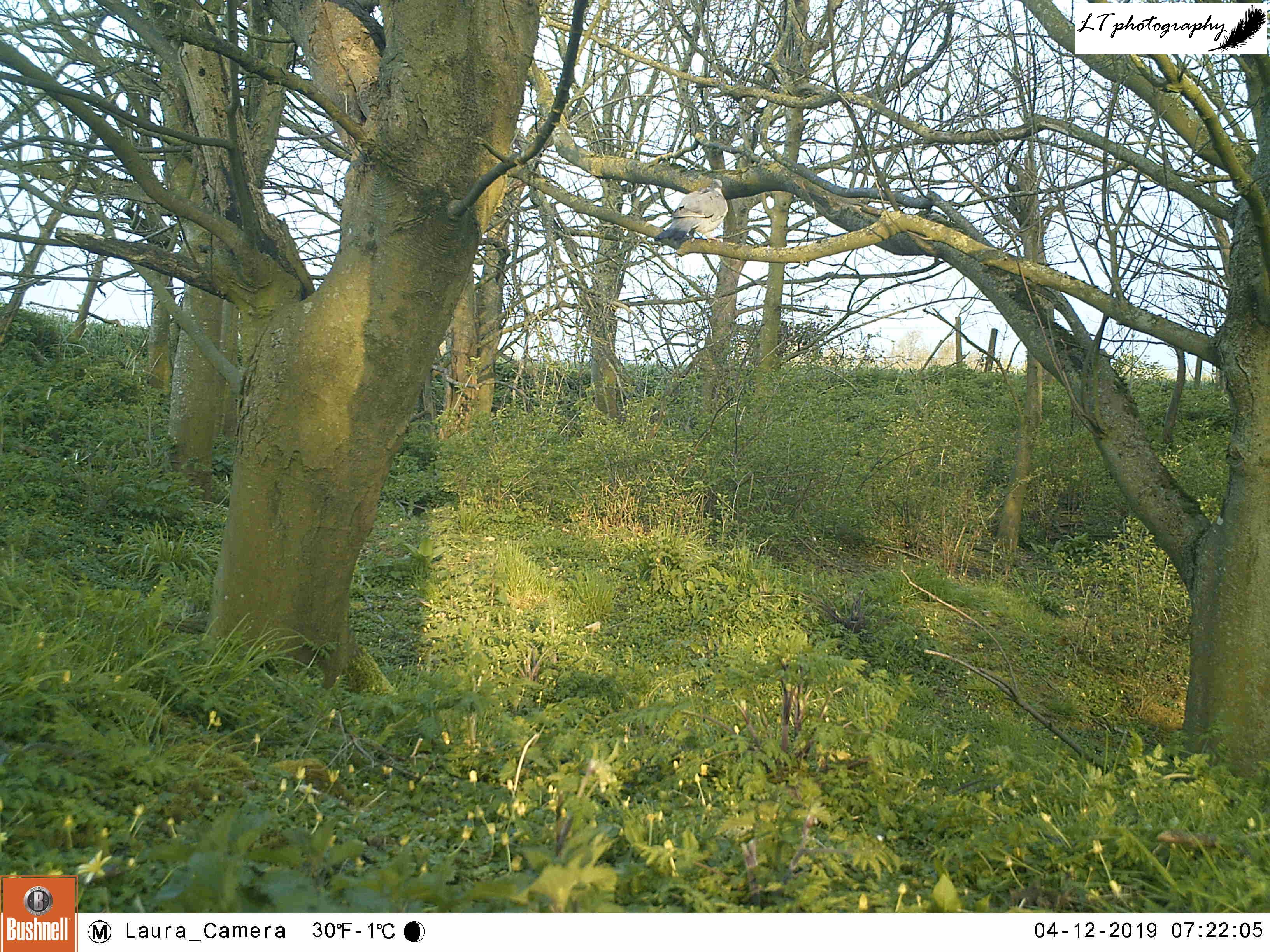
Little Wood Field
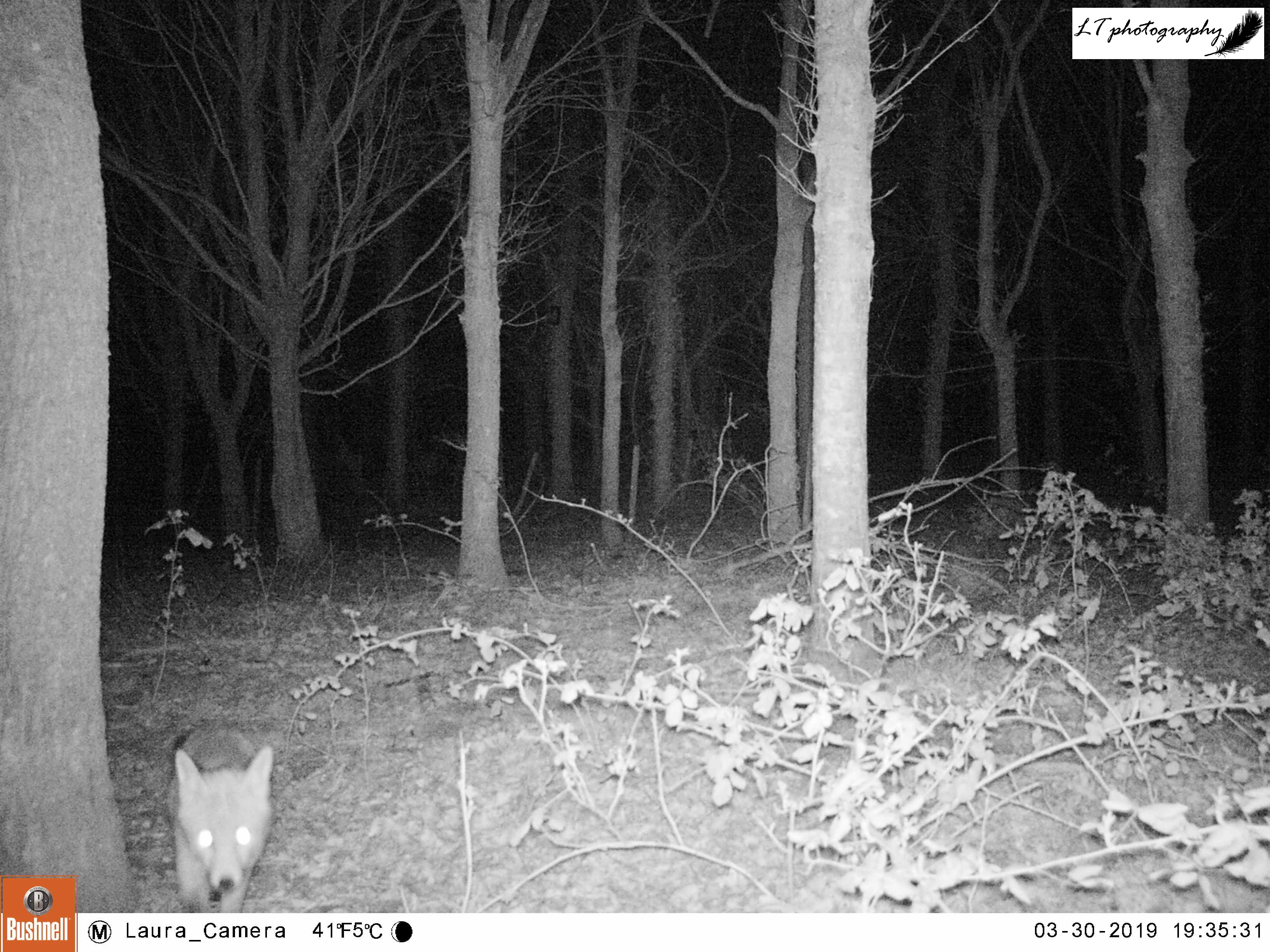
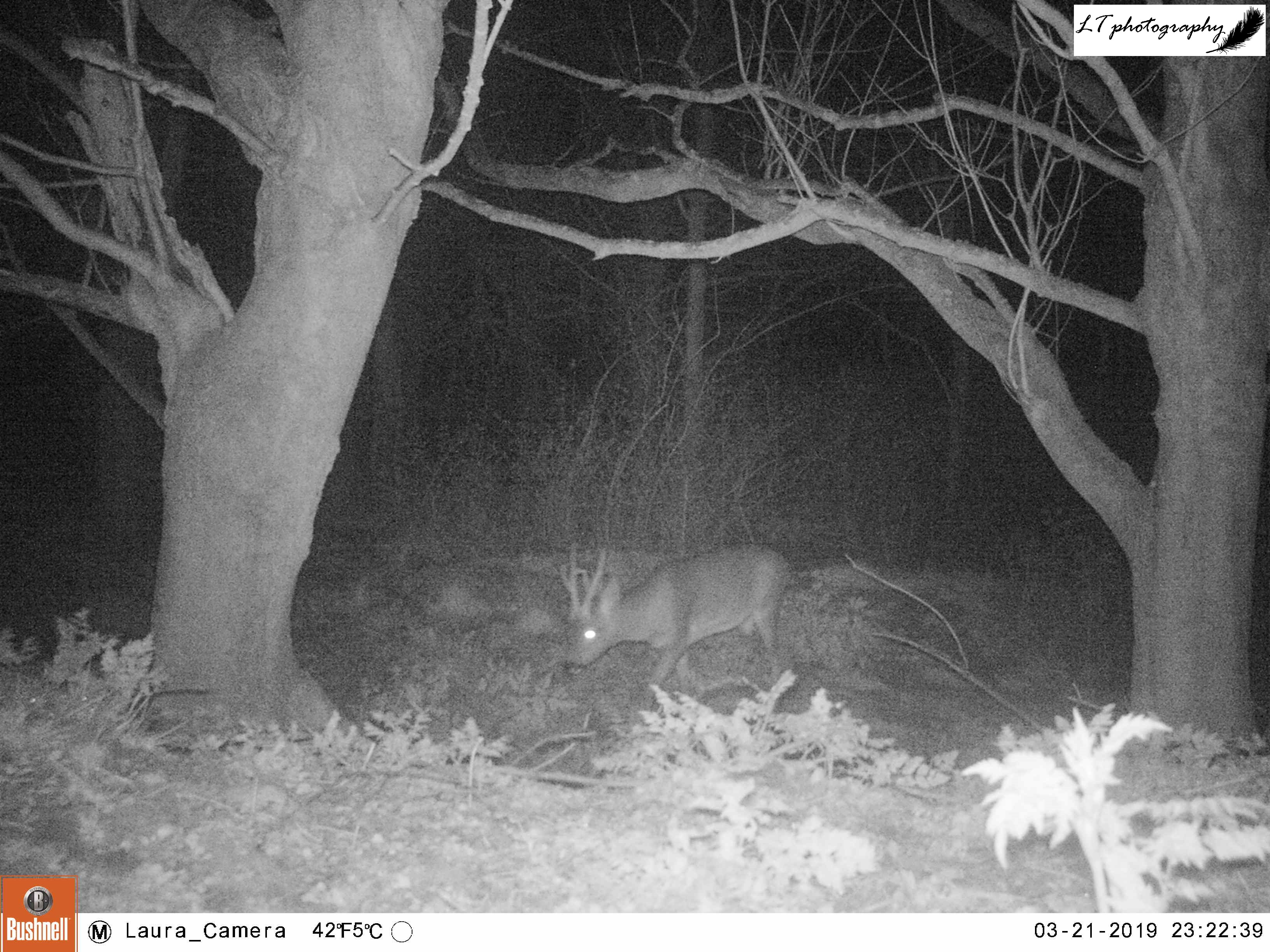
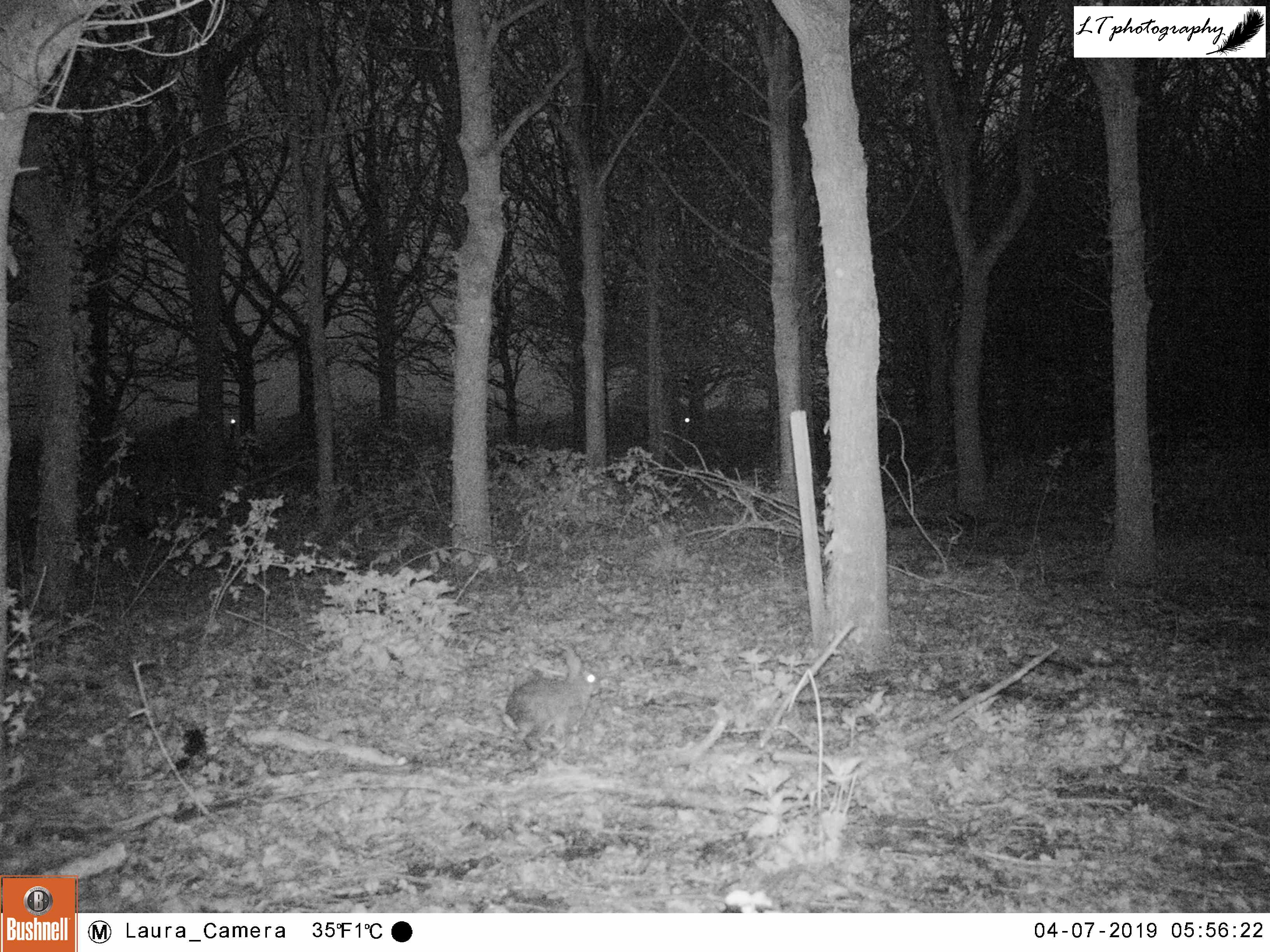
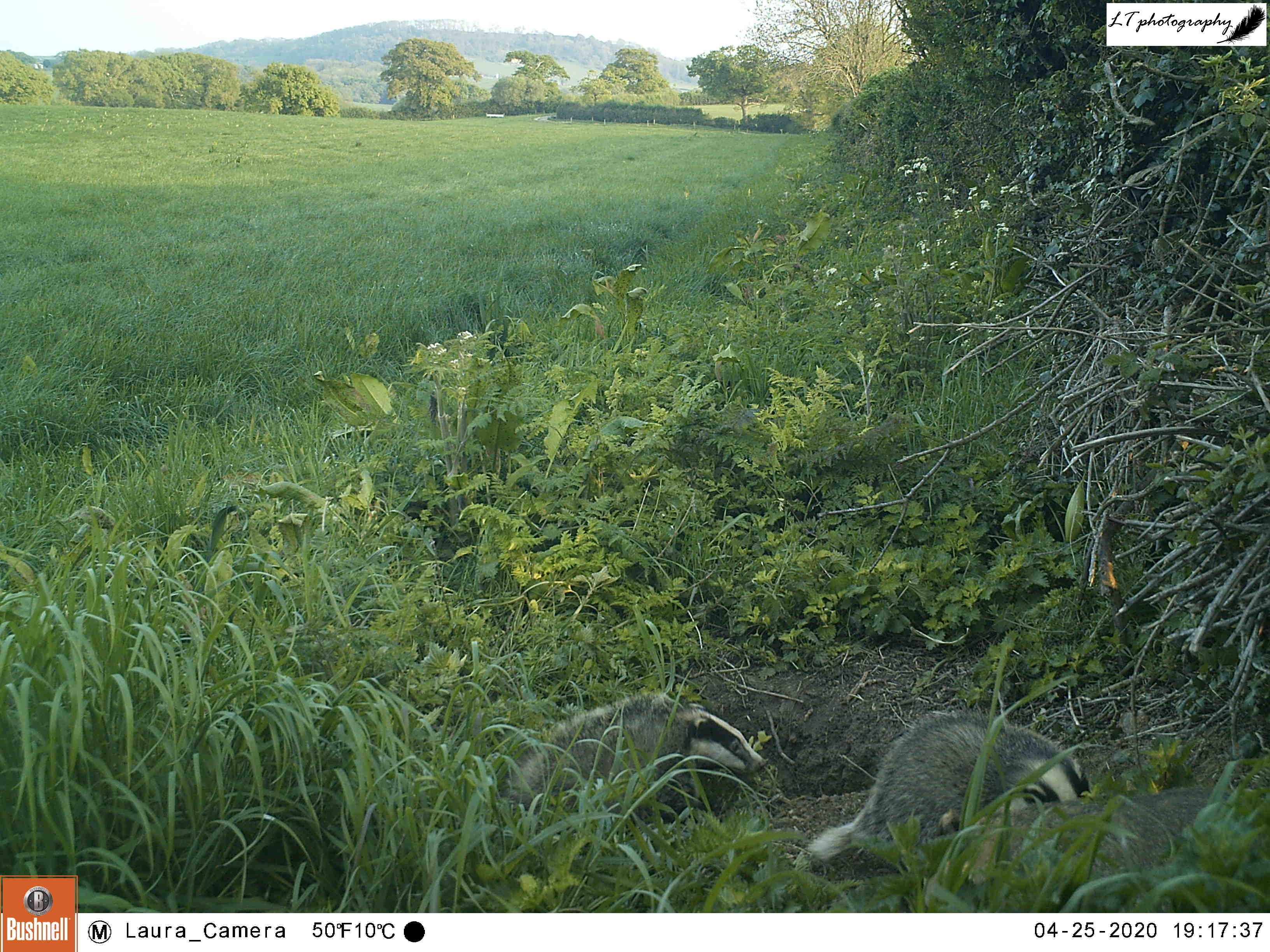
This year I set up my camera trap 12 days earlier than last year, beginning with a new site. I had spotted an interesting tree at the edge of a small field, where a hole had been dug between its roots, and I wanted to know who may have dug it. So I set up my camera watching the track in the field leading to the hole, and left it from 22nd-26th March to see what I could find.
