This year spring has been a blast of colour, abundance, and new beginnings. Though April experienced some cooler weather, and storms blew up here and there, on the whole spring was calm and dry. What characterised this spring most of all though was the weather being warmer in general, making spring 2022 the 5th warmest on average with a quarter less rainfall. Turbulent winter weather led to a slower start to spring, but the increasing warmer days led to spring speeding up and going out in a hurry in my home area of Dorset.
Last year weather patterns had a big influence on spring events, with events moving earlier or later as a result. For many species, events actually occurred later in spring in Dorset in 2021 due to cooler and wetter weather overall. For example, compared to 2020, oak leaves unfurled 31 days later, bluebells flowered 4 days later, and swallows arrived 5 days later. It was an unsual spring that was still joyful, but showed the unexpected impact that climate change is already having on spring events.
After the unpredictability of spring 2021, it will be interesting to see how spring events have fared this year in 2022. How is spring looking as a season overall in 2022? Did specific spring events get back on track or continue to become later? And did spring events continue to follow weather patterns? Read on to find out!
Trees
This year on my family’s farm we have seen a general trend for tree budburst, first leaf and first flowering occurring earlier than in 2021, showing dates more similar to those of 2020 or ones that were even earlier. This was true for beech (Fagus sylvatica), field maple (Acer campestre), horse chestnut (Aesculus hippocastanum), english oak (Quercus robur), wild cherry (Prunus avium), and Norway maple (Acer platanoides) trees, all between 9 and 28 days earlier. This was similar for ash (Fraxinus excelsior) and silver birch (Betula pendula) trees, but ash showed budburst 10 days later and silver birch first leaves 4 days later.
For first flowers, horse chestnut and ash trees shared the earlier trend with them blooming 2 and 34 days earlier respectively. For field maple, english oak, silver birch, wild cherry, and Norway maple flowers though, flowers actually appeared anywhere between 1 to 24 days later.
Shrubs
For blackthorn (Prunus spinosa), dog rose (Rosa canina), elder (Sambucus nigra), hawthorn (Crataegus monogyna), lilac (Syringa vulgaris), and hazel (Crataegus monogyna) first flowering occurred earlier than in 2021. This ranged from hazel flowers 5 days earlier to blackthorn flowers 21 days earlier.
