A majestic oak standing tall in the landscape, watching as centuries pass it by. A silver birch with drooping branches, embellished with leaves, slowly blowing in the breeze. An alder leaning over the edge of a river, spreading its branches to shade the bank beneath it. From capturing the imaginations of children to symbolising strength and life for adults, trees in all their forms are an important part of the landscape and culture within Britain.
With over 70 species in the UK alone, trees come in all shapes and sizes, and can be found anywhere from our highlands to our cities. Trees colonised Britain following the last glaciation, and have since become intertwined with our very own history. They provide us with so much, including resources, such as medicines and building materials, improved air quality, homes for wildlife, and even cultural services, such as therapy through forest bathing. Thus, they are a very important part of our environment!
Now, as our reliance on trees grows and the threats to them increase, it is surprising how little people know about trees in general. For example, the average Brit is unable to name more than five tree species, and a third even believe a money tree is a real species! With two thirds of the public now wanting to learn a little more about the trees in their area, here’s my handy guide to help you identify 10 common tree species that can be found in the UK.
Tree Species
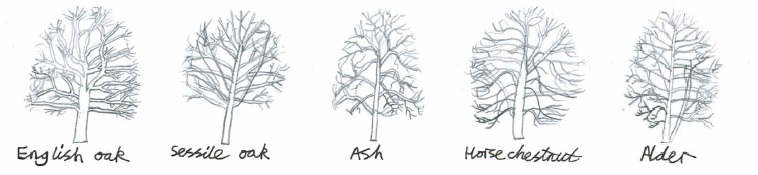
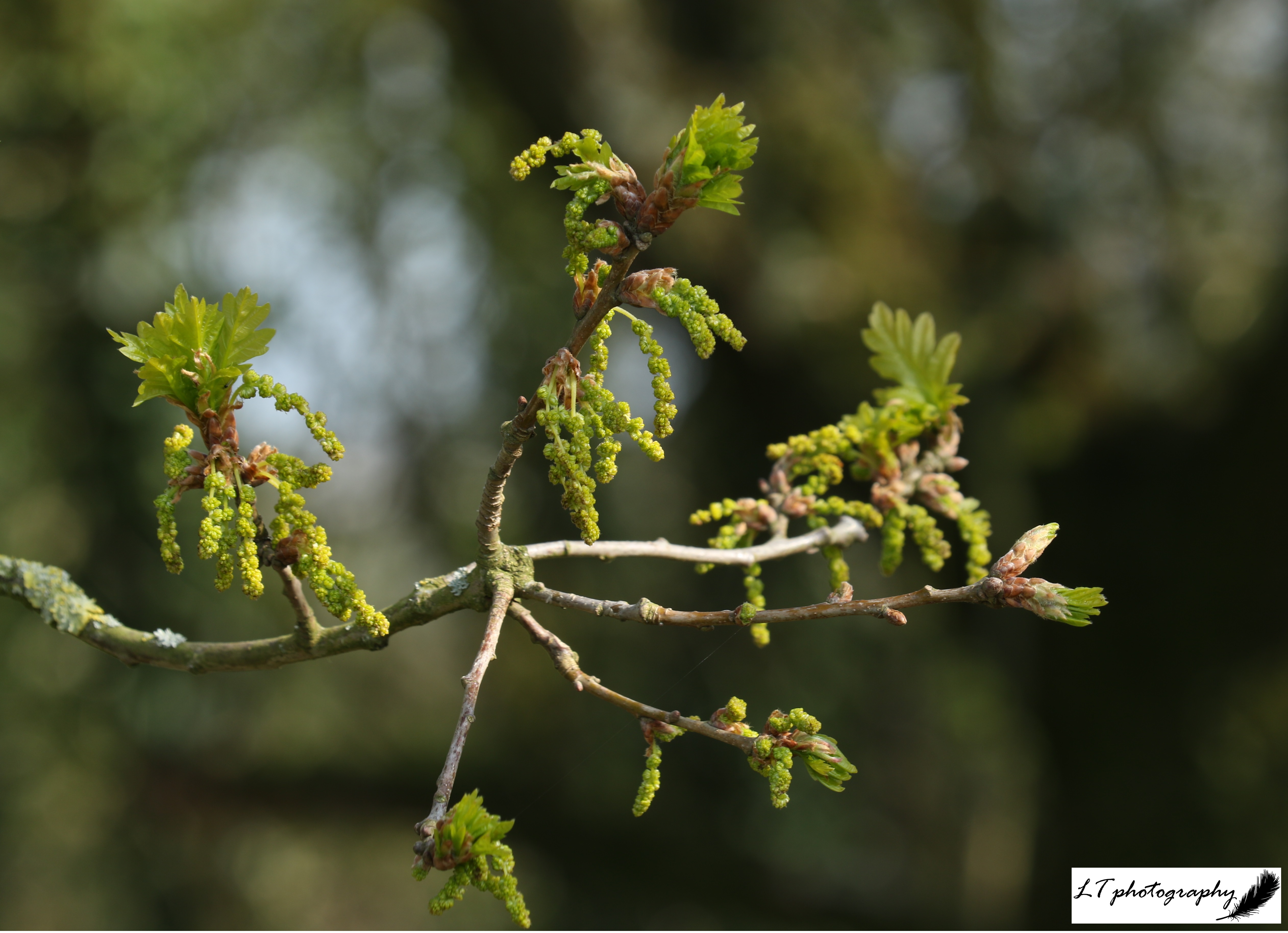
1. Pedunculate or English Oak (Quercus robur)
- Family: Fagaceae – related to species such as beech and sweet chestnut
- Origin: Native
- Shape and size: Up to 40m tall, upward-reaching and broad crown
- Stems and twigs: Massive rugged grey-brown trunk
- Leaves: 10-12cm long, oblong, and lobed, turning brown in autumn
- Flowers: On the same tree and flowering April-June. Male flowers= yellow-green catkins; female flowers= pinkish and on short stalks
- Seeds: Produces the familiar acorn, with scaly cups and clusters carried on long stalks
- Range & habitat: Widespread and common throughout Britain, found in habitats ranging from deciduous and mixed woodlands to open grassland and hedgerows
In Winter: Look for rounded buds that have overlapping scales and are found in clusters at the end of each shoot



2. Sessile oak (Quercus petraea)
- Differs to Pedunculate Oak in that the leaves taper to an unlobed base and have long stalks.
- Buds in winter have more scales (more than 20).
- Also, the clustered acorns are almost stalk-less with downy cups.
- Narrower in shape, prefers more acid soils, and is more common in the West of Britain.