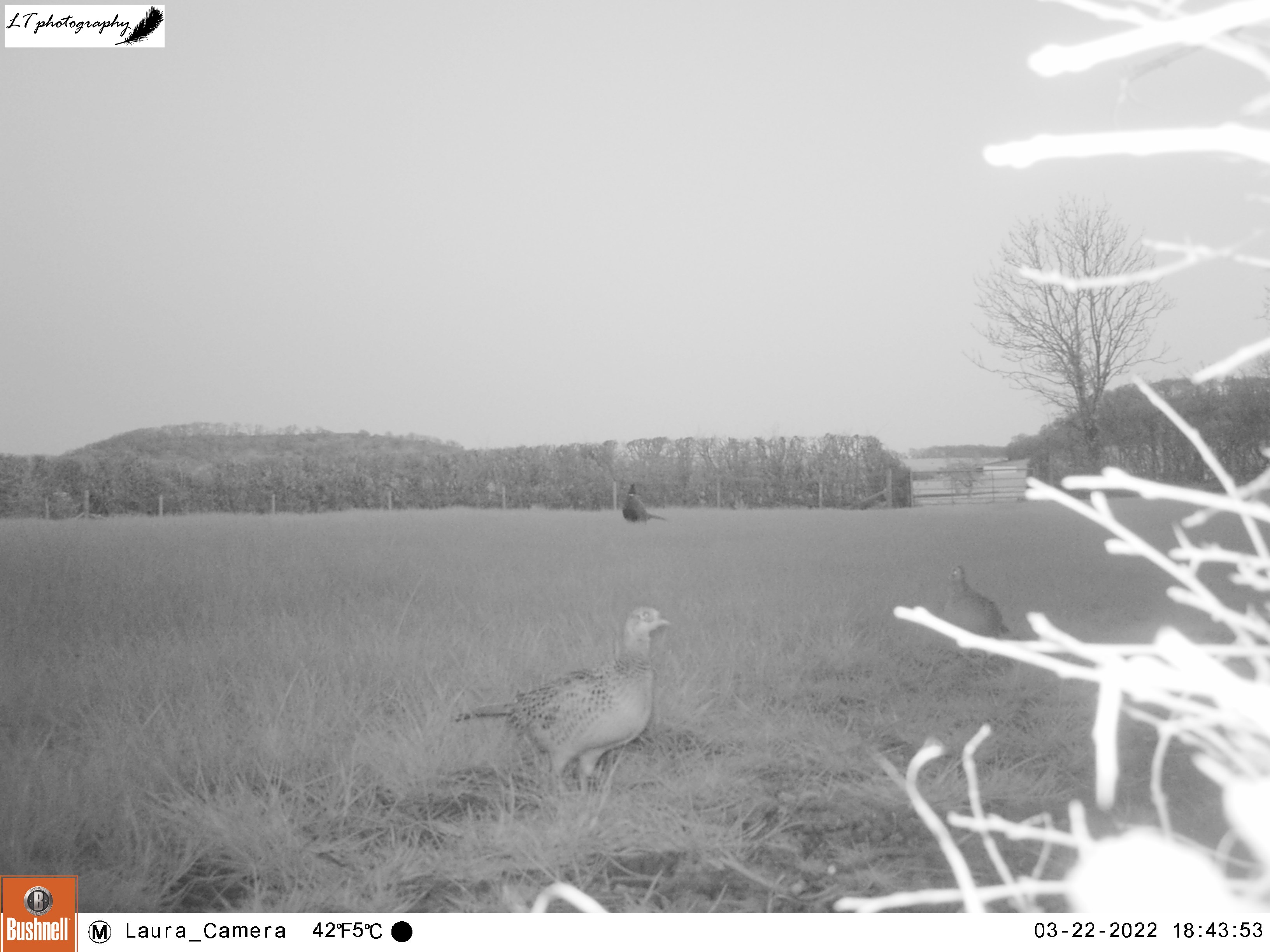


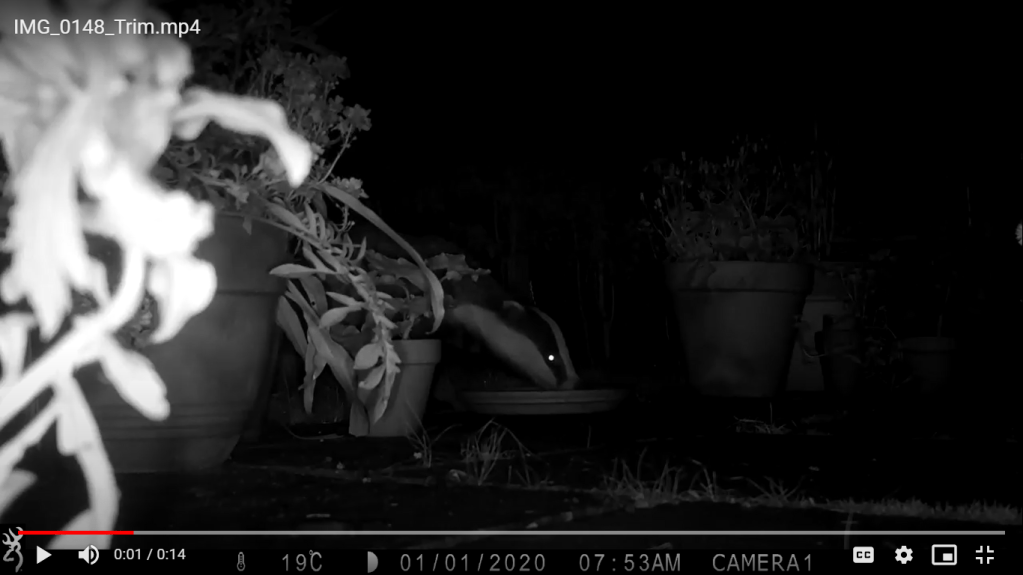
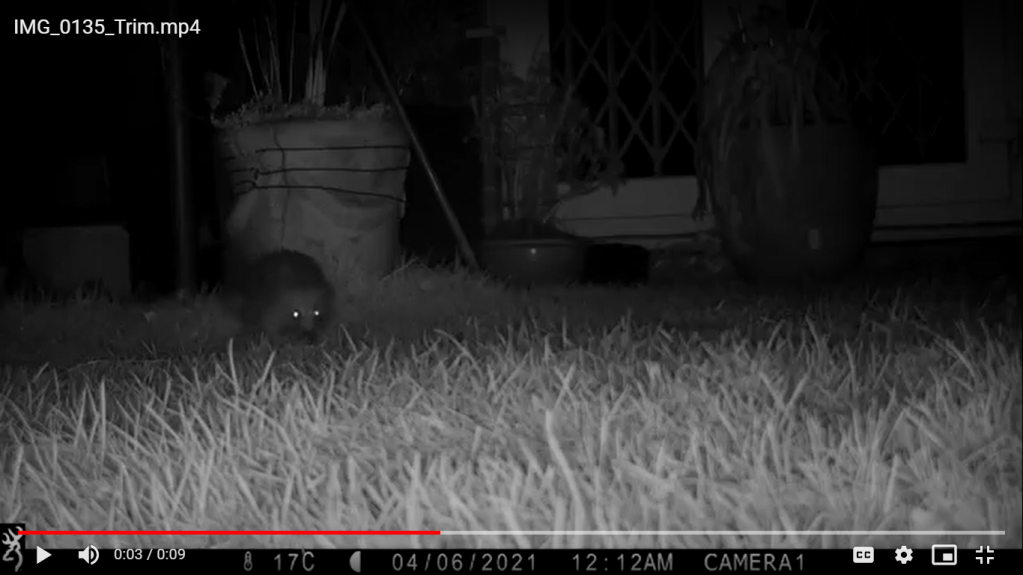
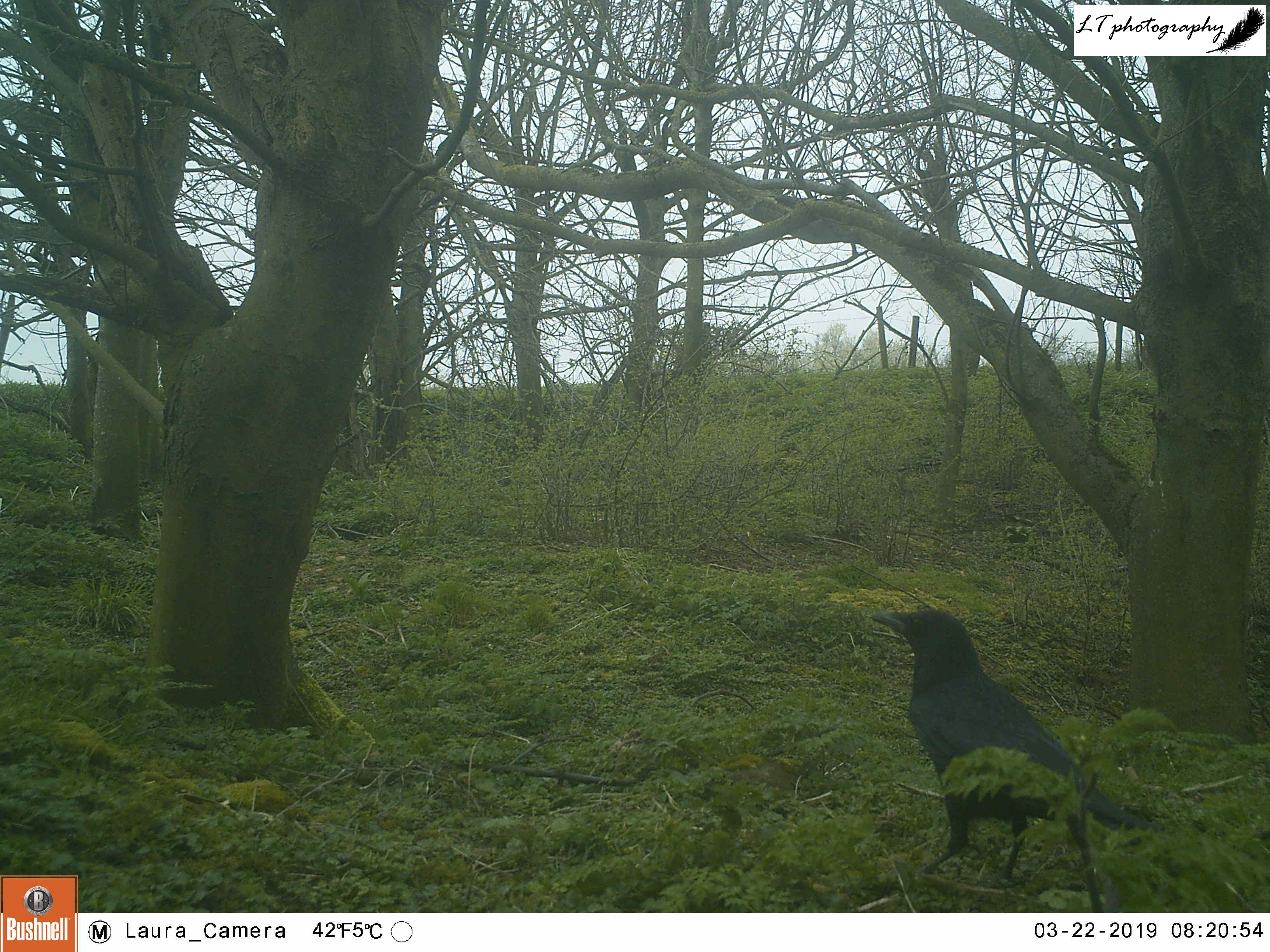
It was a good start to spring camera trapping, but with mixed results. Different arrangements of male and female pheasants made an appearance every day, birds in the form of magpies, a woodpigeon, and a carrion crow were seen, and potential home owners came in the form of a fox and a badger. Though the badger may have possibly been using the hole, in the end I came to the conclusion that the hole was not currently in use.