Surprisingly for first budburst and first leaf, the opposite trend was actually shown. For blackthorn, dog rose, elder, hawthorn, and lilac these spring events were seen to occur on the same day as 2021 or later by 2-13 days. As these shrub events occur more towards the start of spring, maybe the slow start to spring was having an effect. Hazel budburst occurred 12 days earlier instead, but first leaf was delayed and ended up fitting the trend, unfurling 13 days later on 24th March.
Flowers
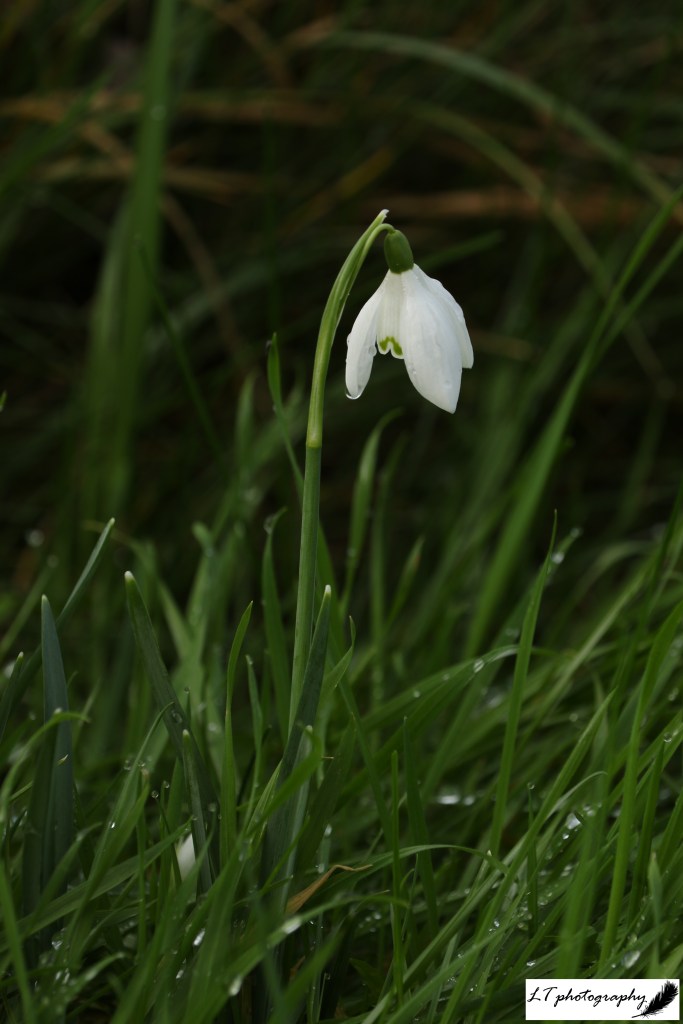
Though snowdrops (Galanthus spp.) first showed their snowy heads 12 days earlier on 6th January, first flowering was 6 days later for daffodils (Narcissus spp.) on 25th January, 11 days later for lesser celandines (Ficaria verna) on 26th January, and 45 days later for primroses (Primula vulgaris) on 14th February.
Other spring flowering species had a more mixed response to the season, either appearing earlier or later compared to 2021, as we moved from March to April. The earlier appearers were:
- Bluebell (Hyacinthoides non-scripta) – 6 days earlier on 26th March
- Early purple orchid (Orchis mascula) – 11 days earlier on 7th April
- Yellow archangel (Lamium galeobdolon) – 22 days earlier on 11th April
- Wild garlic (Allium ursinum) – 1 day earlier on 19th April
- Oxeye daisy (Leucanthemum vulgare) – 16 days earlier on 18th May
The later appearers were:
- Wood anemone (Anemone nemorosa) – 2 days later on 1st April
- Greater stitchwort (Stellaria holostea) – 3 days later on 4th April
- Cuckooflower (Cardamine pratensis) – 2 days later on 10th April
- Cowslips (Primula veris) – 9 days later on 11th April
Grasses
This year all recorded grass species flowered earlier. Meadow foxtail (Alopecurus pratensis) first flowered 18 days earlier on 22nd April, Yorkshire fog (Holcus lanatus) 33 days earlier on 10th May, and cocksfoot (Dactylis glomerata) 21 days earlier on 19th May.
Birds
With birds, the first spring events of the year occurred later on average. For example, song thrushes (Turdus philomelos) were first heard singing 18 days later on 19th January, rooks (Corvus frugilegus) were first seen building their nests 2 days later on 27th February, and blackbirds (Turdus merula) were first heard singing 6 days later on 16th February.
As we reached March, events occurred earlier than in 2021, with chiffchaffs Phylloscopus collybita) arriving 3 days earlier on 13th March, cuckoos (Cuculus canorus), blackcaps (Sylvia atricapilla), and yellowhammers (Emberiza citrinella) first singing 3, 7 and 14 days earlier respecitvely in April, and great-spotted woodpeckers (Dendrocopos major) first fledging 10 days earlier on 6th June. Swallows (Hirundo rustica) were an exception though first returning to our land 1 day later on 11th April.