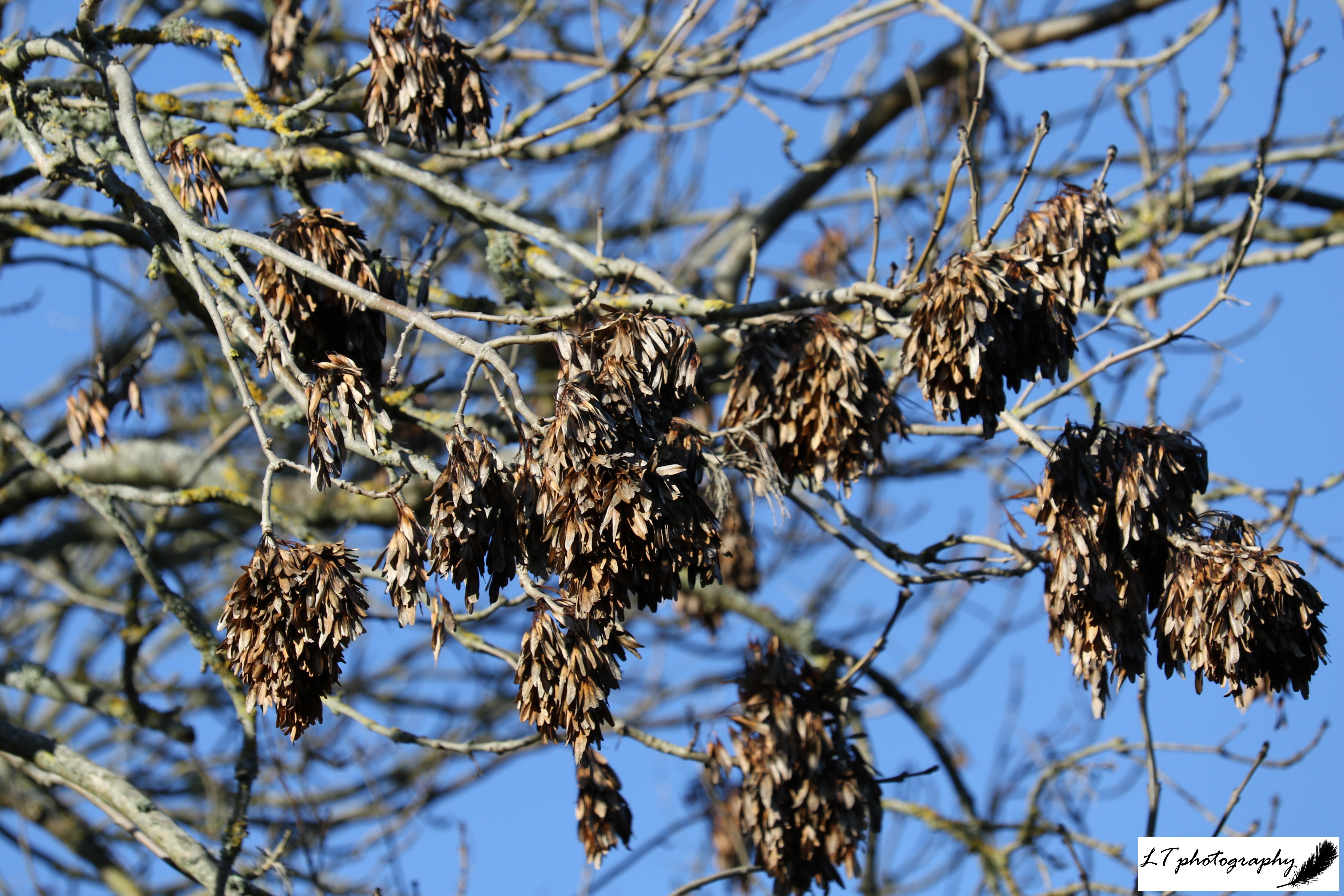
3. Common Ash (Fraxinus excelsior)
- Family: Oleaceae – related to olive trees and lilac
- Origin: Native
- Shape and size: Tall and domed with widely spaced branches, growing up to 35m
- Stems and twigs: Bark is pale brown to grey, becoming rugged with age
- Leaves: Opposite and toothed, with 9-13 stalked leaflets that have long tips
- Flowers: Male and female flowers typically grow on different trees, but both have purple flowers growing in clusters before the leaves
- Seeds: Single seeds with a long wing (known as keys)
- Range & habitat: Woods and hedges, in particular flourishing on a lime-rich/well-drained soil
In Winter: Smooth twigs with distinctive hairless black buds, and ridged bark on adult trees that resembles a diamond pattern



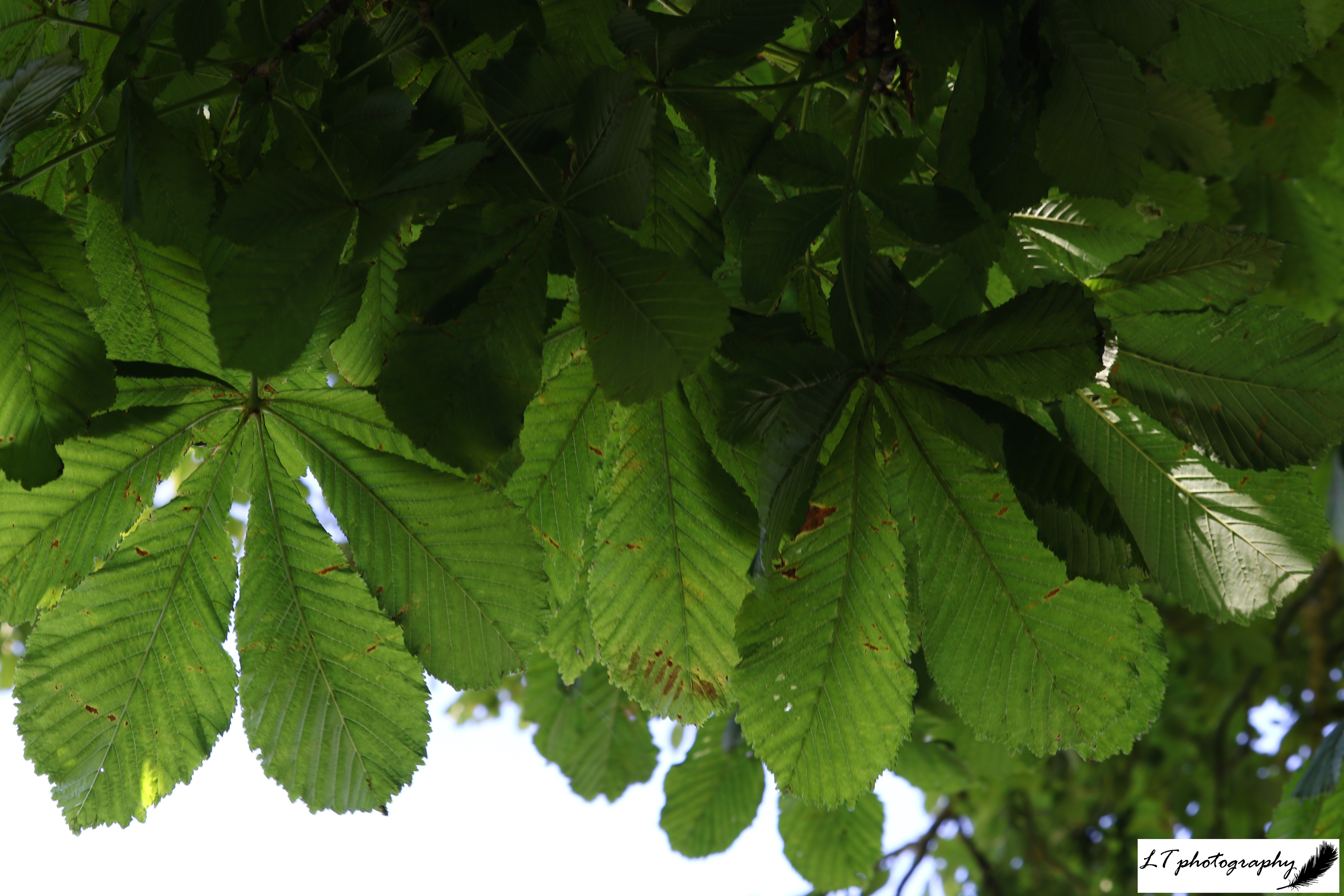
4. Horse Chestnut (Aesculus hippocastanum)
- Family: Sapindaceae – related to lychee and maples