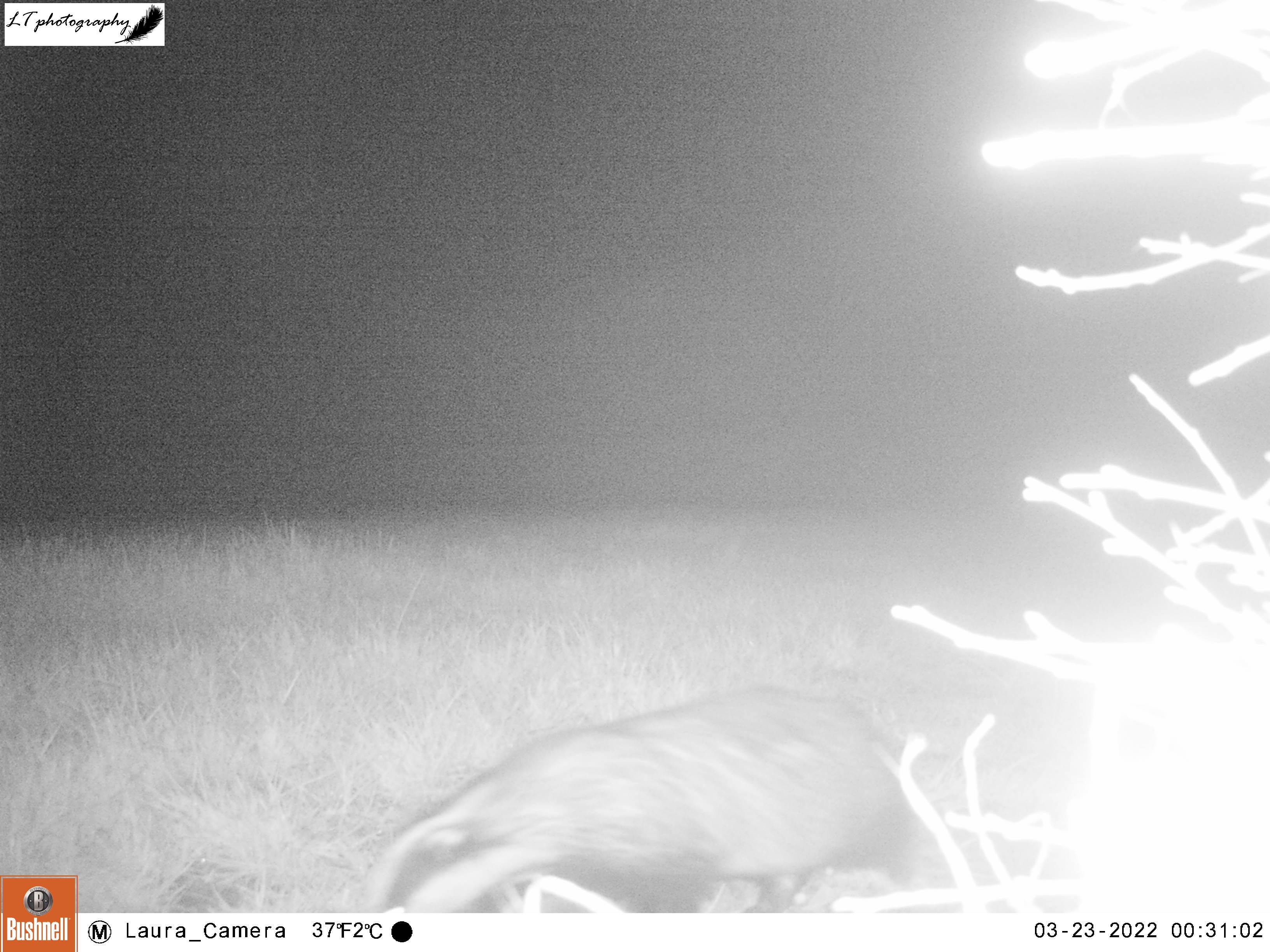


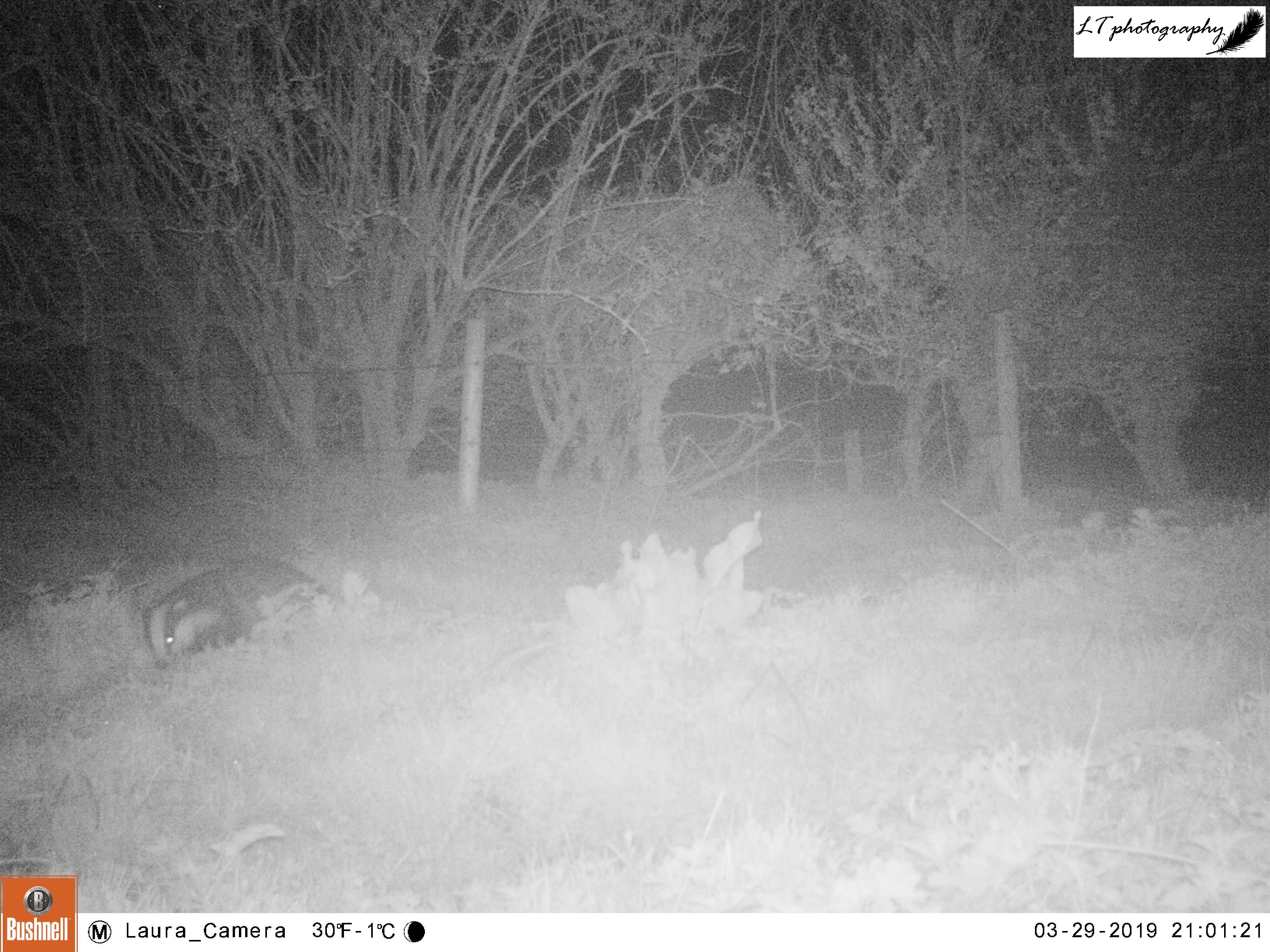
Monkwood Field
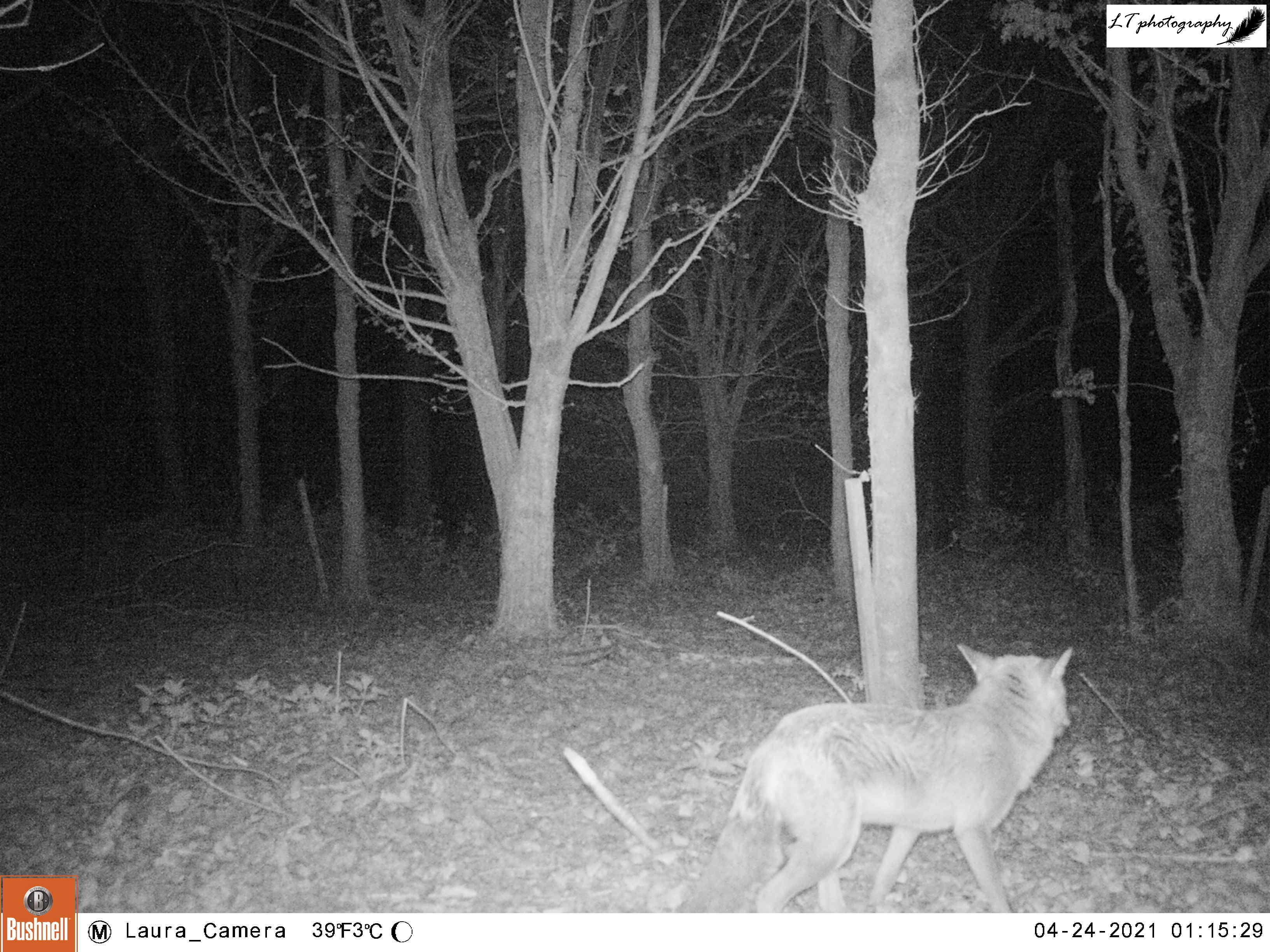
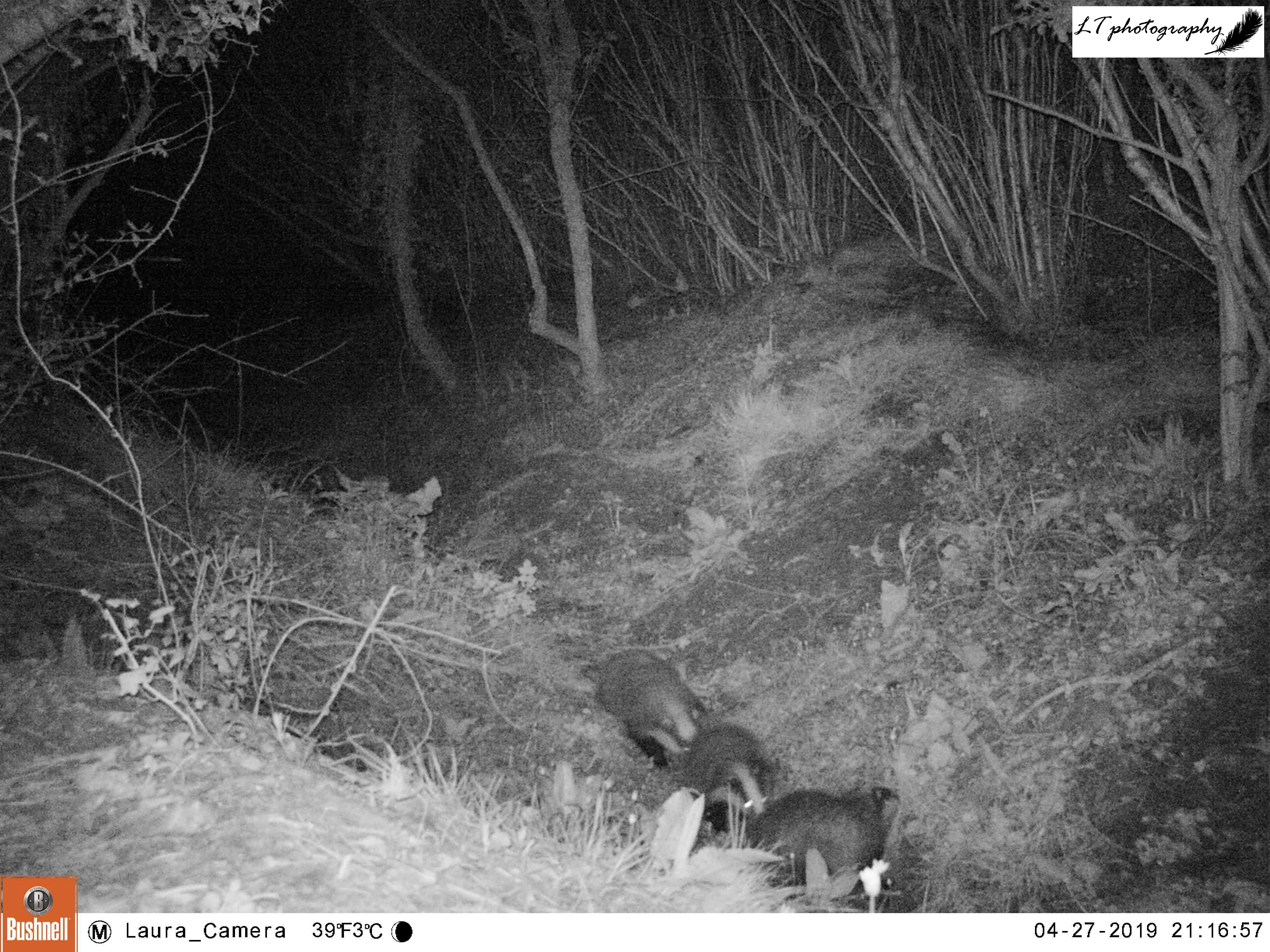
For my next site, I returned to a new site from last year, a small abandoned satellite badger sett that had been home to a family of foxes. When I went to put out my camera, I could see that a new hole had been dug in the sett, so I set my camera to watch the track heading from the field directly to this new hole over 2 nights (26th-27th March), due to stormy weather.
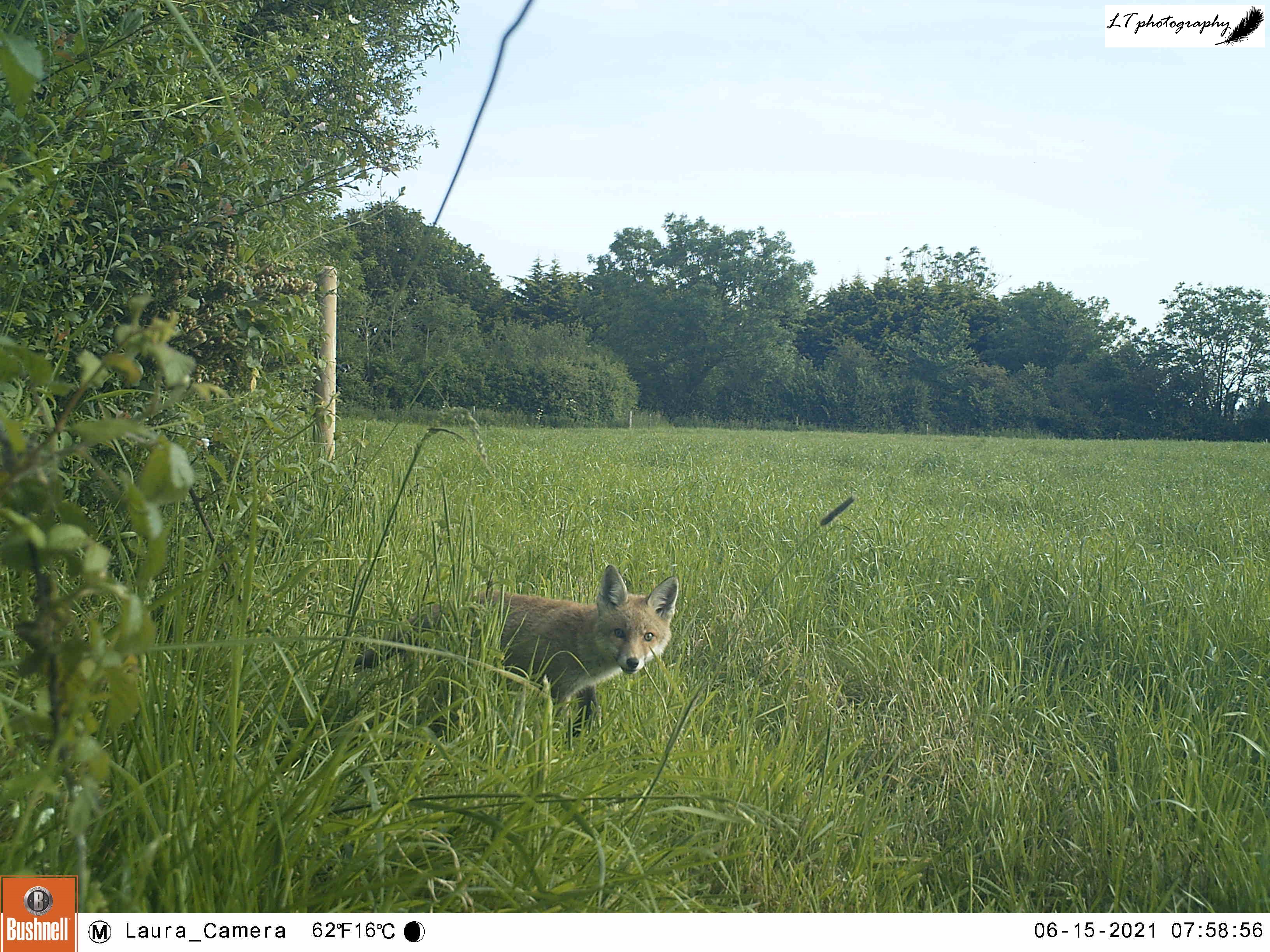


In the short time it was operating, my camera trap was productive, with a displaying male pheasant, a fox passing through (maybe the same from Little Wood?), and the sett’s current resident. My camera was able to show that the new hole belonged to a lone badger, most probably a male.
