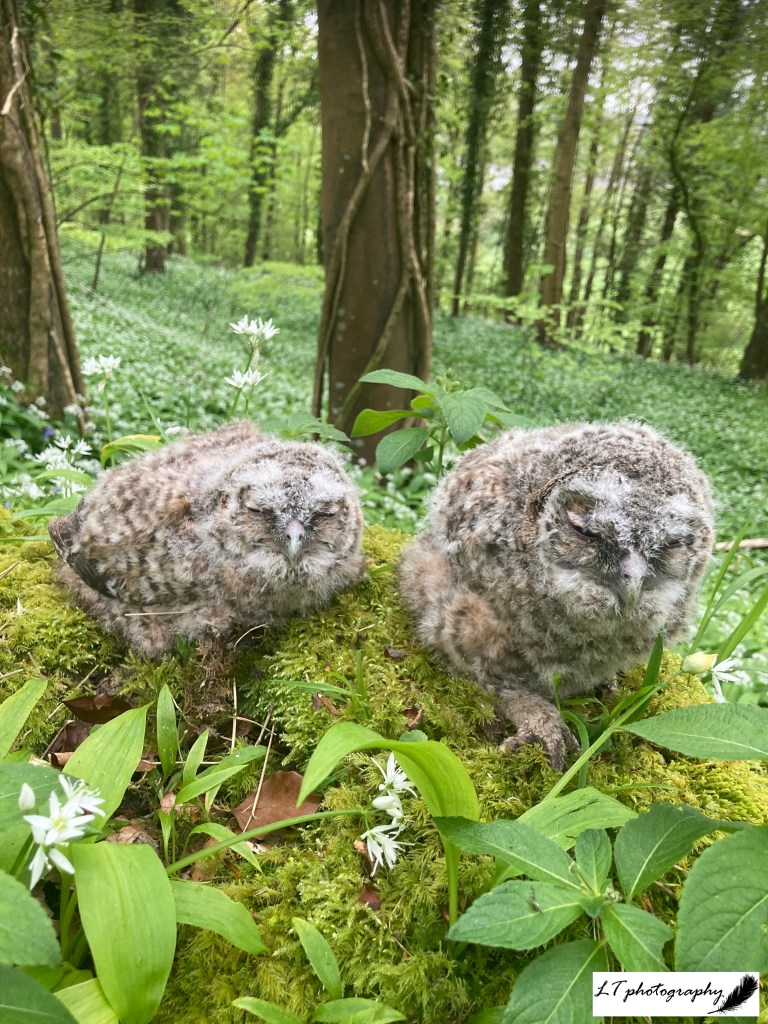
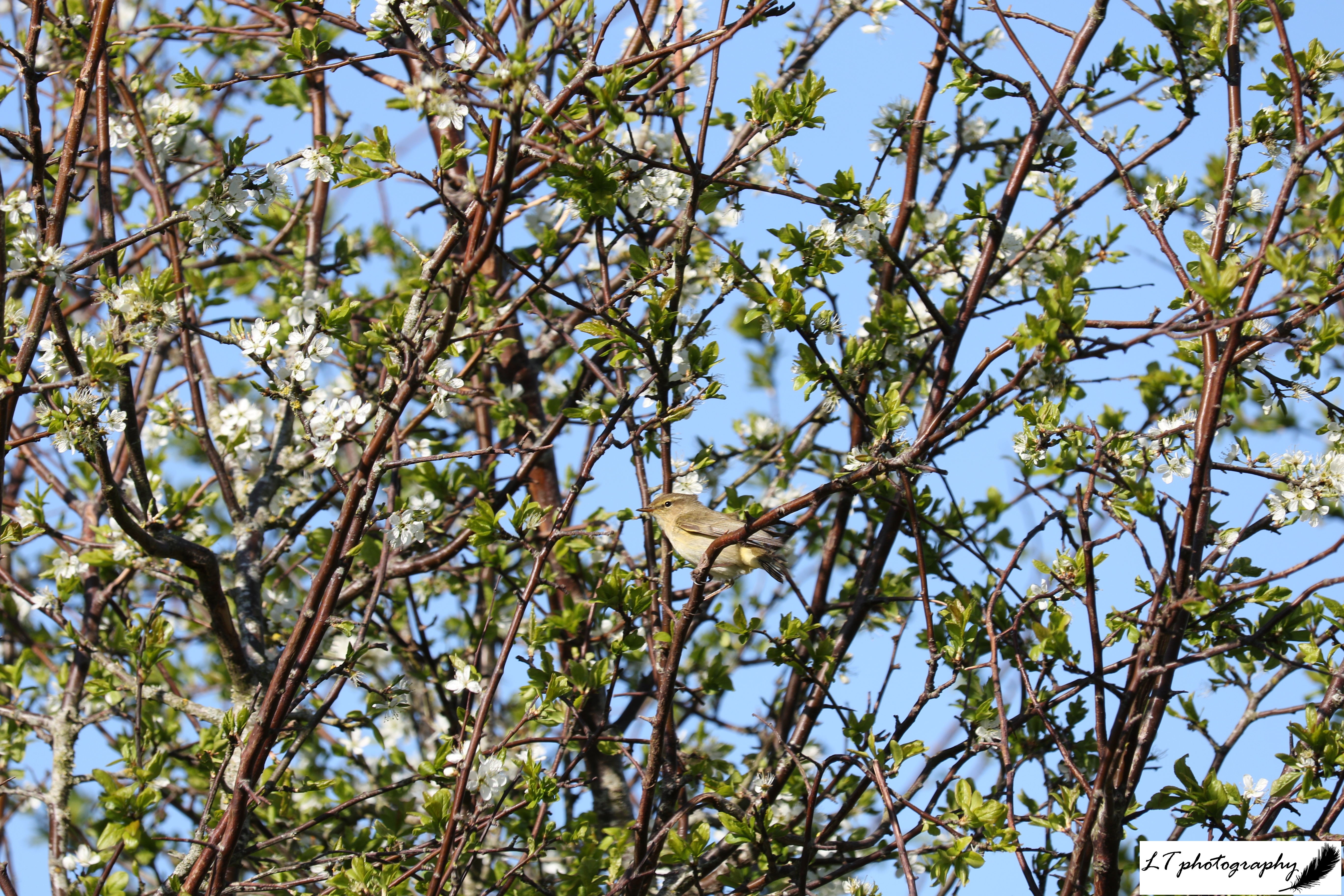
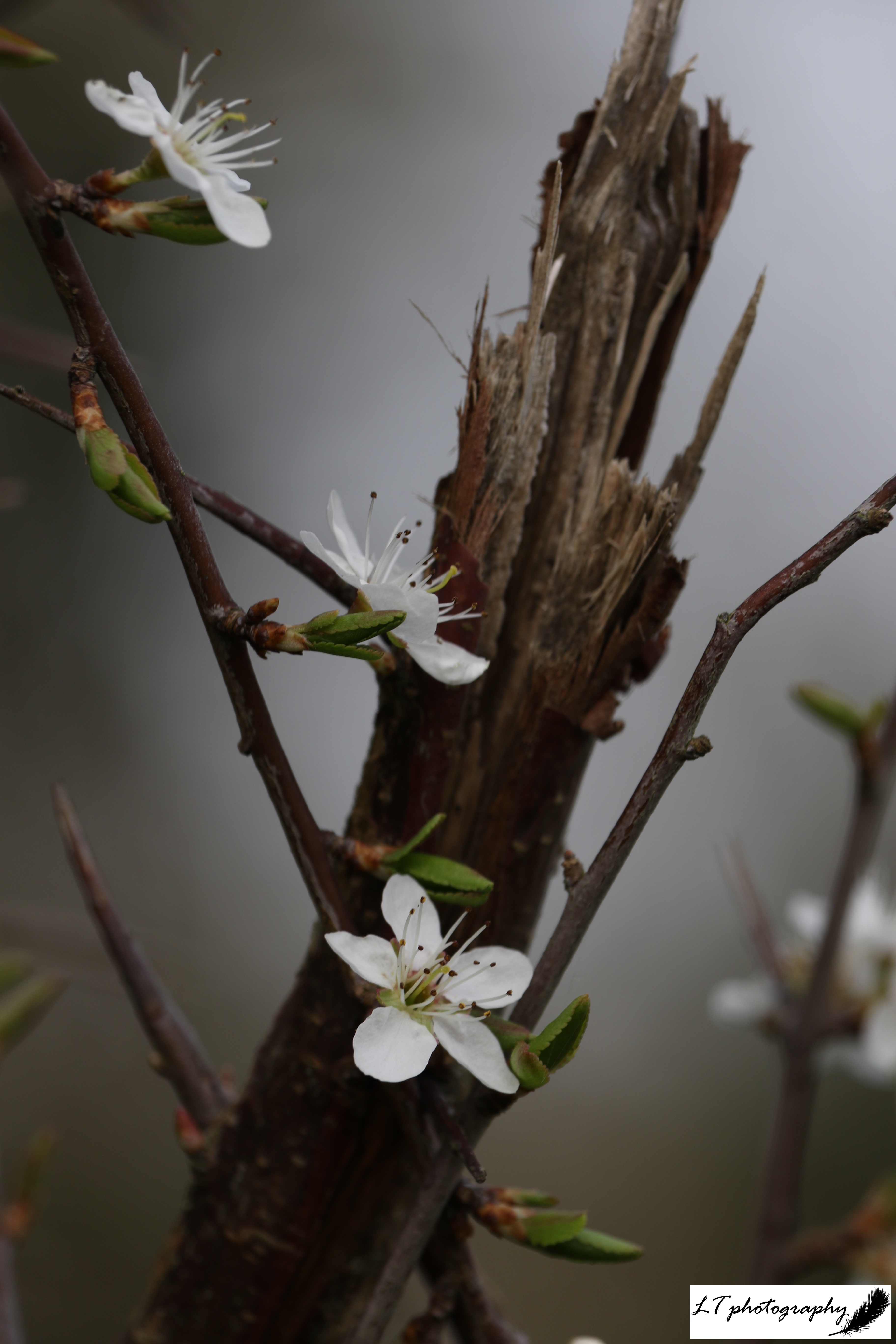
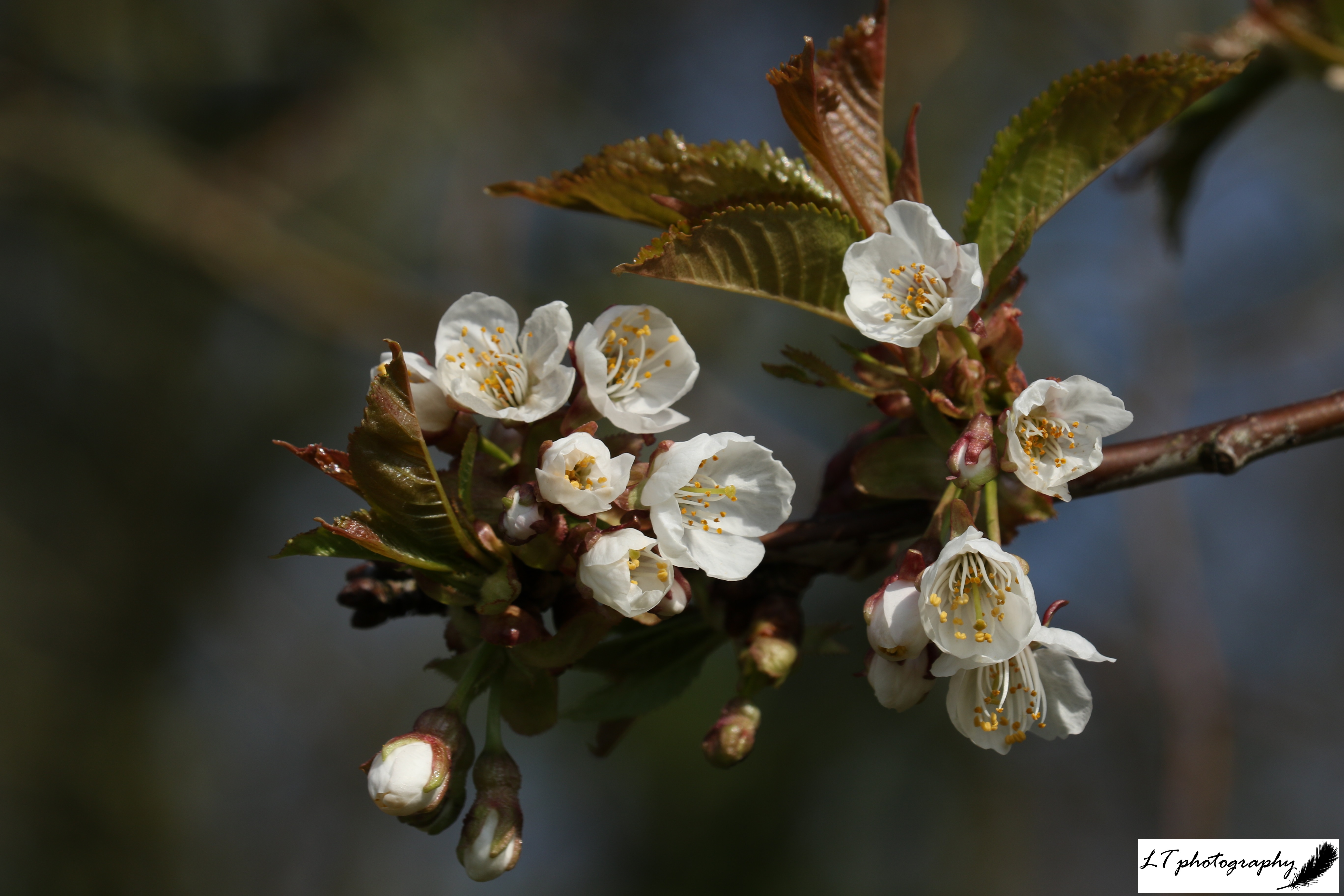
Spring 2025 felt like an unusual spring this year, with unpredictable weather patterns and trends being hard to pinpoint. Looking