- Origin: Non-native (introduced in the 1500s from the Balkan peninsula in southeastern Europe)
- Shape and size: Arching branches, usually turned up at the ends, growing up to 35m tall
- Stems and twigs: Bark is scaly and red-brown or dark grey-brown
- Leaves: Five to seven large, thick, stalkless leaflets with pronounced veins and a long, tapering base
- Flowers: Showy spike (candle) of white flowers with a yellow to pink spot
- Seeds: Spiny fruit contains one or more shiny conkers
- Range & habitat: It has now become a widespread and common sight across Britain, tolerating a wide range of soils
In Winter: Smooth bark and sticky buds



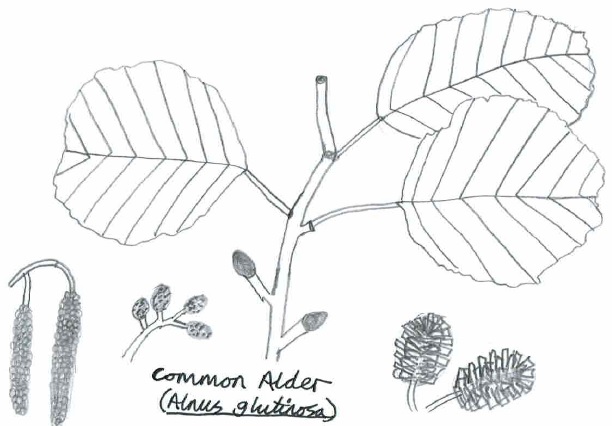
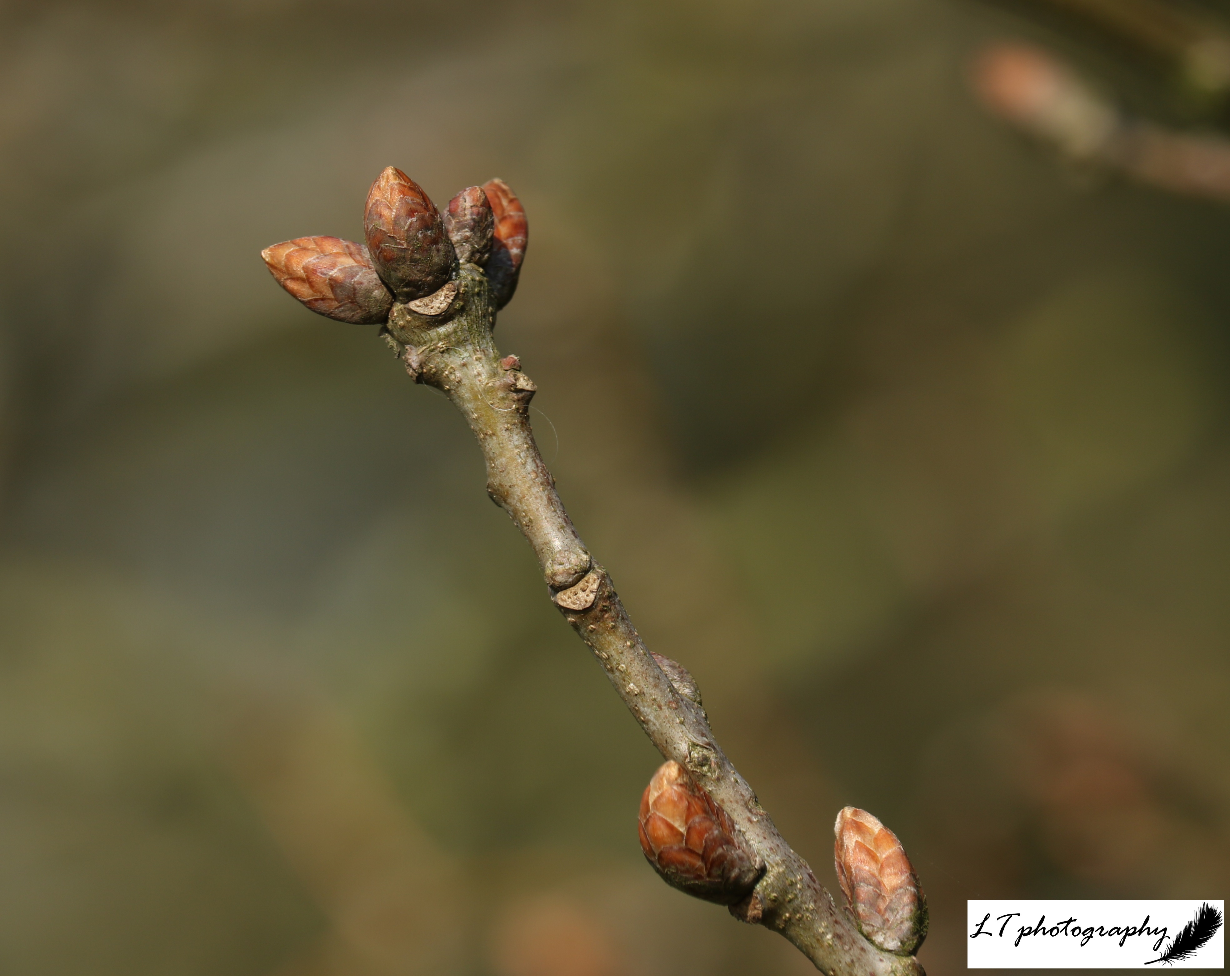
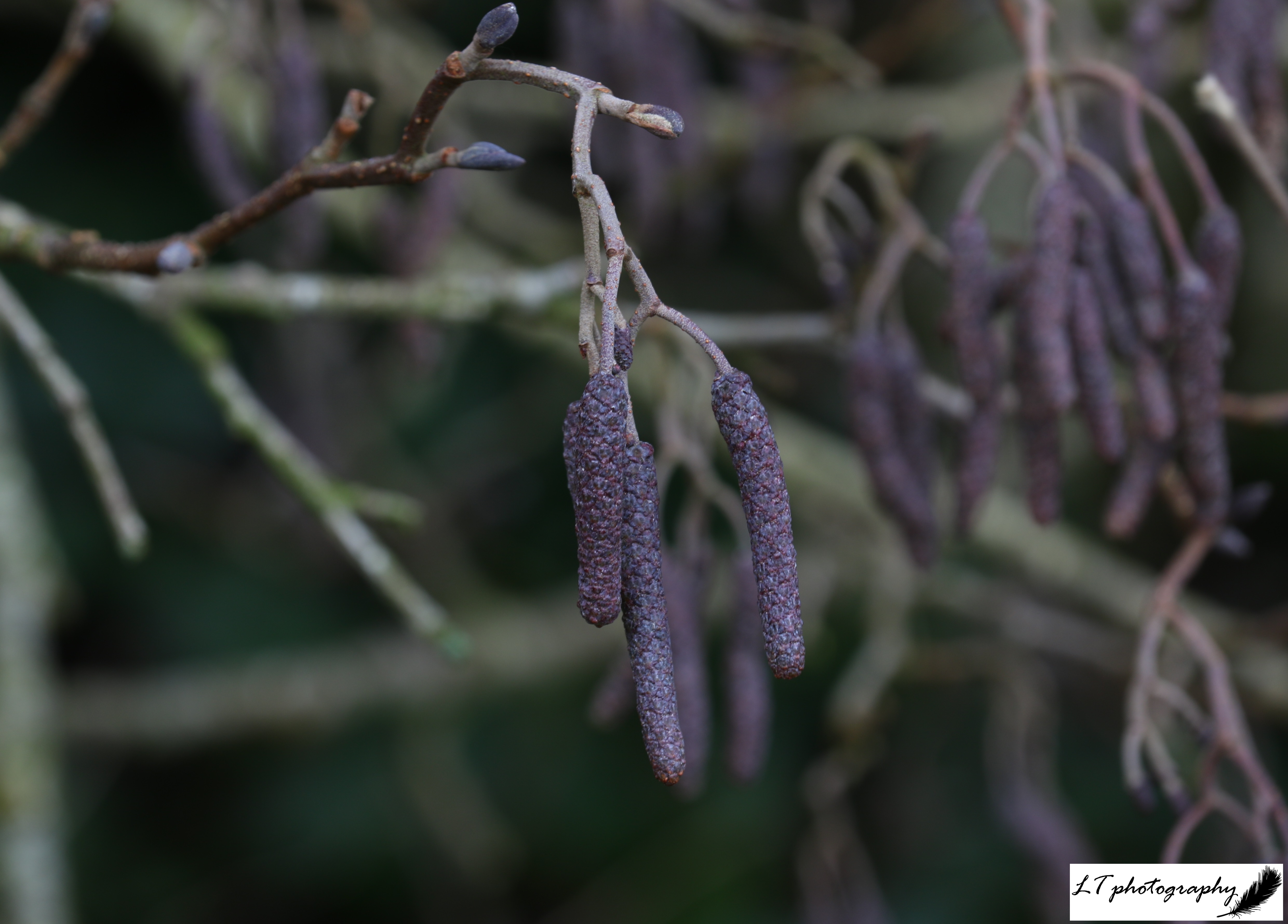
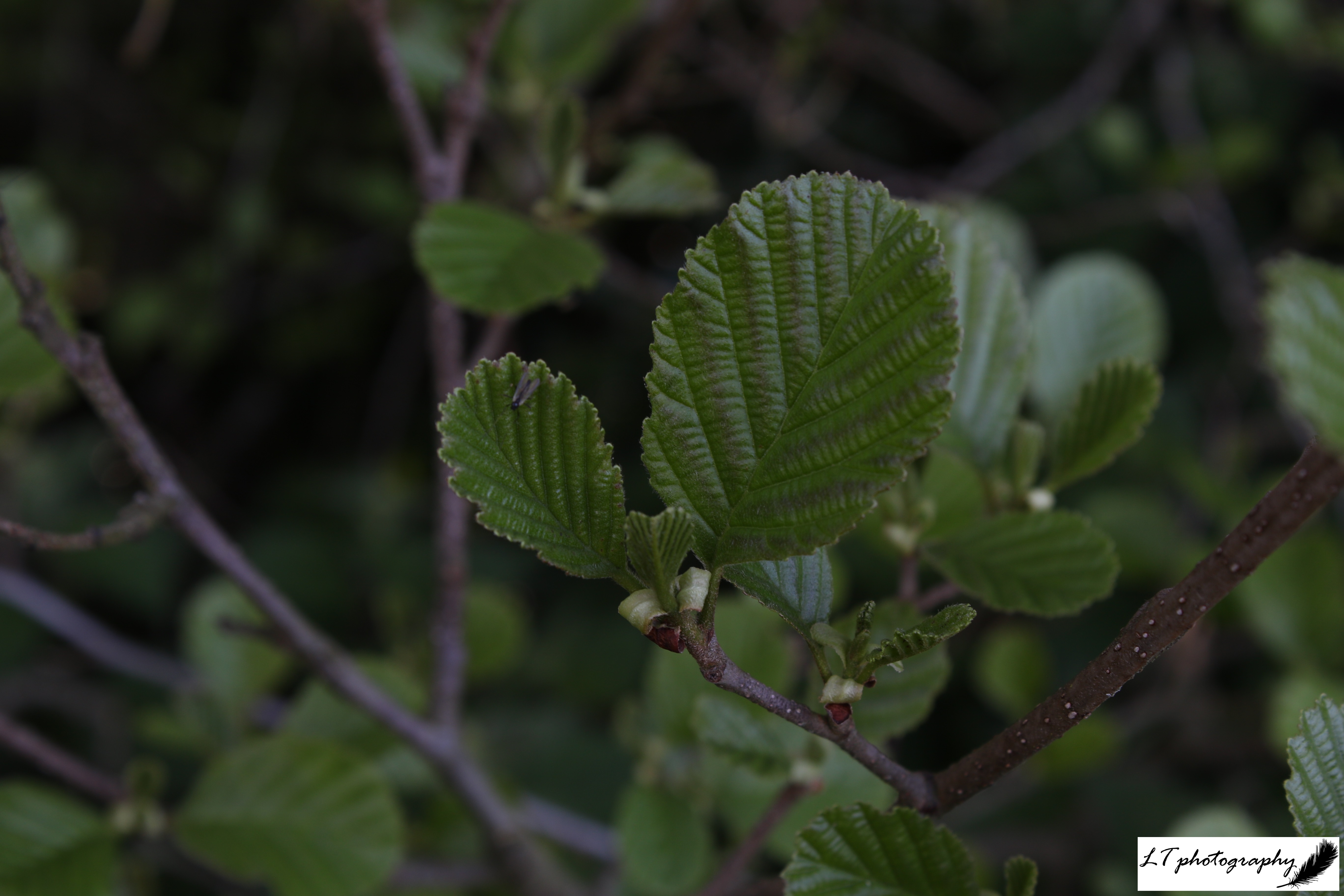
5. Common Alder (Alnus glutinosa)
- Family: Betulaceae – related to hazel and birches