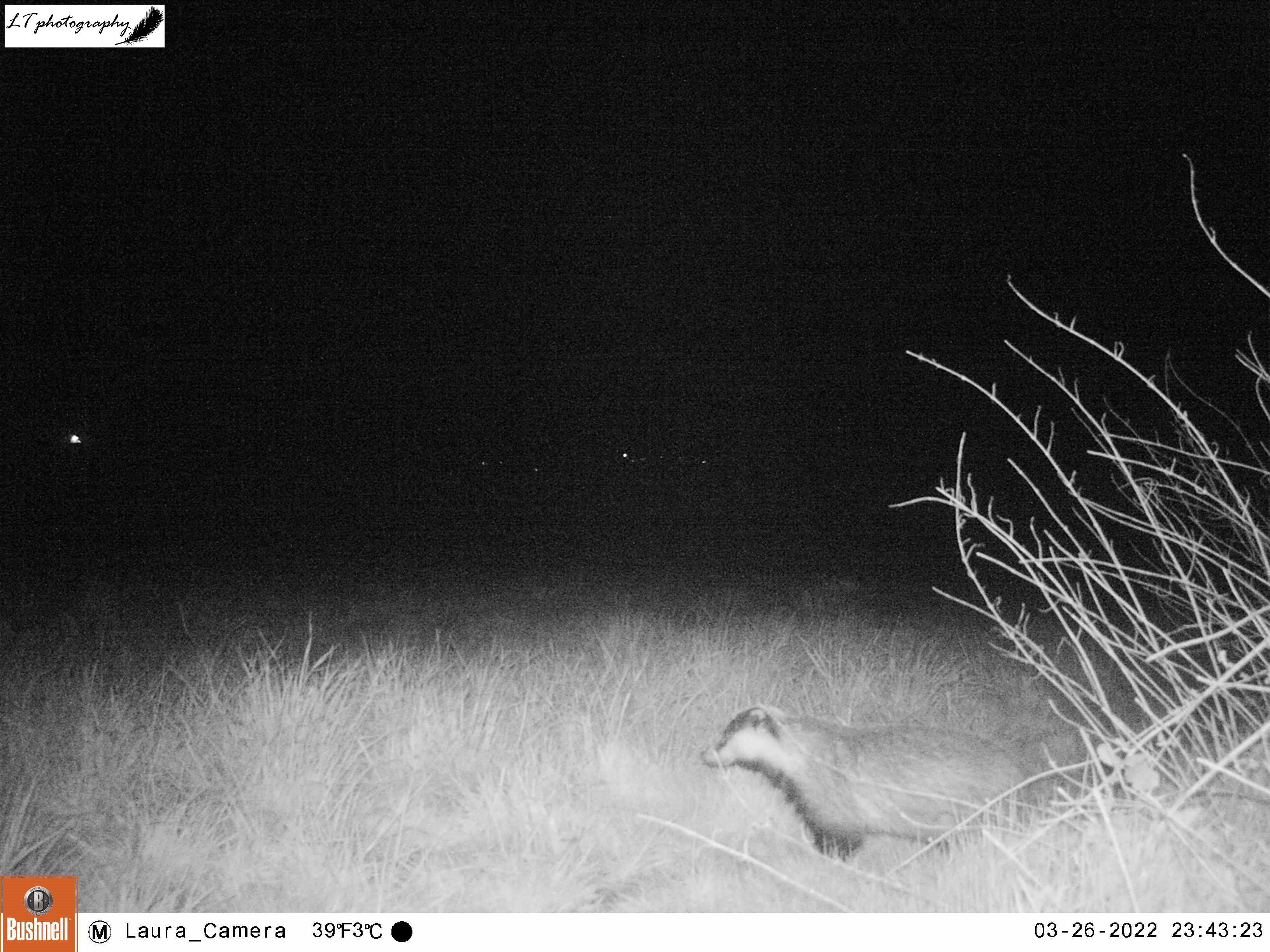


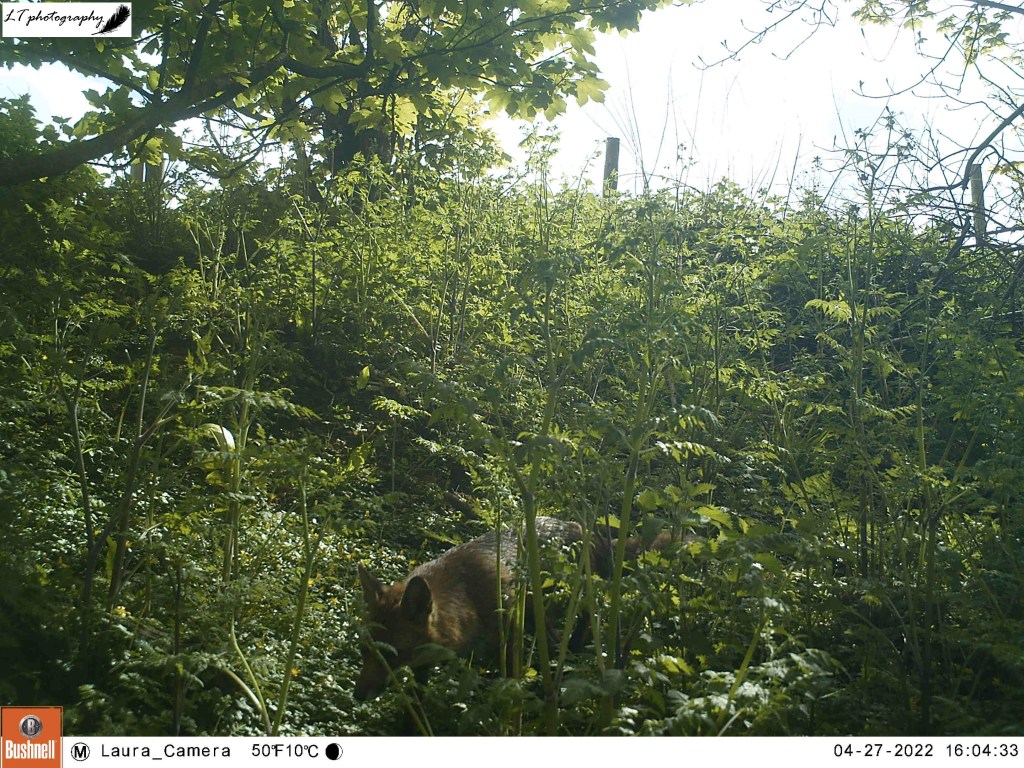
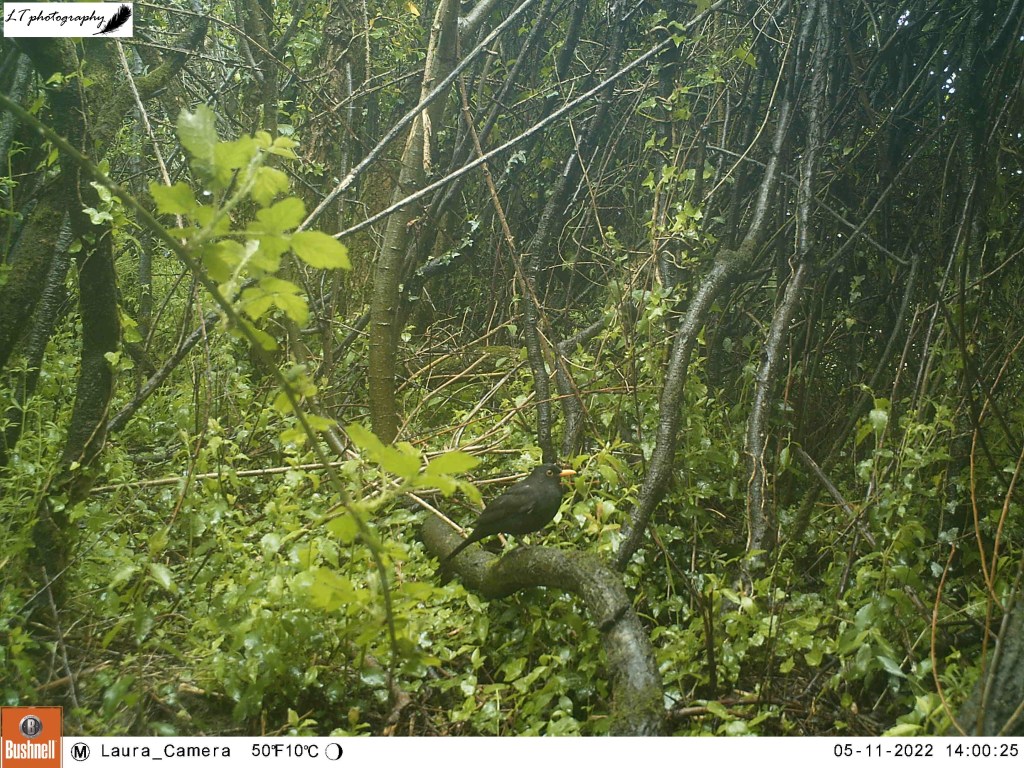
Later on in the season I decided to see where the fox may have been coming from, and returned to Monkwood Field. I chose to set my camera trap in the corner of the field on a tree trunk within the hedge, looking at the animal tracks that run through it. I did not know what results I would get, but after nearly a week (8th-13th May), my camera actually did quite well, despite not pinpointing where the fox may have been coming from. I caught sight of the fox a few times, and got some nice photos of a territorial male bullfinch and territorial male blackbird.
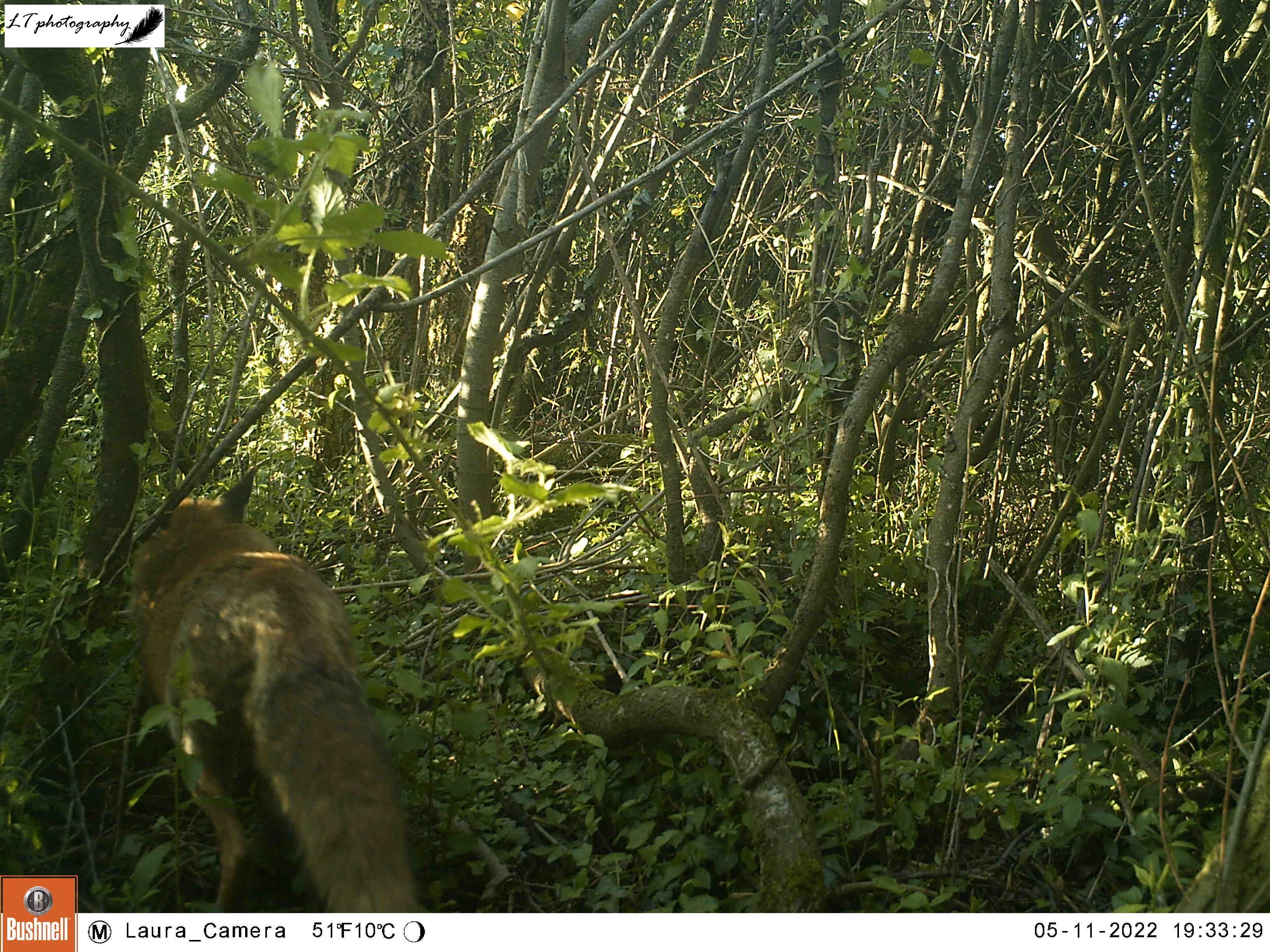



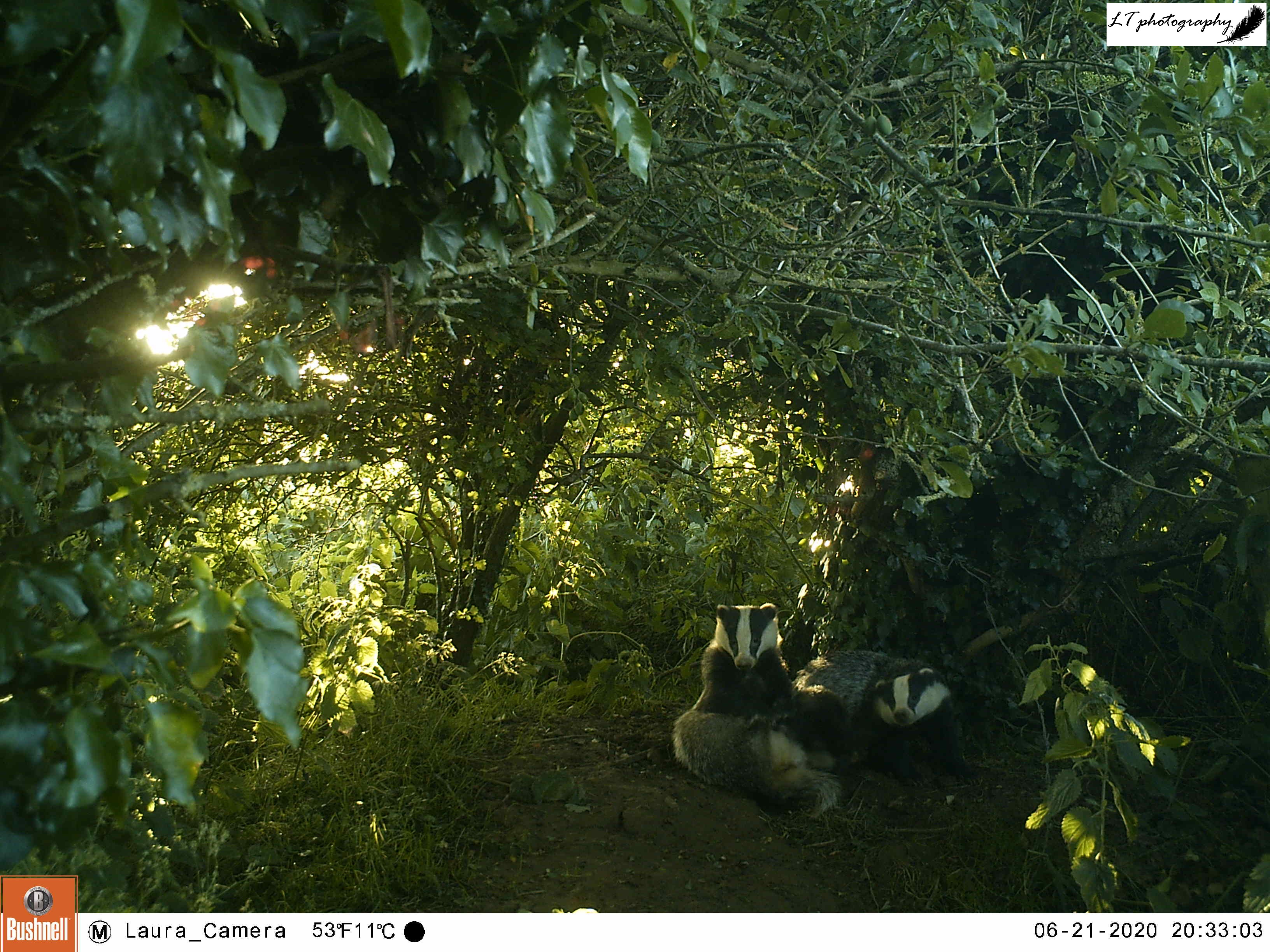
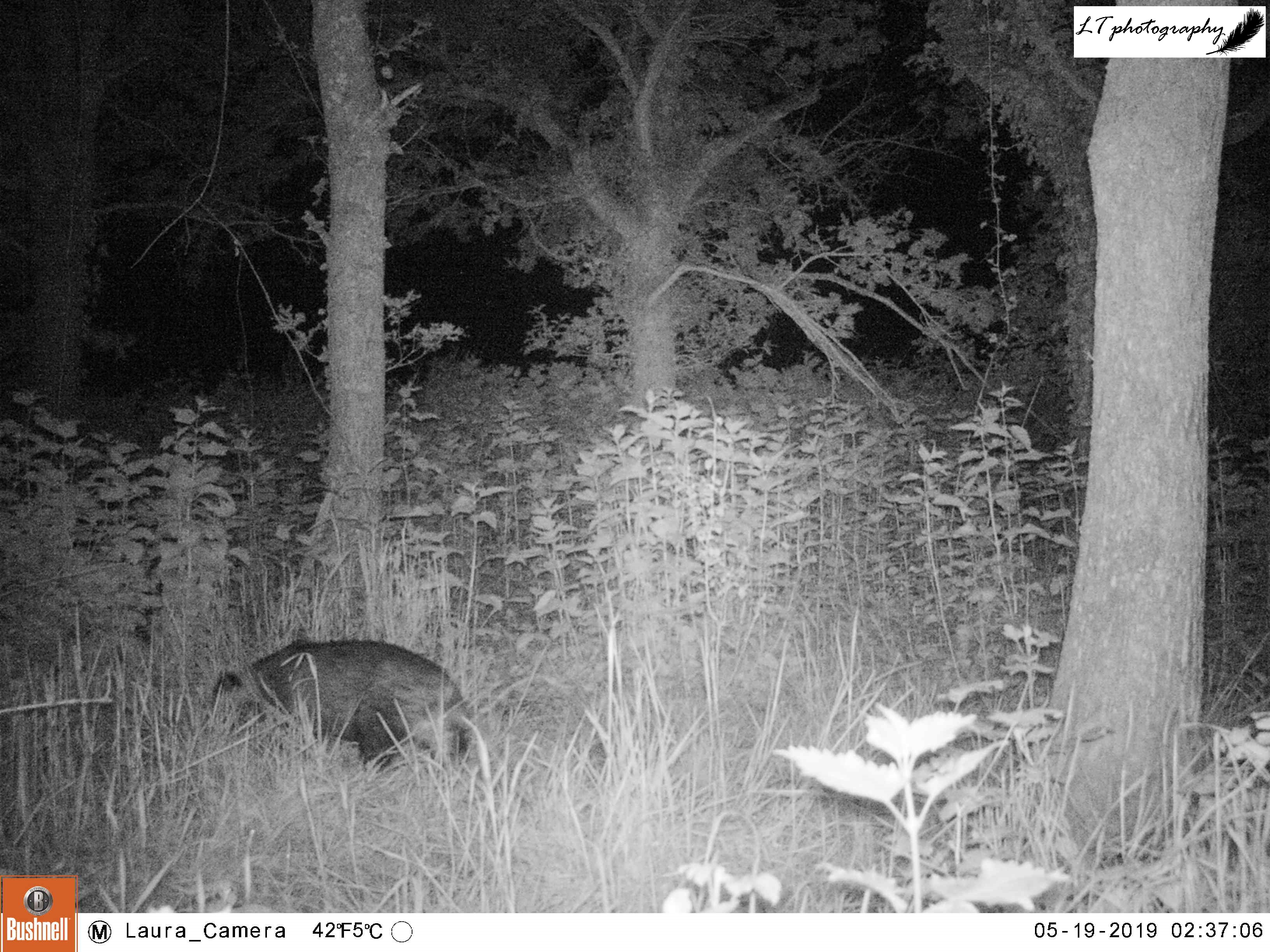
Quarry Field Badger Sett