Insects
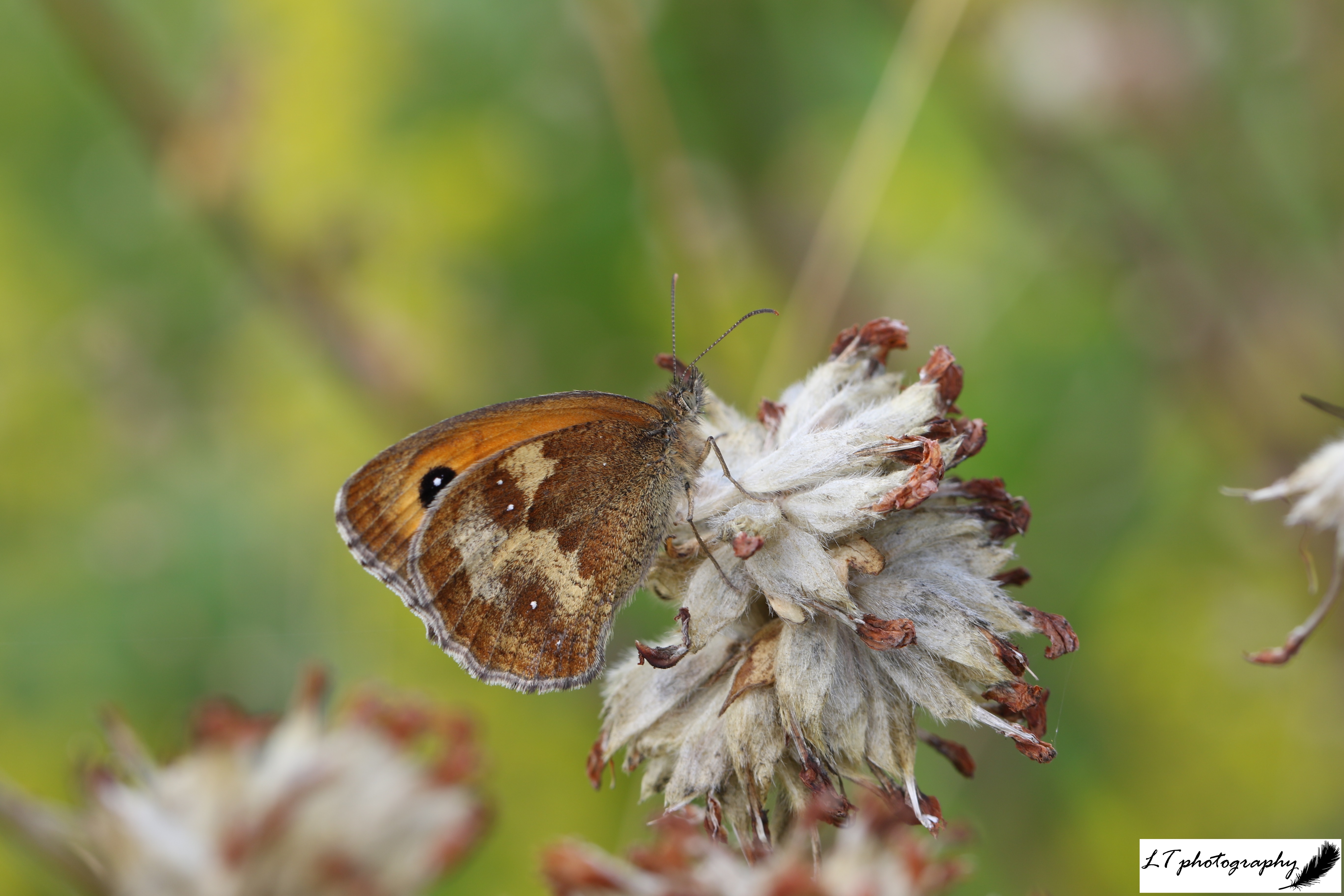
The majority of insects I recorded were first seen on the wing on our land earlier than in 2021, making the most of our more stable weather, These were:
- Red-tailed bumblebee (Bombus lapidarius) – 27 days earlier on 3rd March
- 7-spot ladybird (Coccinella septempunctata) – 1 day earlier on 19th March
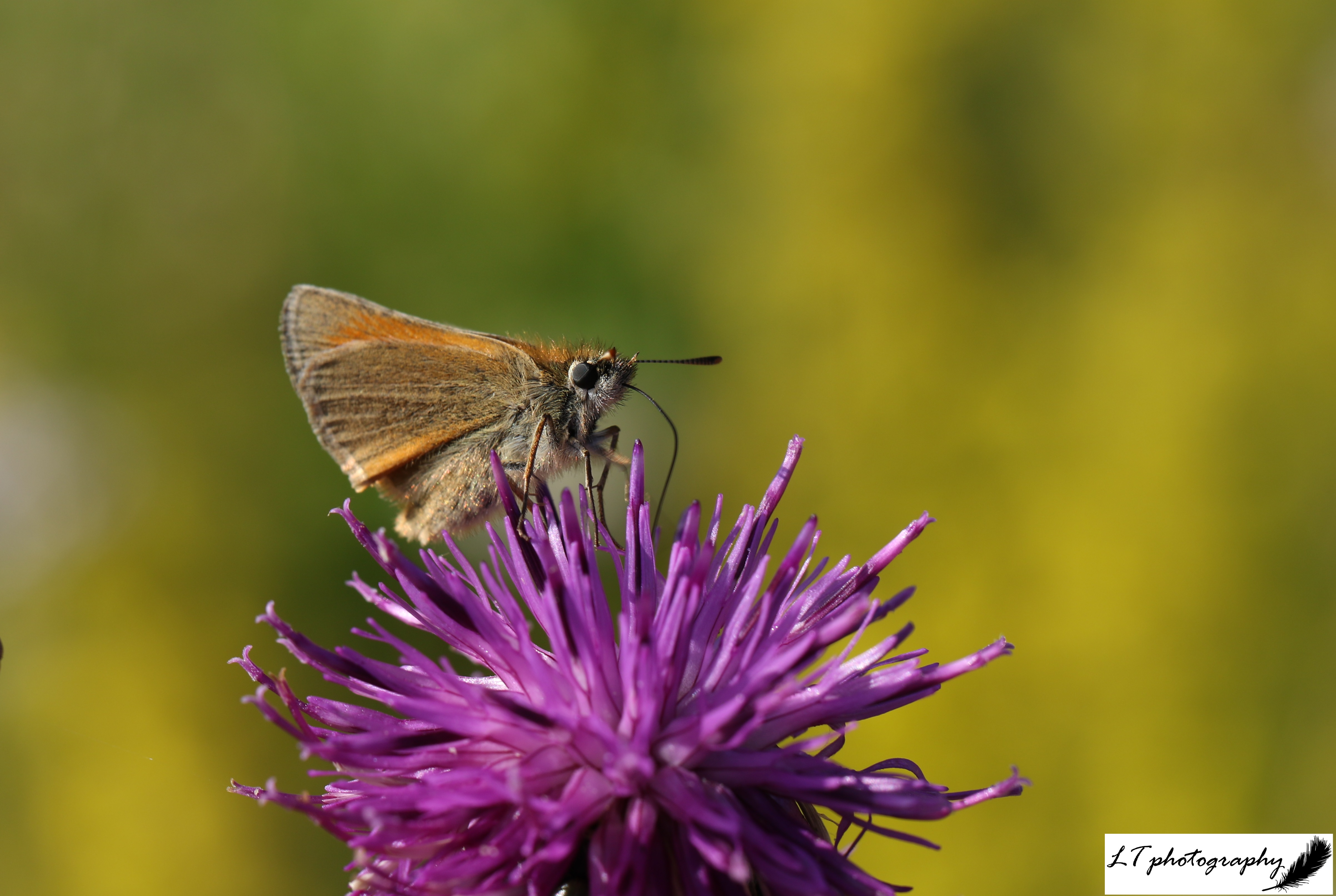
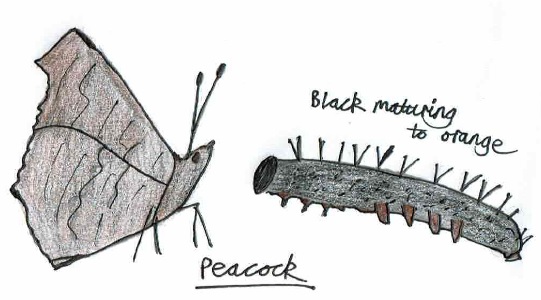