- Origin: Native
- Shape and size: Regular branching and conical shape, growing up to 25m
- Stems and twigs: Dark brown bark that is often rough and sprouts young shoots
- Leaves: Alternate, rounded, sometimes notched at the tip, and dark green
- Flowers: Male and female catkins grow on the same tree, before the leaves. Male catkins= lambs’ tails; female catkins= small and egg-shaped
- Seeds: Female catkins turn into a small cone, drying from green to brown, releasing the seeds. The seeds have corky outgrowths that keep them afloat on water
- Range & habitat: Thrives in wet ground and is often seen lining the banks of rivers and streams across Britain
In Winter: Appears dull purplish due to purplish buds



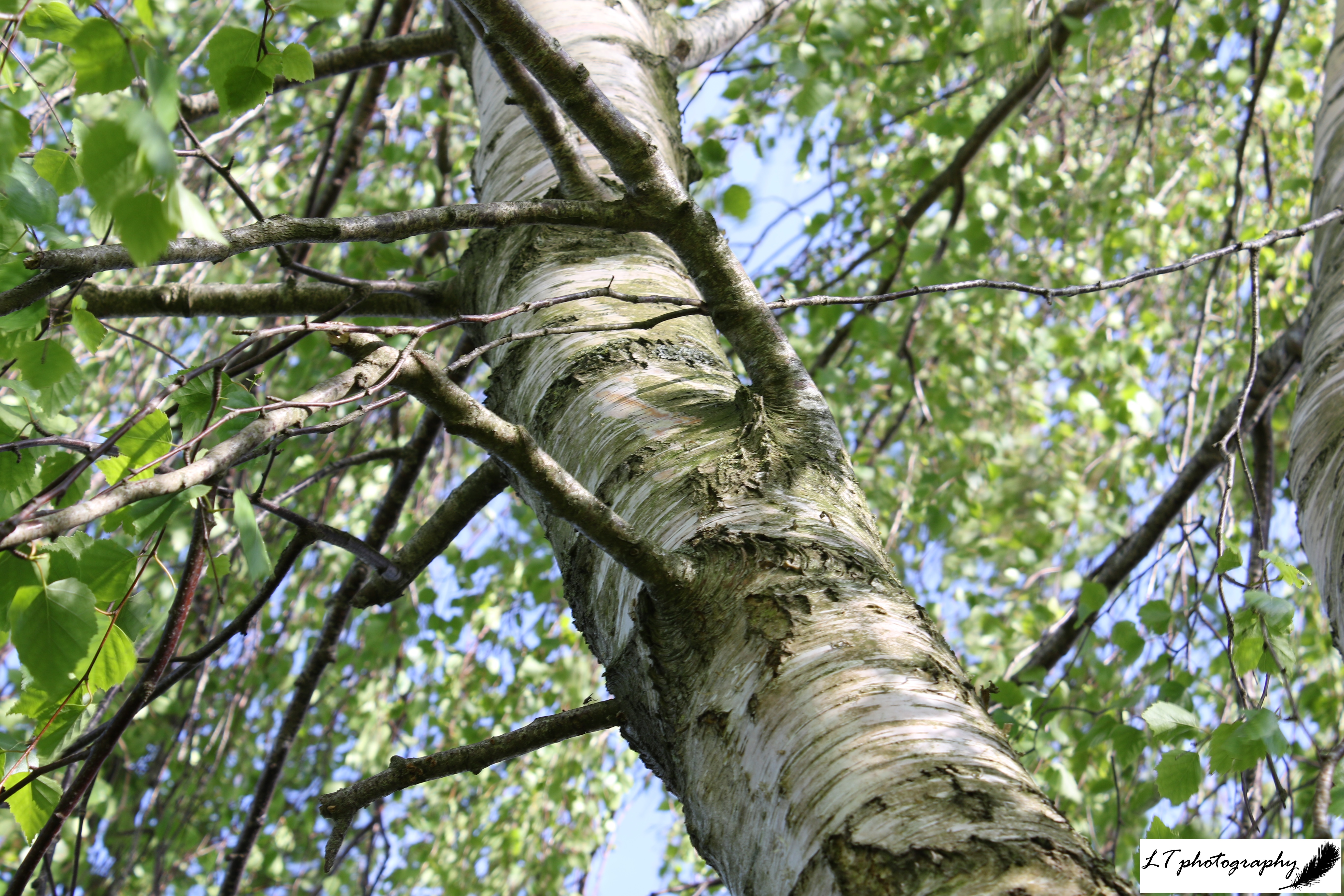
6. Silver Birch (Betula pendula)
- Family: Betulaceae – related to alders, hazels and hornbeams
- Origin: Native