For the last 3 years running, I returned my camera trap to my highly successful site at the active Quarry Field badger sett. Each year I have set my camera up on a fence post in an open space within a hedge lying directly above the sett, pointing in one of 2 directions. Previously, it has been a great site to capture the resident badger family and the other animals sharing the sett, in particular fox families. Last year, in this way, I got to watch the antics of 2 fox cubs living in the sett.


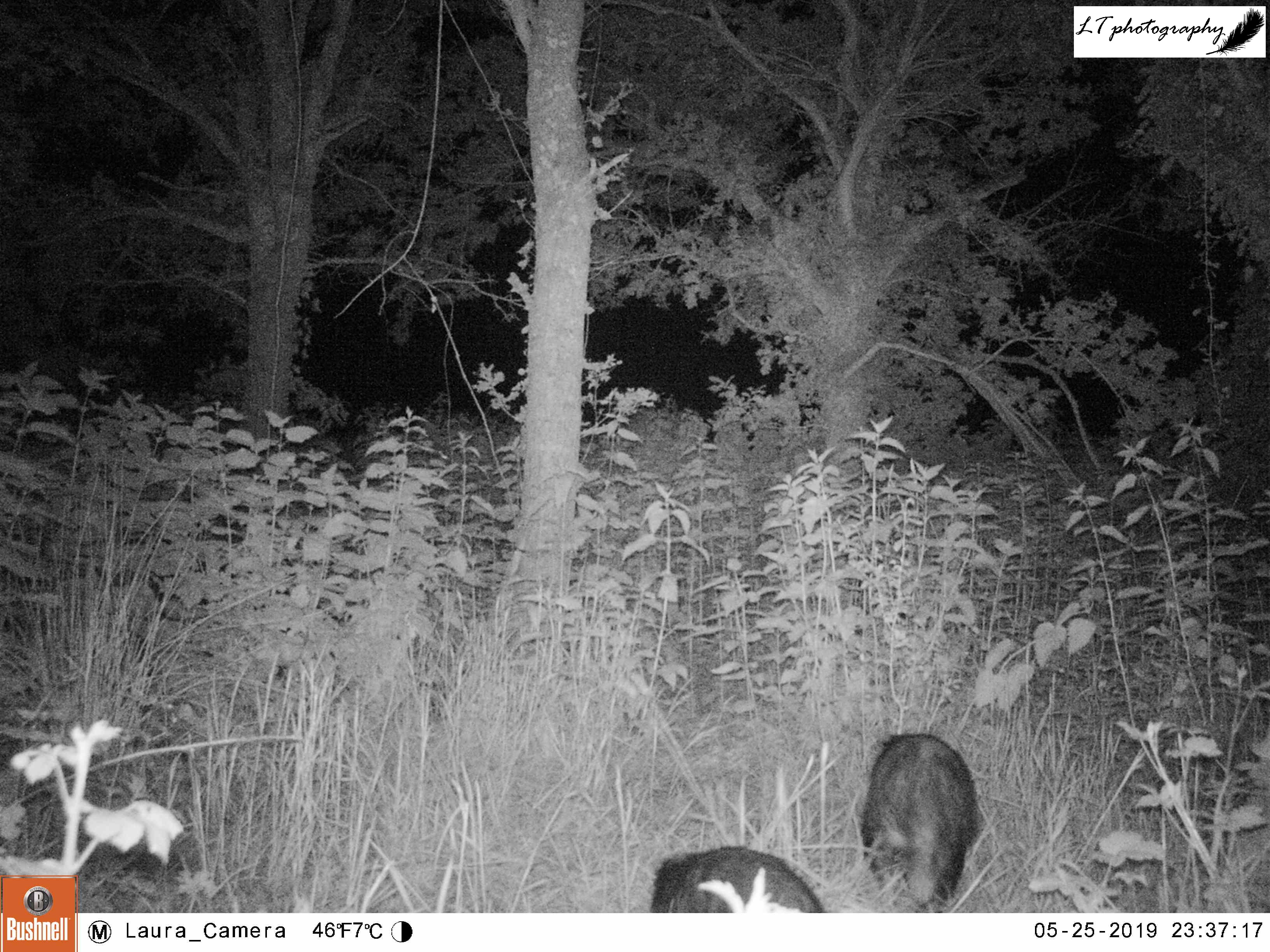
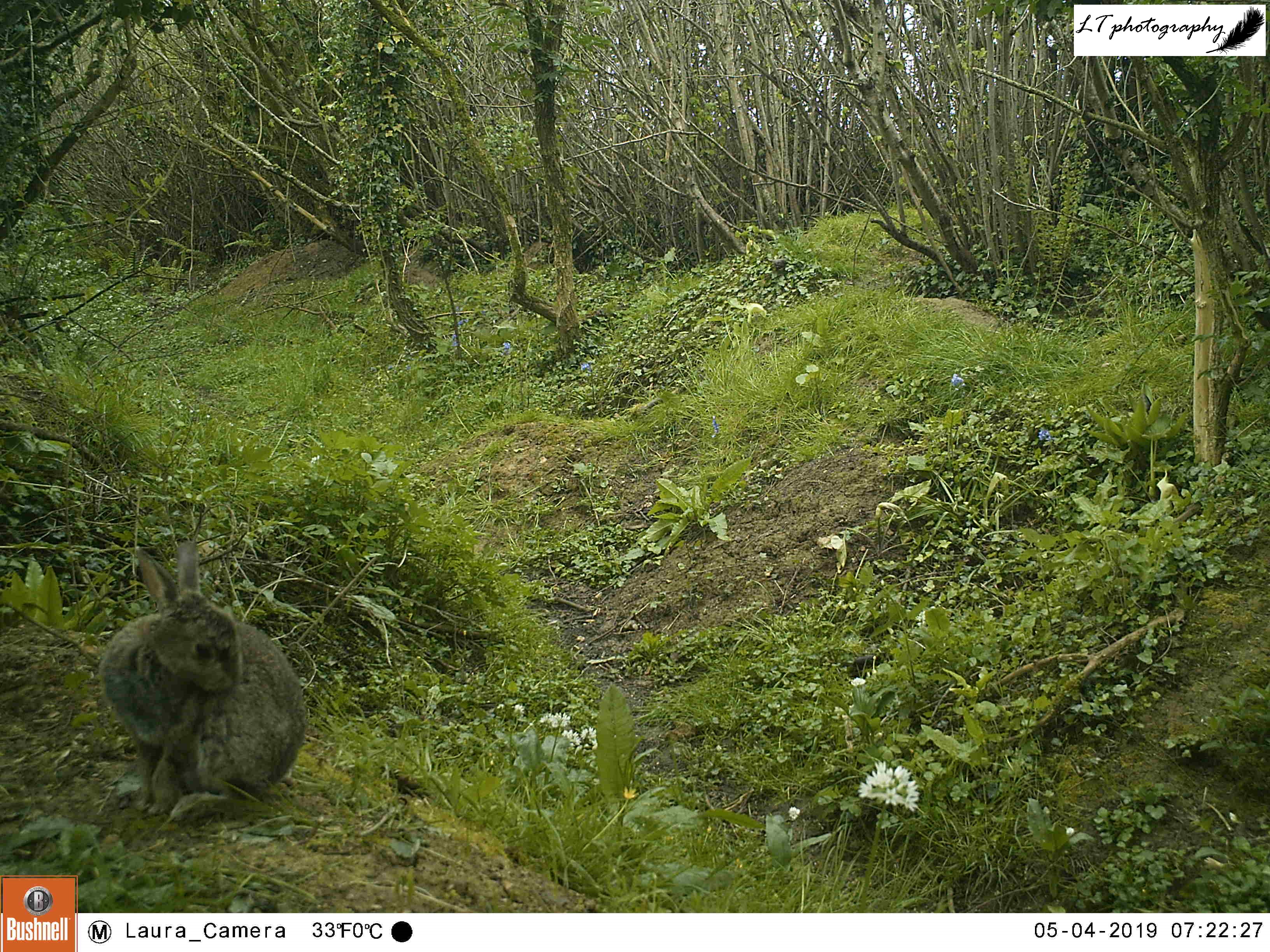
For a week during April (16th-23rd), my camera trap watched this site. During this time, rabbits were a common sight every day, day and night, along with a busy badger every night. So far there was no sign of any foxes at the sett, as in past years.