- Peacock butterfly (Aglais io) – 10 days earlier on 20th March
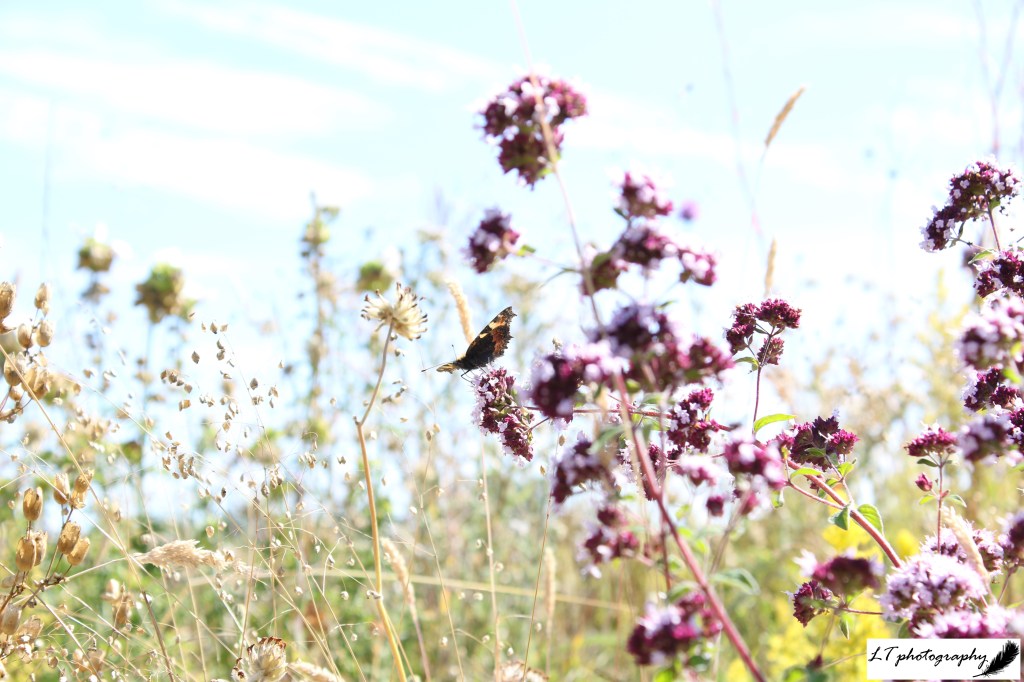
- Small tortoiseshell butterfly (Aglais urticae) – 16 days earlier on 22nd March
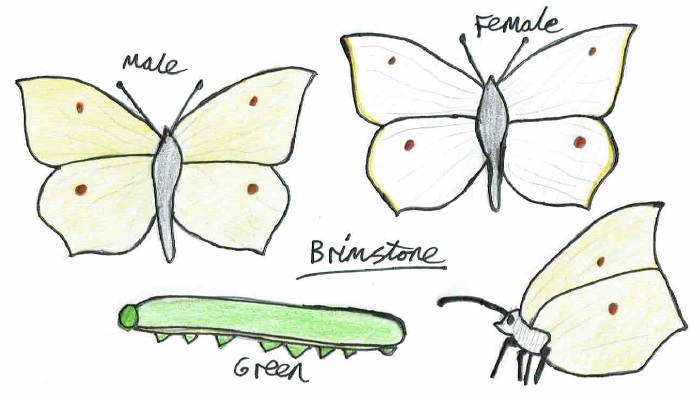
- Brimstone butterfly (Gonepteryx rhamni) – 26 days earlier on 23rd March
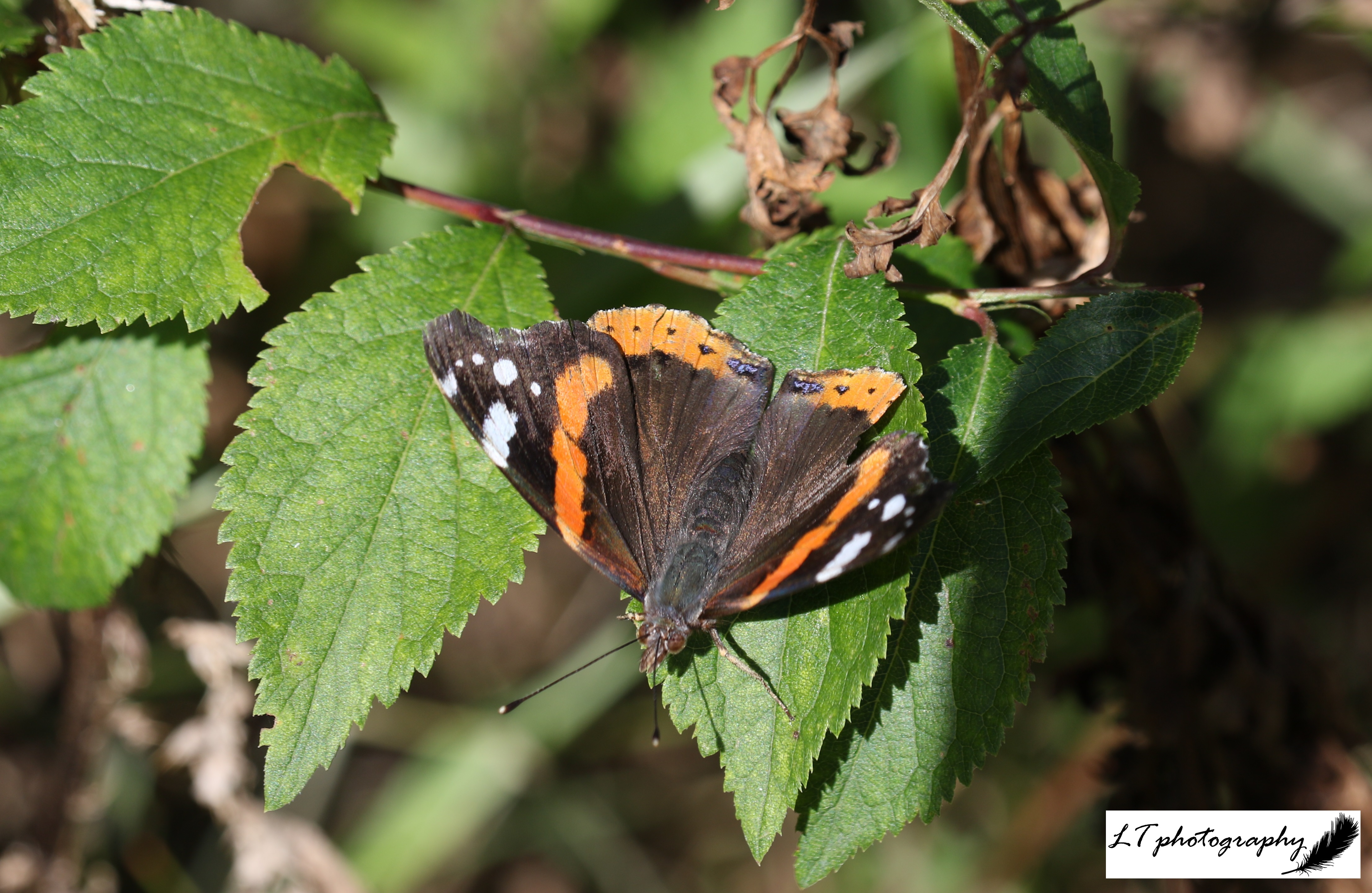
- Red admiral butterfly (Vanessa atalanta) – 14 days earlier on 24th March
- Speckled wood butterfly (Pararge aegeria) – 53 days earlier on 21st April