- Shape and size: Erect with pointed crown and drooping branches, reaching up to 30m
- Stems and twigs: Young bark reddish, maturing to black and papery-white bark. Twigs smooth with small dark bumps
- Leaves: Alternate, triangular and shiny, on slender stalks. Edges are ragged, with smaller teeth between larger main teeth
- Flowers: Male catkins= purply-brown; female catkins= smaller and pale green
- Seeds: Two winged and wind-borne, released in winter
- Range & habitat: Form natural woodlands on light, dry soils throughout Britain
In Winter: Distinctive shape and bark



7. Sycamore (Acer pseudoplatanus)
- Family: Sapindaceae – related to maples and horse chestnut
- Origin: Non-native (introduced from Europe either in the 1500s or by the Romans)
- Shape and size: Massive domed outline, with dense foliage and heavy lower branches, growing up to 35m
- Stems and twigs: Grey fissured bark ages to pinkish-brown
- Leaves: Opposite, five-lobed, and upper side dark green
- Flowers: Greeny-yellow flowers in hanging clusters appear with the leaves
- Seeds: Hairless keys in right-angled pairs
- Range & habitat: Grow vigorously in all parts of Britain, being widely planted on their own for shelter or in woodlands and hedgerows
In Winter: Distinctive shape and bark
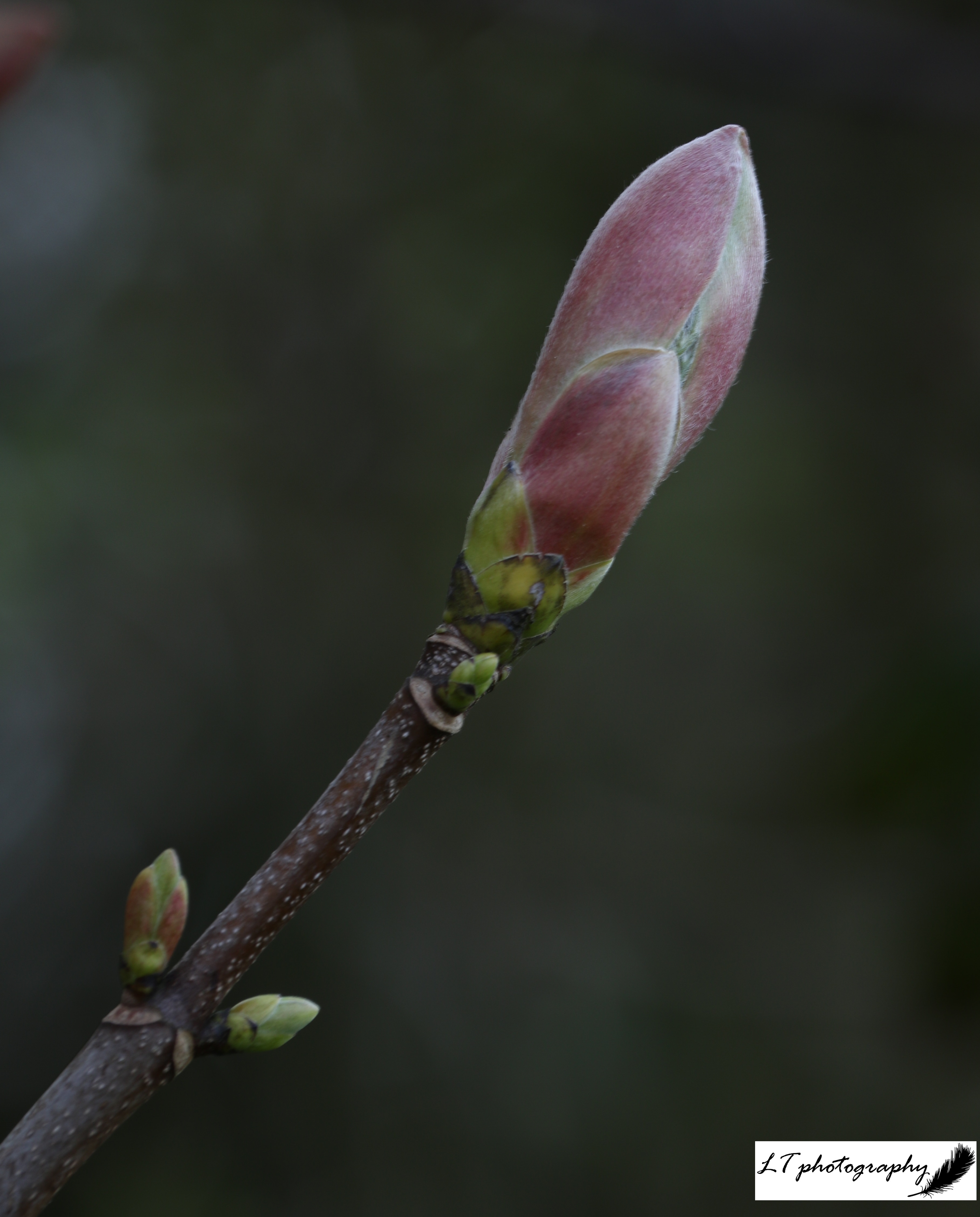
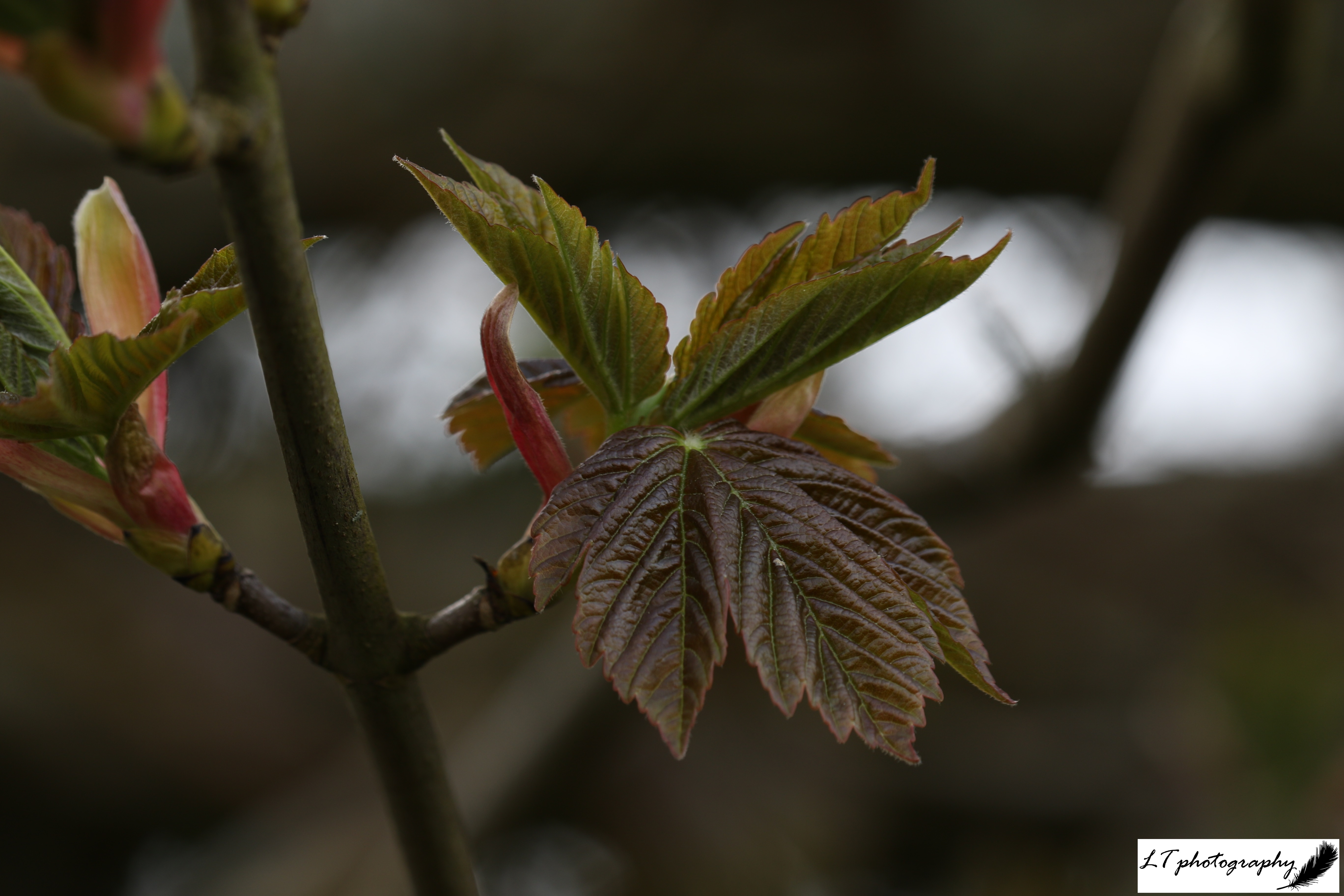



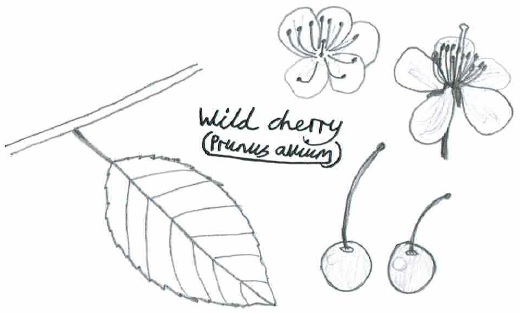
8. Wild Cherry (Prunus avium)
- Family: Rosaceae – related to roses
- Origin: Native
- Shape and size: Pyramidal shape, reaching up to 30m
- Stems and twigs: Shiny, red-brown bark peels in horizontal strips
- Leaves: Alternate and oval with long points and regular, forward-pointing teeth, and two conspicuous red glands at the top of the stalk
- Flowers: White flowers (blossom) appear before the leaves in small, loose clusters
- Seeds: Produces round, red cherries