back at meteorological records though, despite sudden changeable weather and some cold snaps early on, March, April, May and June were in fact on average warmer and sunnier than previous years, with wet ground drying up fast. As a result, this season felt like it went by in a flash this year and was harder to hold on to, in the present and in memory.


Spring 2024 was even more changeable in weather patterns compared to this year, but still showed some consistent phenological trends (check out Spring 2024: How It Happened). Plant species showed events occurring earlier due to warmer temperatures, whilst insect and bird species showed a split in occurrence, affected by some increased rainfall at certain periods. With spring 2025 also exhibiting some changeability, but overall warmer temperatures, I wonder how spring events played out this year. Let’s take a look at tree, flowering, shrub, insect and bird species to get a snapshot of how things turned out this year in comparison to previous years.


Trees
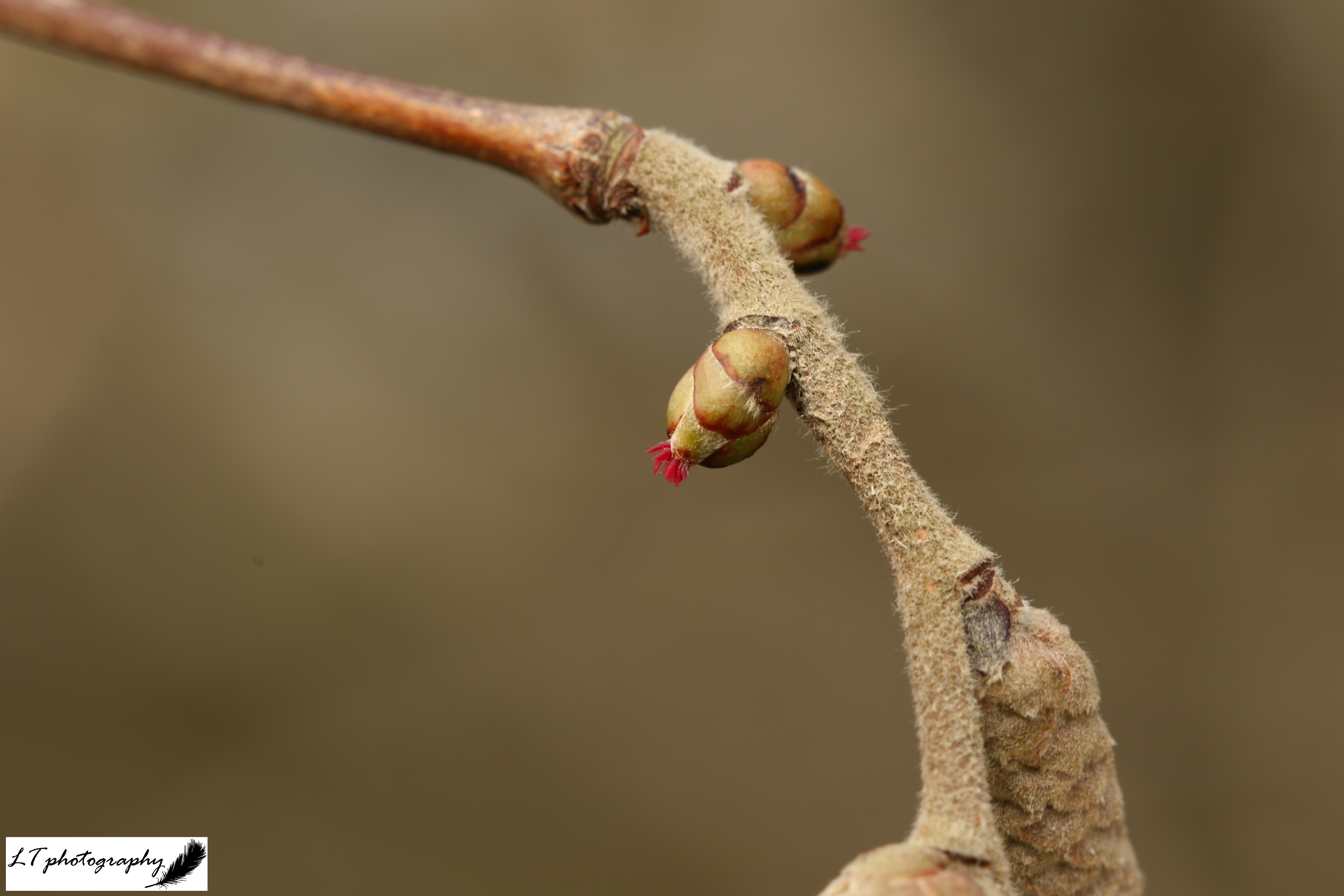
During 2024, spring emergence dates were on average earlier for most tree species due to warmer and wetter spring