- Small white butterfly (Pieris rapae) – 14 days earlier on 8th May
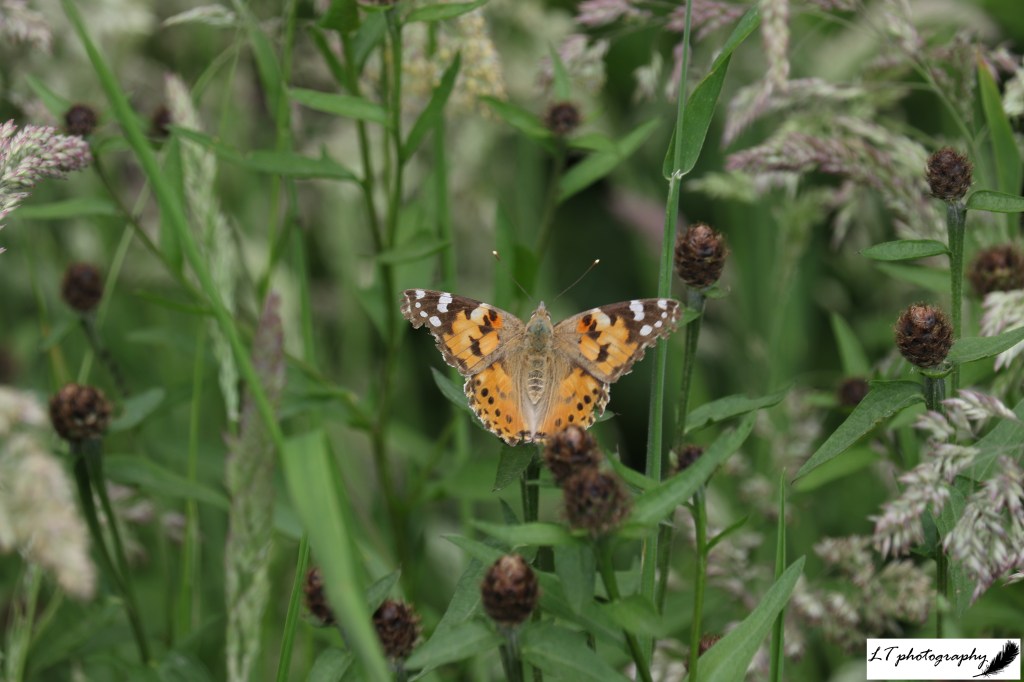
- Painted lady butterfly (Vanessa cardui) – 43 days earlier on 17th May
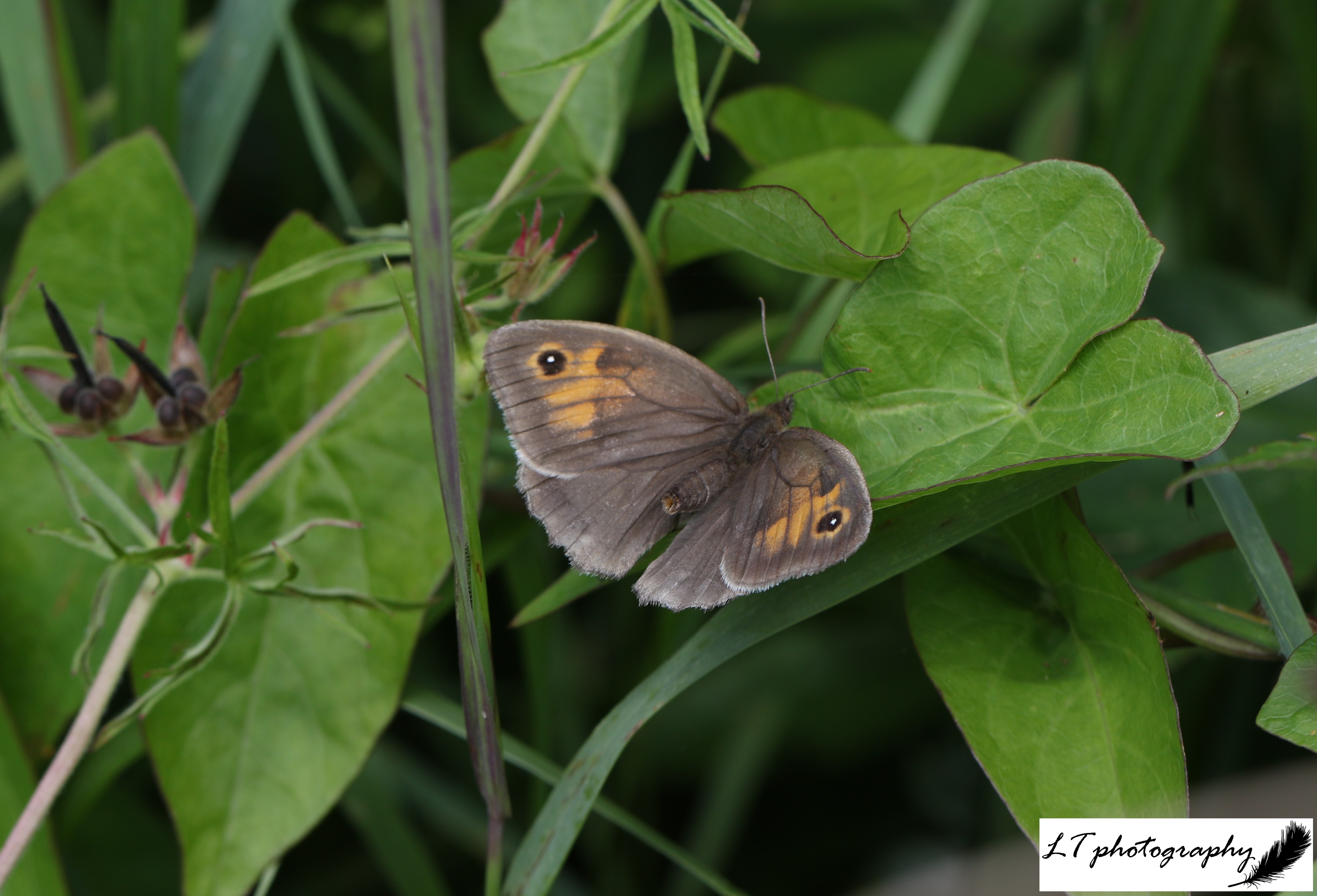
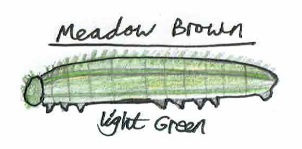
- Meadow brown butterfly (Maniola jurtina) – 27 days earlier on 22nd May
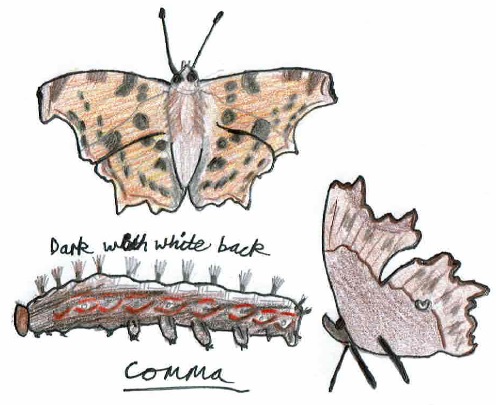
- Comma butterfly (Polygonia c-album) – 31 days earlier on 17th June
The exceptions were the buff-tailed bumblebee (Bombus terrestris) that emerged 19 days later on 18th March and orange-tip butterfly (Anthocharis cardamines) first seen 18 days later on 18th April.
Summary
This year during spring, plants tended to flower earlier, which could be due to the on average less turbulent weather, alongside the possibility of stress responses being triggered by the increasing temperatures at times. As a result flowers appeared earlier and went over more quickly.
Budburst and leaves did not follow as consistent a trend, but on average plants went through these spring events later than 2021. This may be due to many of these events occurring more towards the beginning of spring, when day length and temperature increases would have only just started to take an effect. Bird events followed spring in general with a slow start and a quick finish, whilst insects emerged earlier, as expected after last year’s unpredictable weather.
This year I have enjoyed all that spring had to offer, though it felt like once it got started it rushed through to its finish. In the moment it was a glorious season, but was cut short in its splendour. Being my favourite season, this year I was particularly sad when the season went over in to summer. Let’s see what will happen during the seasons to come and enjoy the adventures to be had!