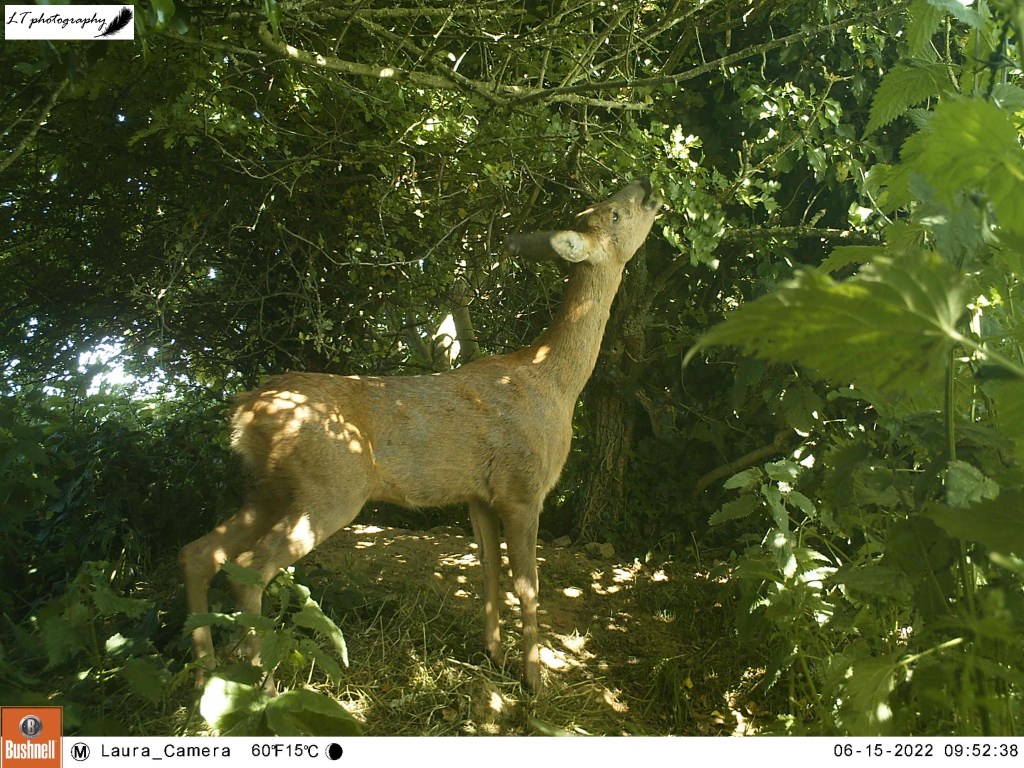
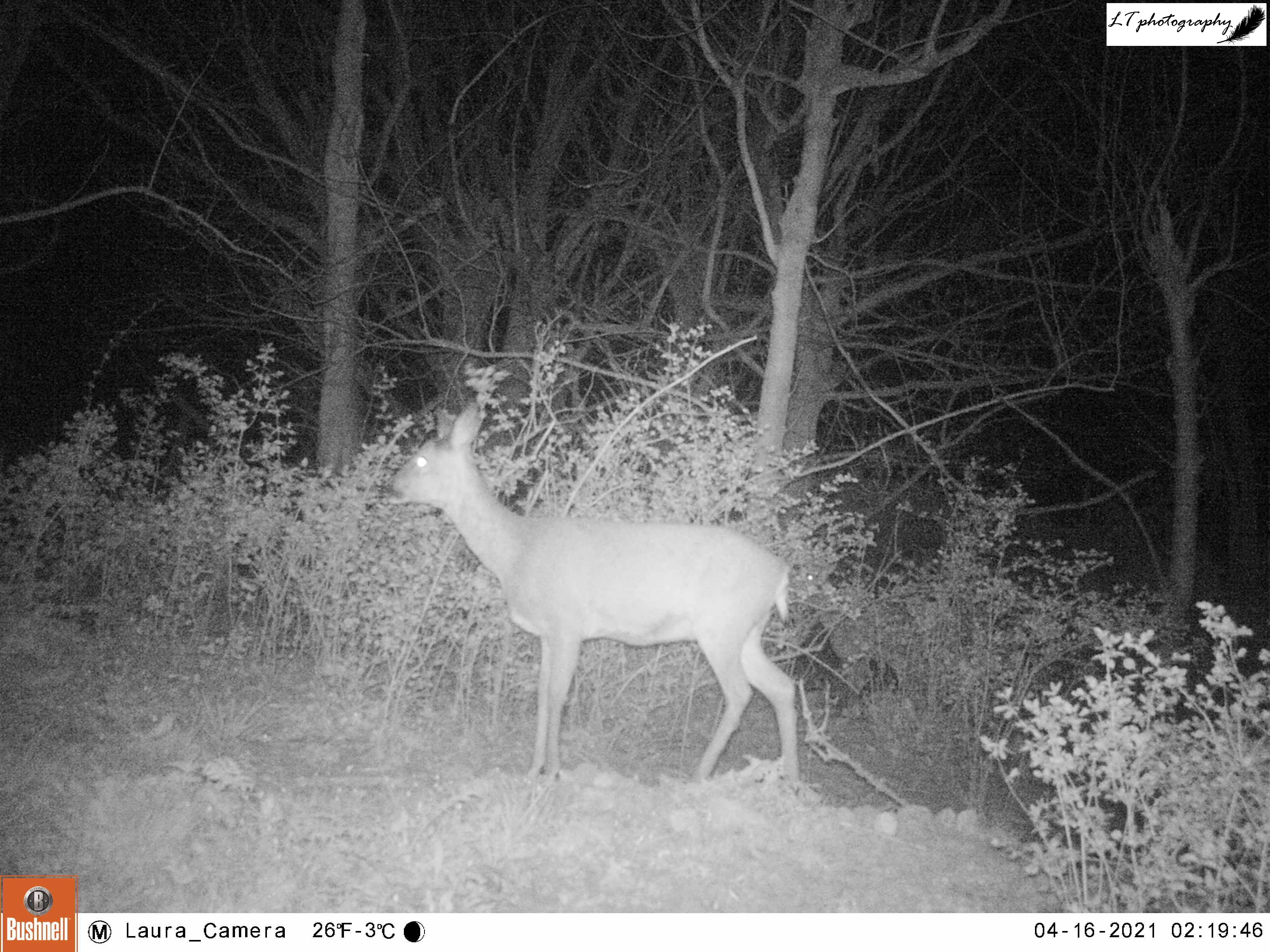
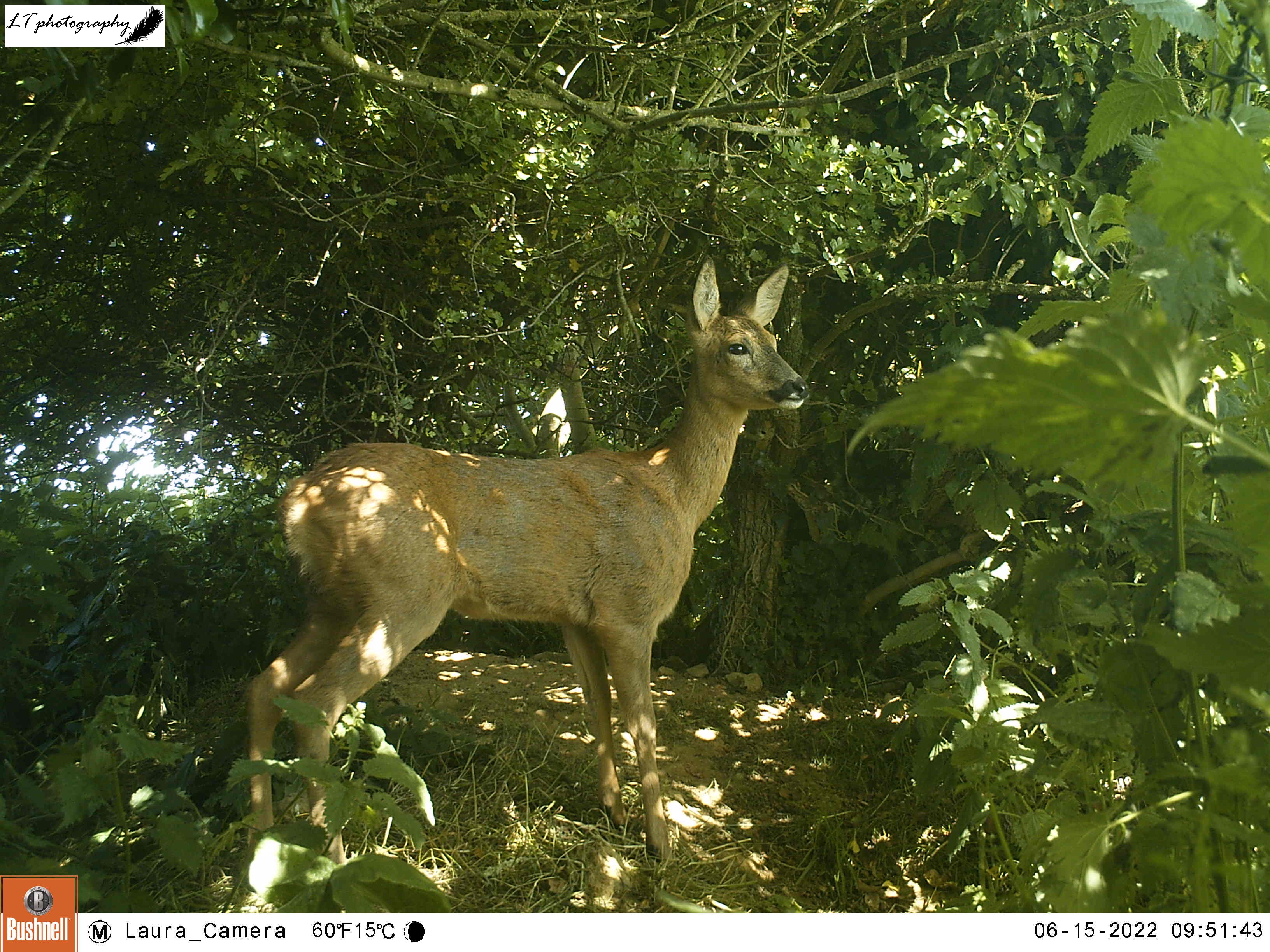
As this site still seemed to be a productive one, I returned to the sett with my camera trap for a second round once some time had passed. For 2 weeks (6th-20th June), my camera was very busy, capturing rabbits, male and female roe deer, a territorial male blackbird, and at least one fox passing through. The best photos though came in the form of the sett’s resident badgers, and two small editions. An active family, it was amazing to watch the cubs and adults feeding, grooming and playing each day.

Gill Hill Copse
This copse has been another of my regular camera trapping sites over the past 3 years. At this site, I tend to set my camera up on a tree, as with this year where I set it watching an animal track passing through the copse.


This year, over 6 days (23rd-29th April), my camera was not particularly busy, but did capture one of the many male pheasants in the area, as well as a fox passing through.
Dorset County Council Wood
The small piece of wood close to my home is another site that I have used over the last 3 years, situated next to this year’s new Little Wood site. This year, I first visited the wood at the beginning of