- Range & habitat: Native throughout the UK, being found in woodlands and hedgerows
In Winter: Distinctive bark
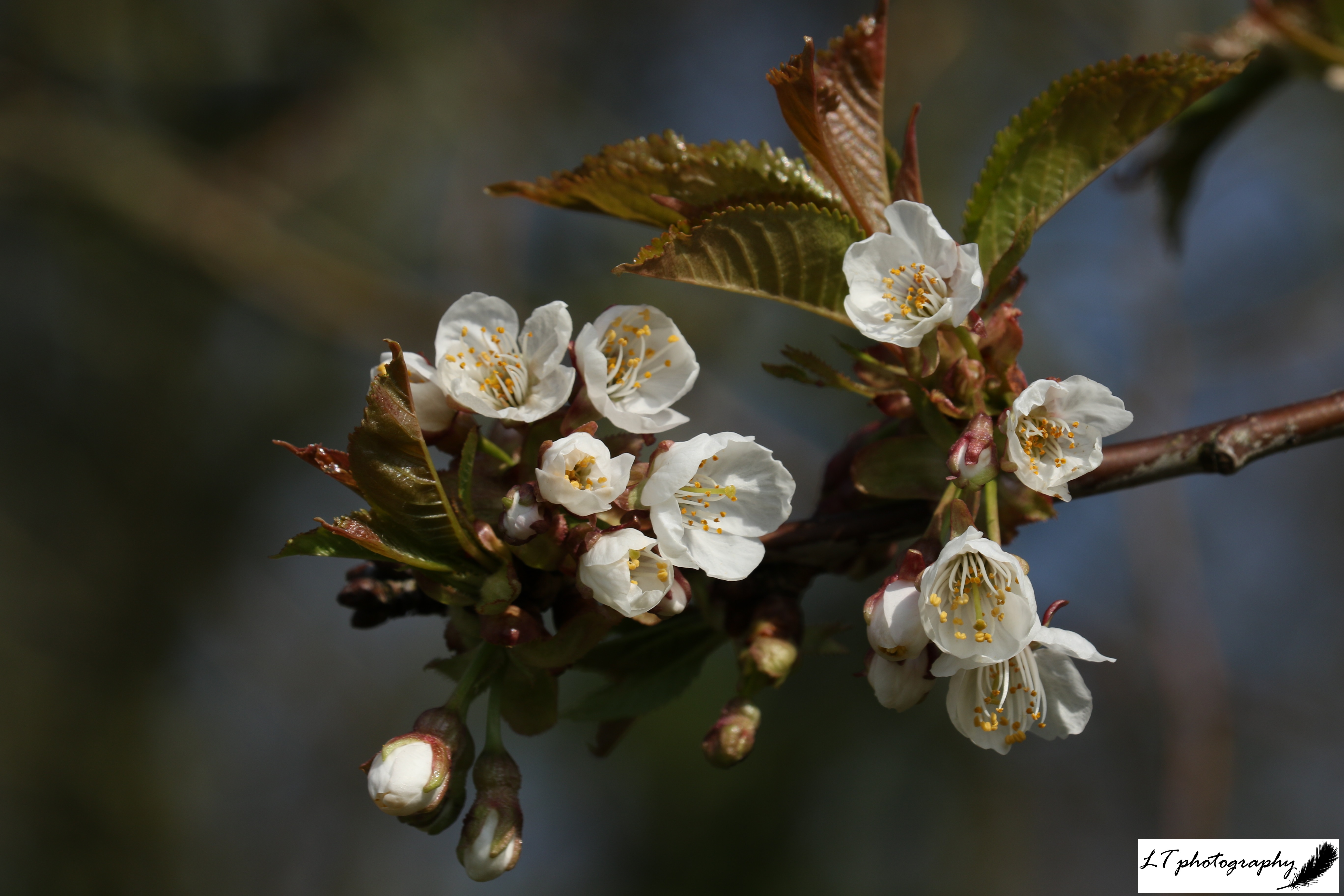


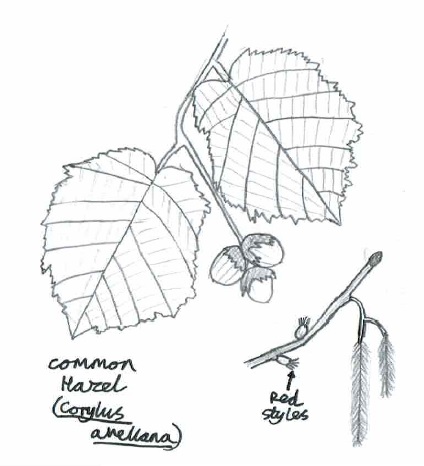
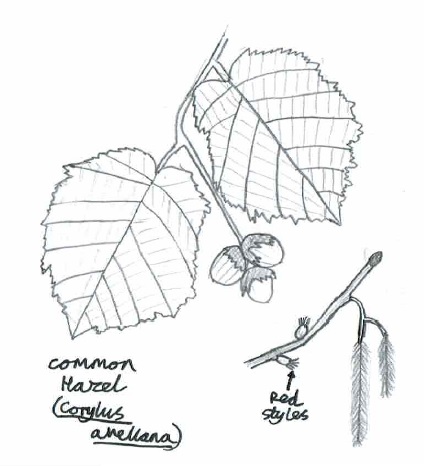
9. Common Hazel (Corylus avellana)
- Family: Betulaceae – related to birches, alders and hornbeams
- Origin: Native
- Shape and size: Many stems rise from the ‘stool’, which if left uncut can reach 9m
- Stems and twigs: Bark coppery brown, smooth and tending to peel
- Leaves: Alternate, almost circular with sawtooth edges, hairy, and soft to the touch
- Flowers: Male and female flowers found on the same tree. Male= lemon-yellow lambstail catkins; Female= tiny buds with red tassels
- Seeds: An edible nut encased in a thick-green husk, ripening in autumn
- Range & habitat: Grows throughout Britain, often found in woods, scrub areas, and hedges