May, setting up my camera on a tree to face an animal track coming off a quiet road into the wood. After a week (2nd-8th May), my camera had caught photos of a one off woodpigeon and a regular badger.
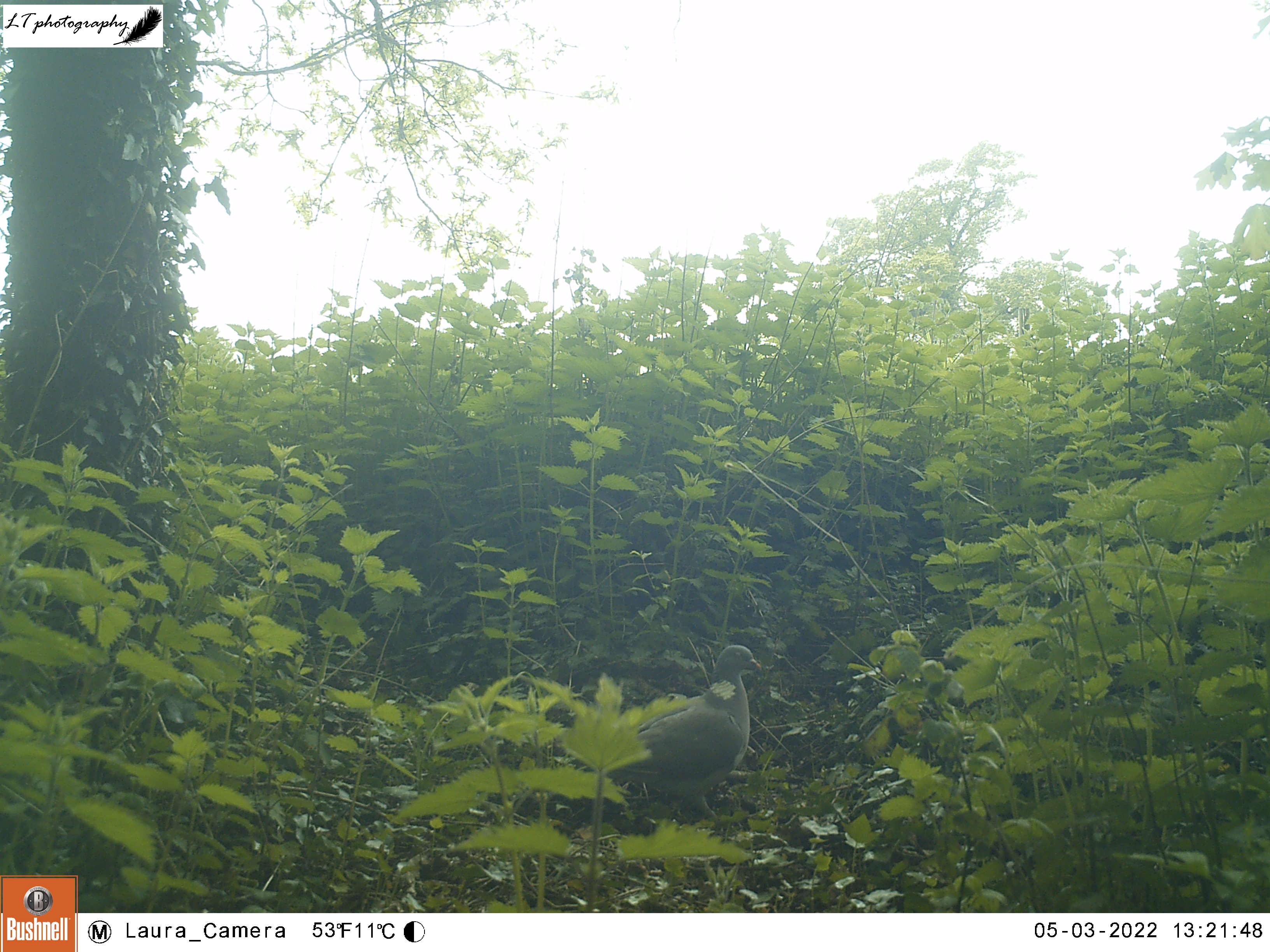


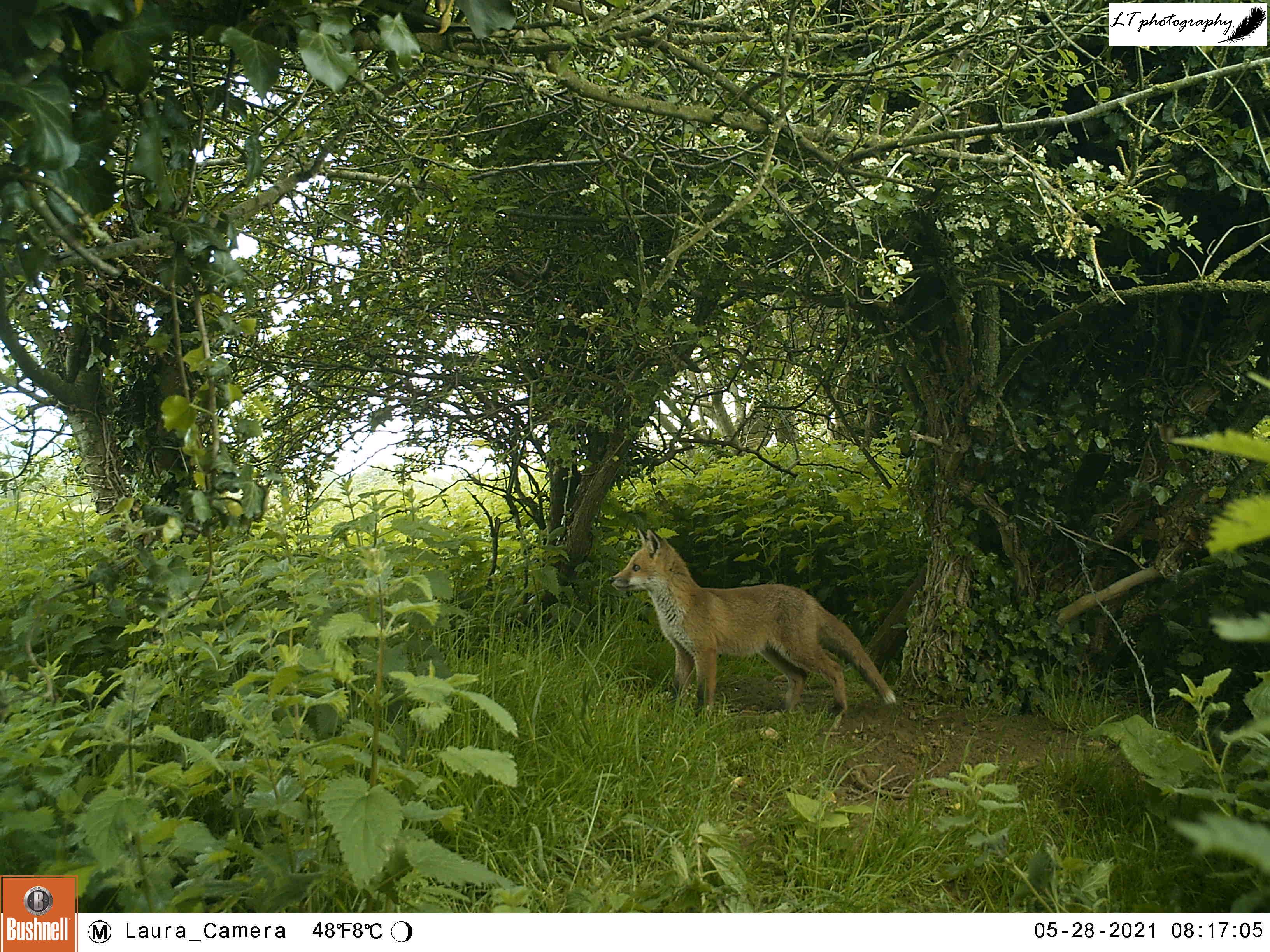
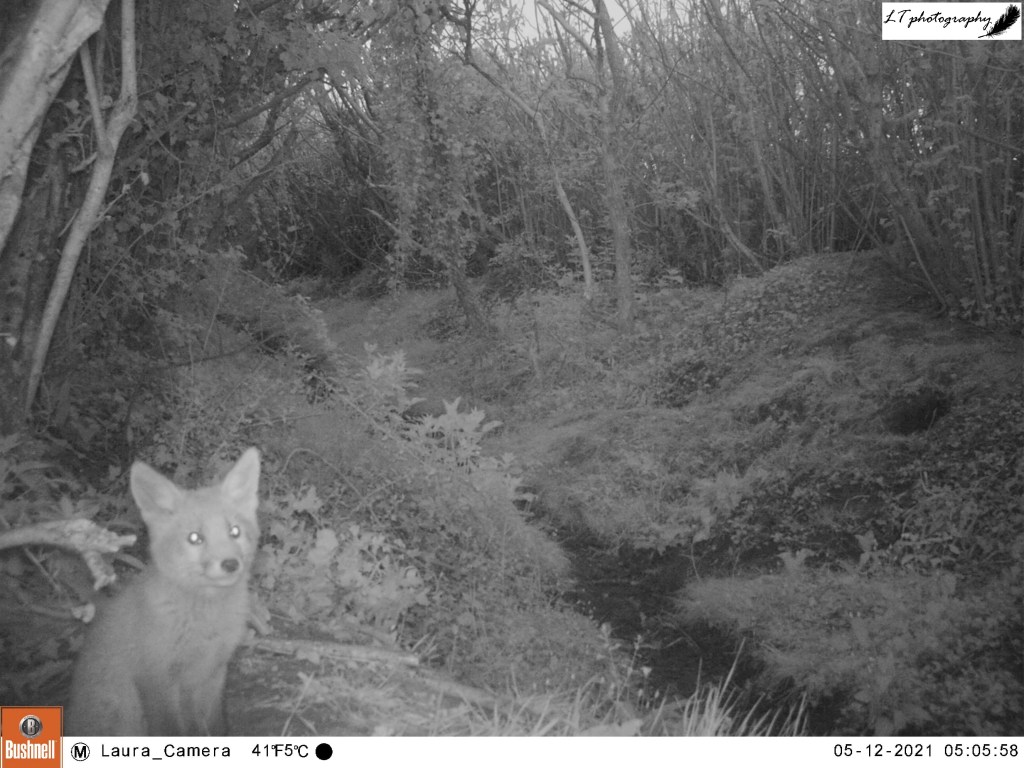
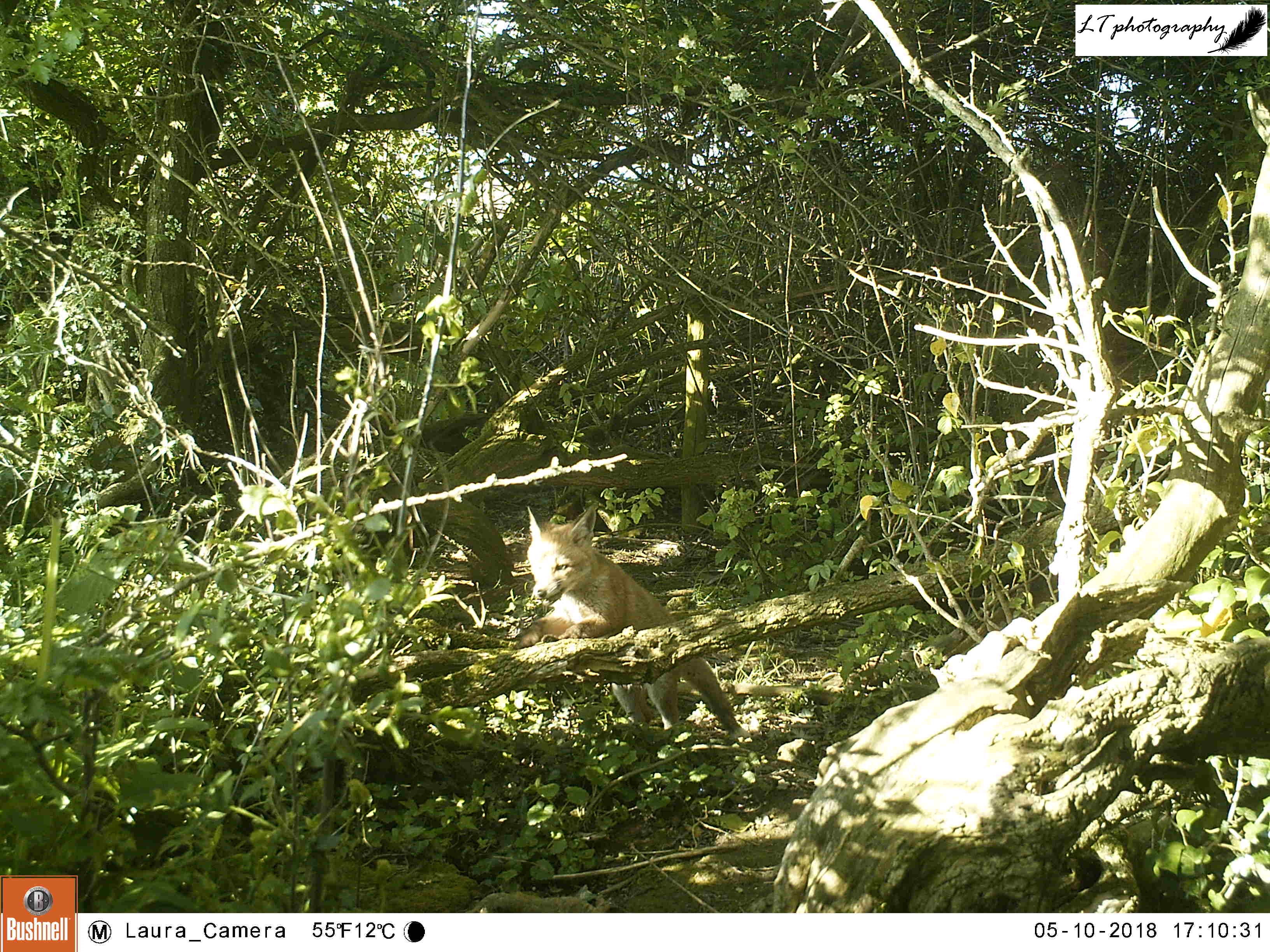
As spring passed away, I decided to give my camera trap one last go in the wood, over 4 days between 20th and 24th June. This time I set up my camera further within the little wood, facing a clearing. Though the only animal photographed during this time was a fox, I was still excited to see the charismatic species passing through.
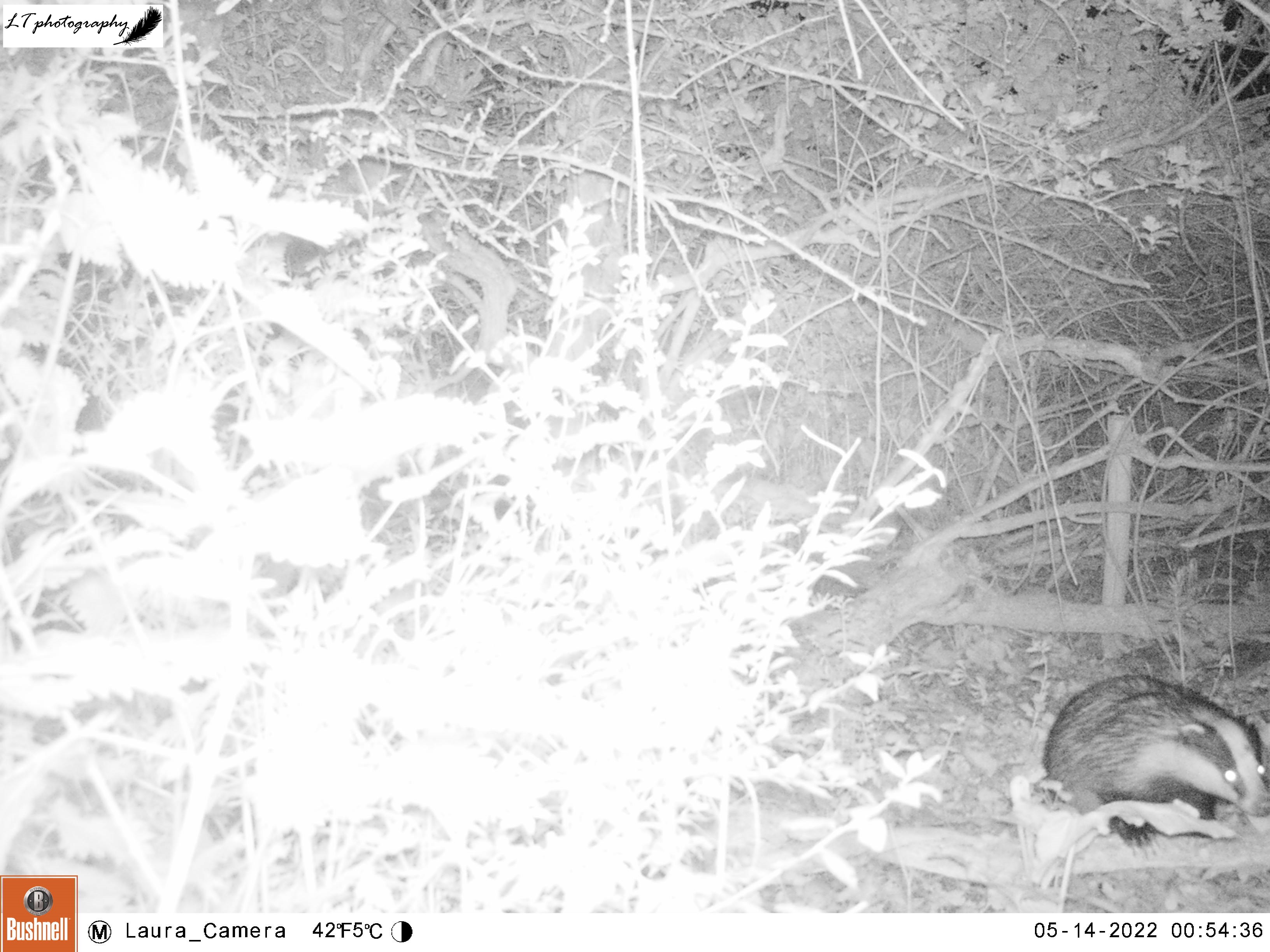
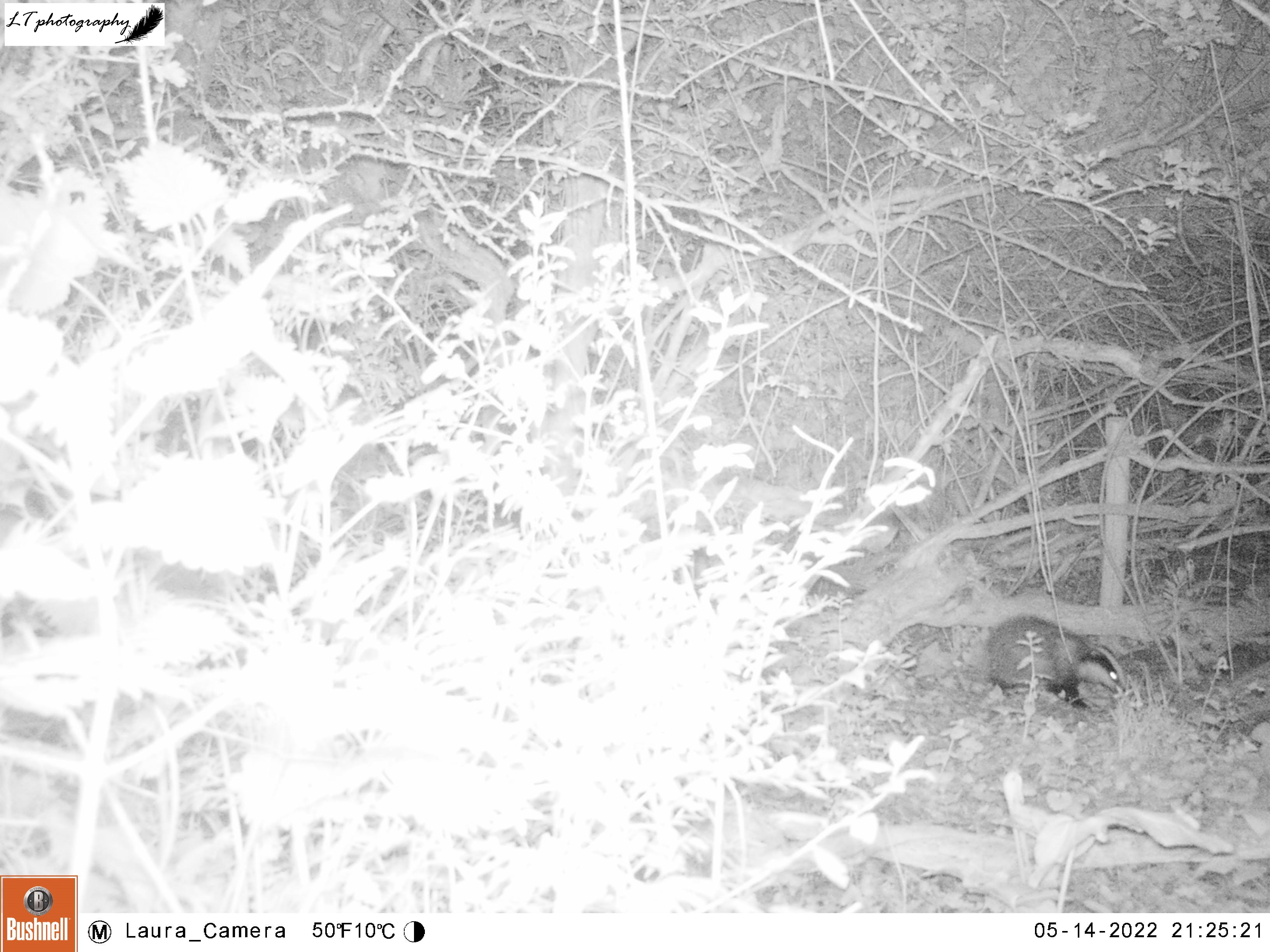
Badger Field Badger Sett
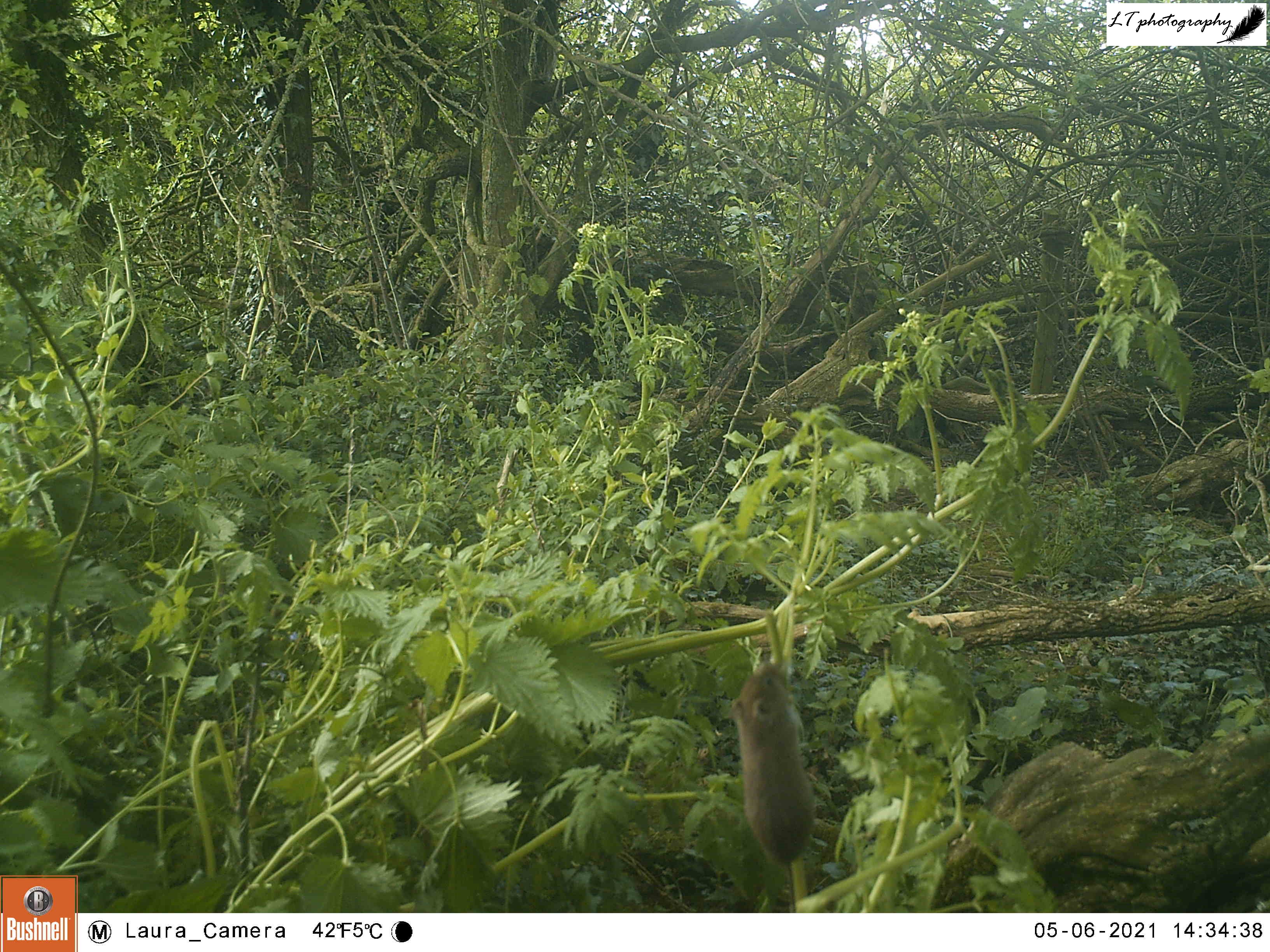
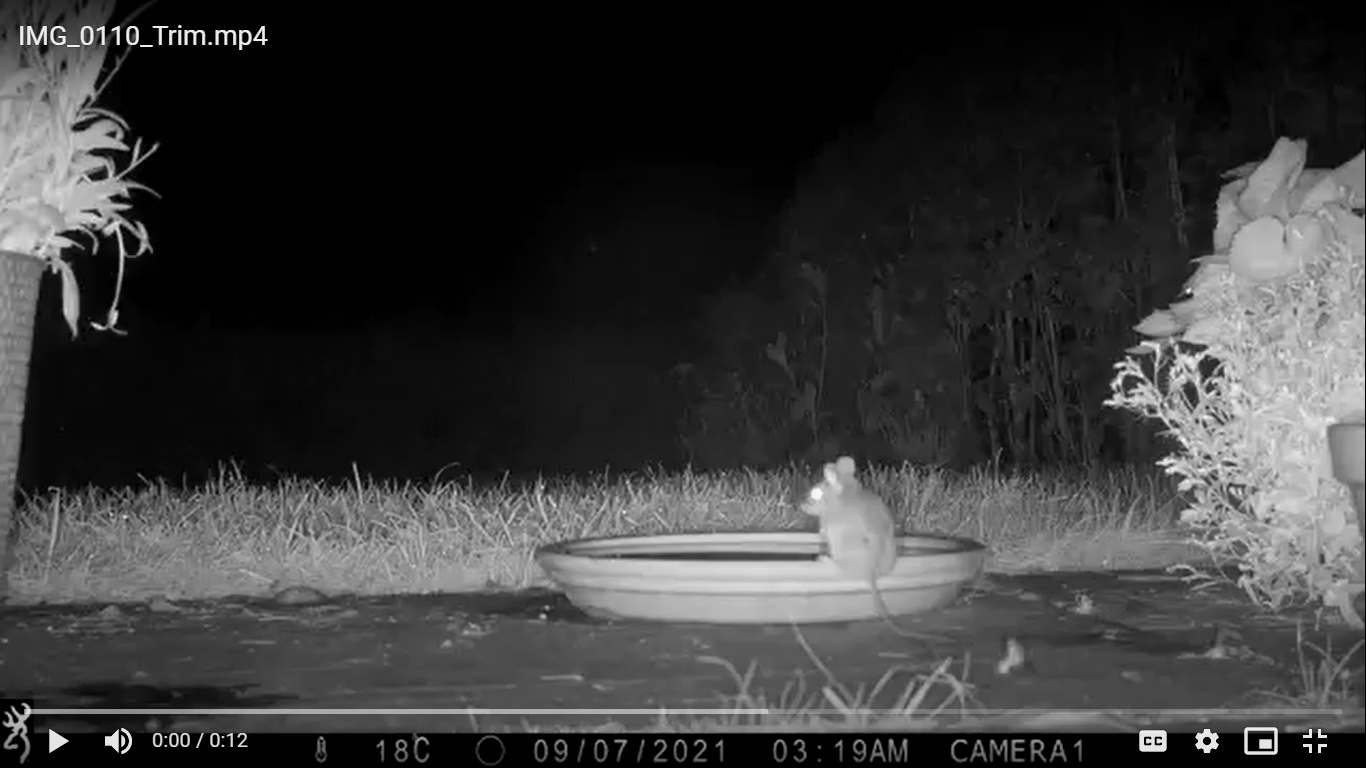
My oldest camera trap site is an active badger sett in a hedgerow between two fields. Over the years this sett has given me badgers, fox cubs, and even a field mouse. This year I returned and set my camera up in its usual spot on the trunk of a small tree in the open space within the hedge above the sett. Within a week (13th-21st May), I caught sight of a blackbird, a fox, and a badger. Though no fox cubs, this active sett excitingly had badger cubs again, like the Quarry Field sett.