In Winter: Distinctive shape and bark, accompanied by the male catkins from December
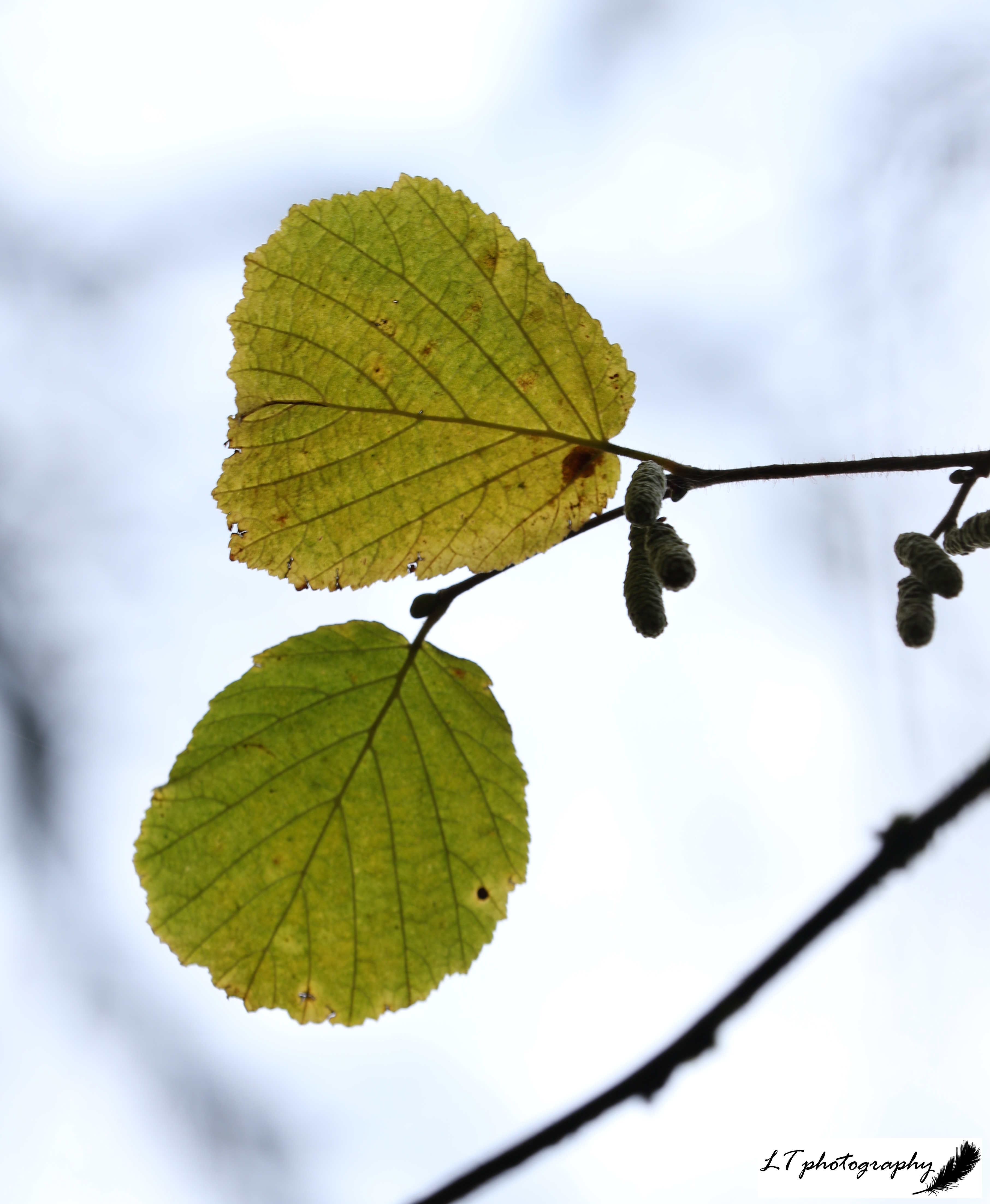



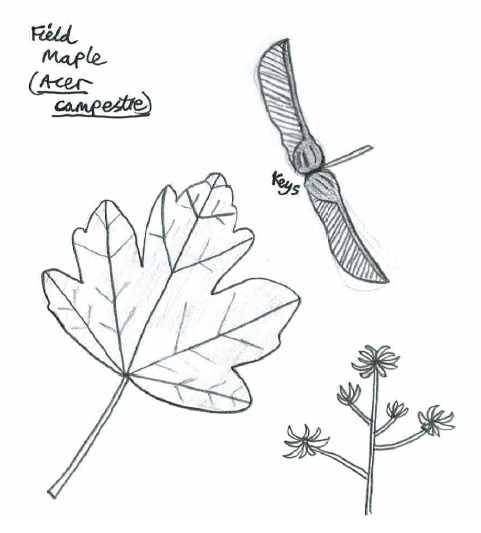
10. Field Maple (Acer campestre)
- Family: Sapindaceae – related to lychee and horse chestnut
- Origin: Native
- Shape and size: Round-shaped tree with branches that droop at the end, growing up to 26m
- Stems and twigs: Bark is grey or light brown and twigs downy, later corky
- Leaves: Emerging leaves have a pinkish tinge, turning dull-green, and are opposite and small, with three main, round-tipped lobes and two smaller basal lobes
- Flowers: Small yellow-green flowers form erect clusters
- Seeds: Each pair of seed wings lie in an almost straight line, are often tinged with pink
- Range & habitat: Frequent in England and East Wales in woods and hedgerows
In Winter: Sinuous trunk and distinctive shape



Drawings and photos all my own