Cowleighs Paddock
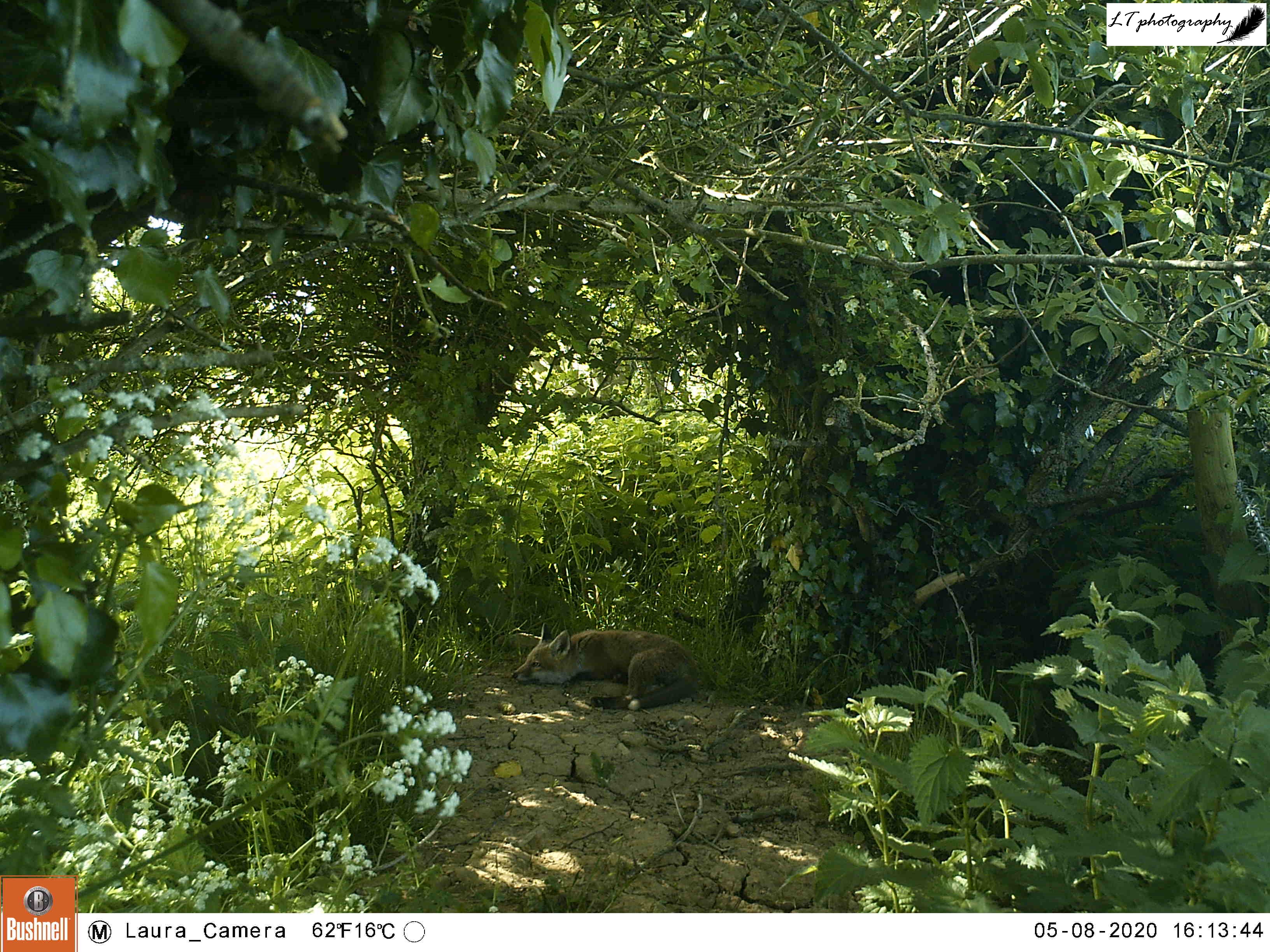
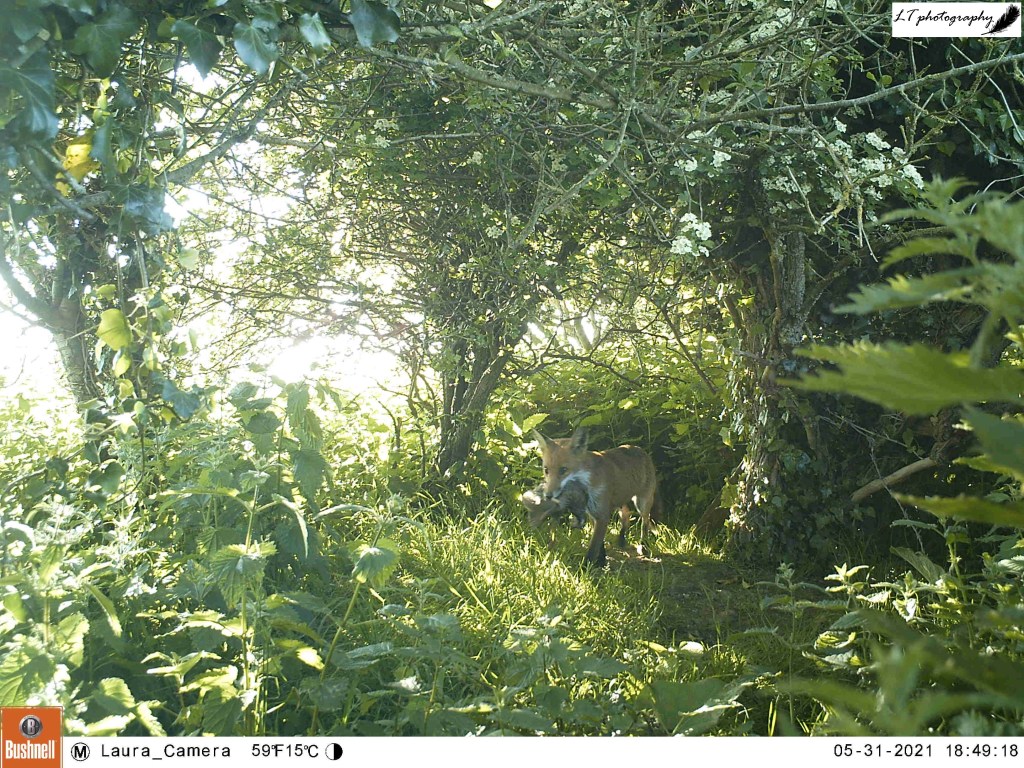
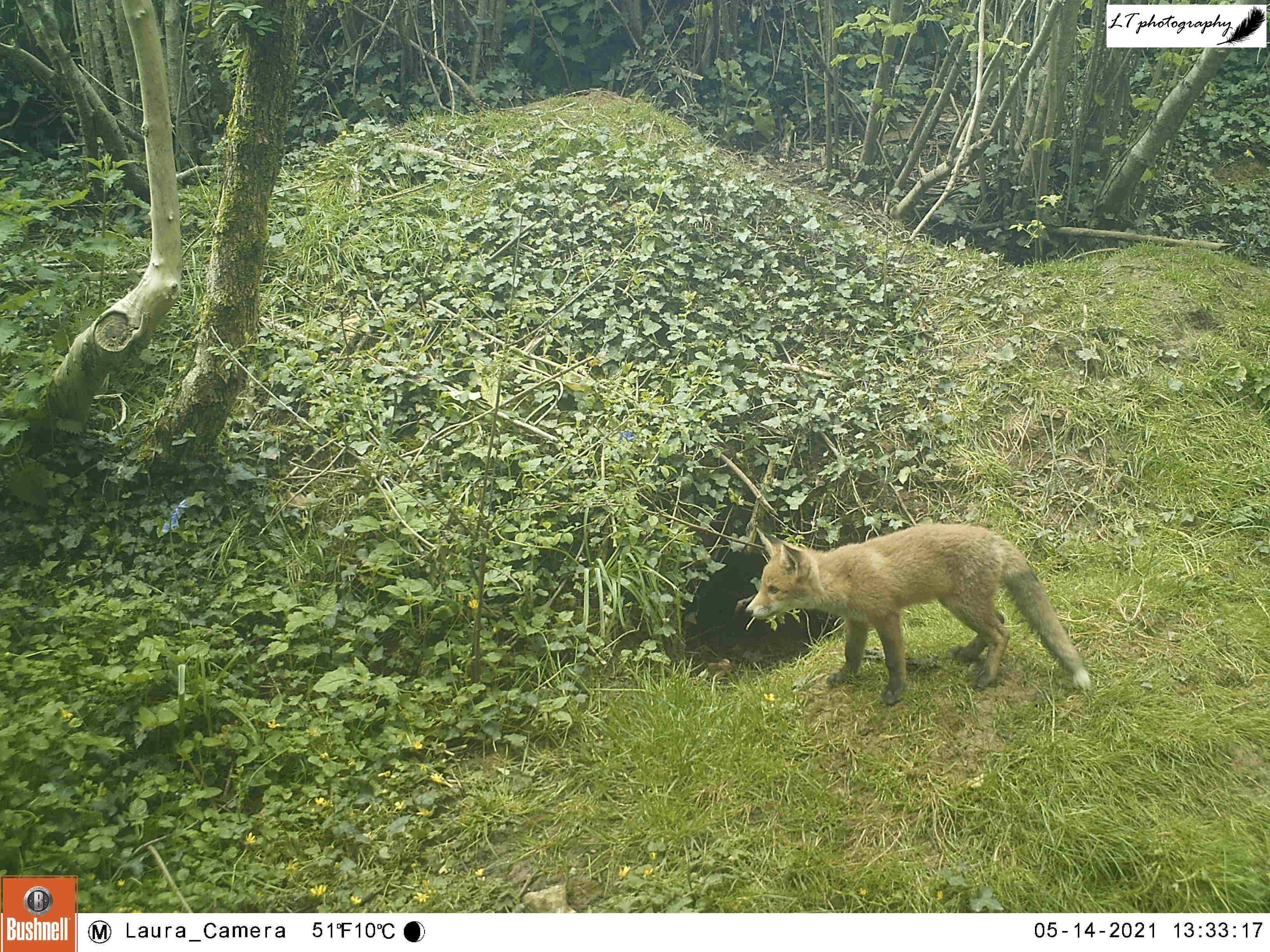
Towards the end of my spring camera trapping, I tried another new site in the hope of capturing sight of a particular species. This year has been a very good year for foxes on our farm, for example with 3 potential breeding females living along the same connecting hedgeline. Though at the beginning of spring I had discovered one litter of fox cubs (check out next week’s blog post), I had yet to find any others. I had a hunch about one den though, potentially situated in a ditch alongside a small paddock. I set up my camera trap and waited 2 weeks to see what I would find (22nd May-4th June).

My camera trap did not fail me. Alongside a showy male pheasant, my camera caught the photos I had hoped for. At least one fox cub can be seen playing and exploring in the long grass in the paddock outside the ditch, along with photos of an adult female bringing food to the same spot. Though from these photos I cannot confirm how many fox cubs are in this litter, it is great to know that they are there and doing well! A great spring this year!