weather. In 2025 though, the trend is less easy to discern, with events ranging anywhere from 1 to 30 days earlier, 1 to 21 days later, or even the same day. The trend does not relate to month, but timing of events differed between species, with all english oak events occurring later, whilst all sycamore events occurred earlier, which may signify varying factors at play. There’s also no trend occurring with tree species between the years either, such as becoming earlier or later over time. This year’s spring did feel like the weather was highly changeable at times though, switching from warm to cold, wet to dry, and may have created small scale fluctuation from week to week, despite overall warmer weather.


Flowers
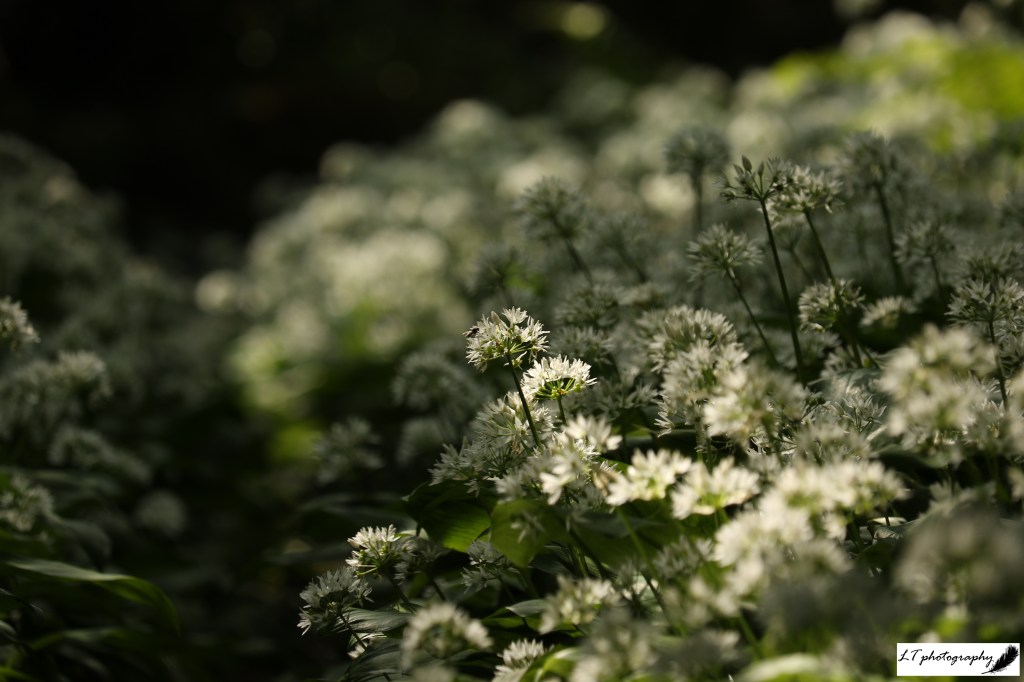
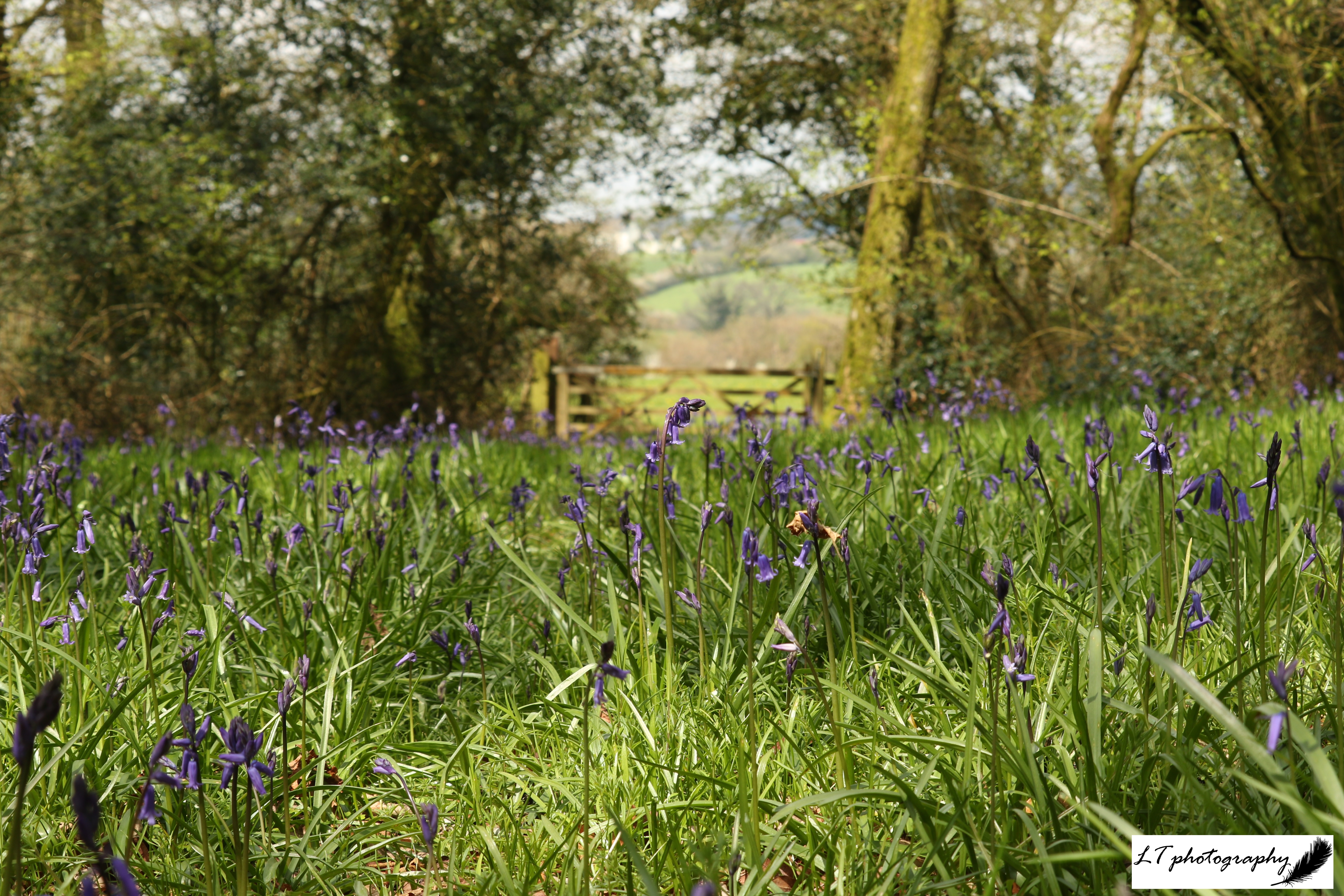
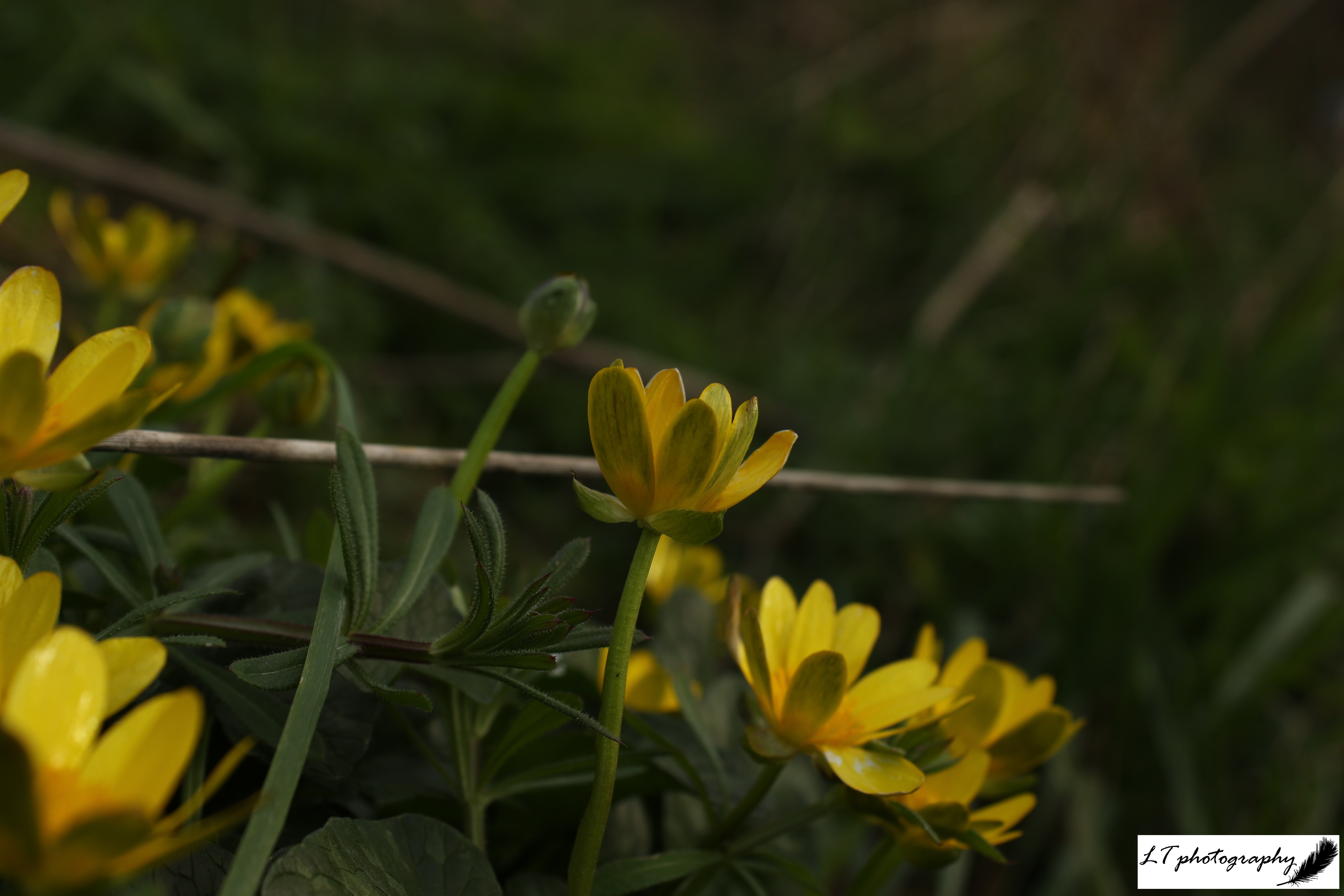
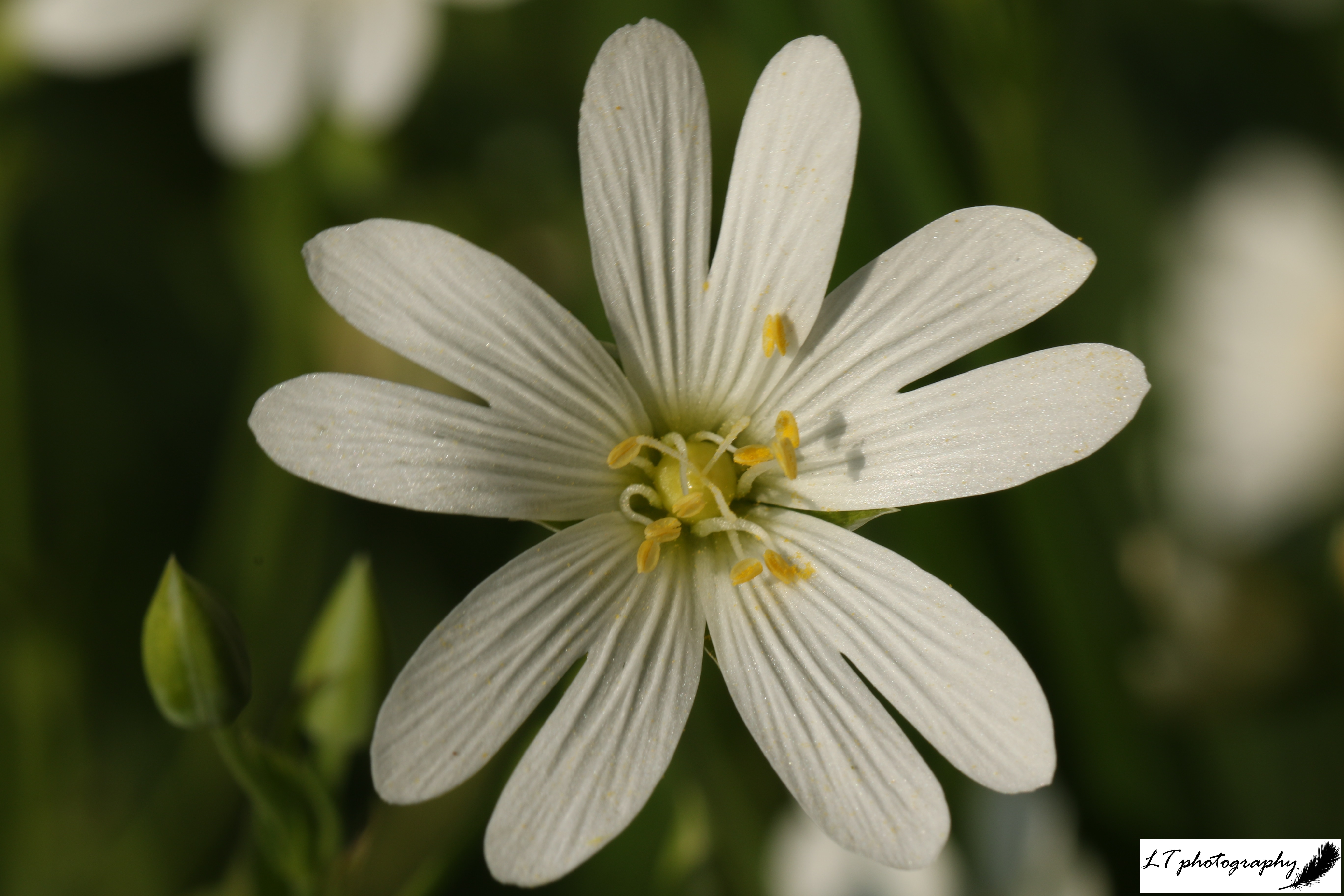
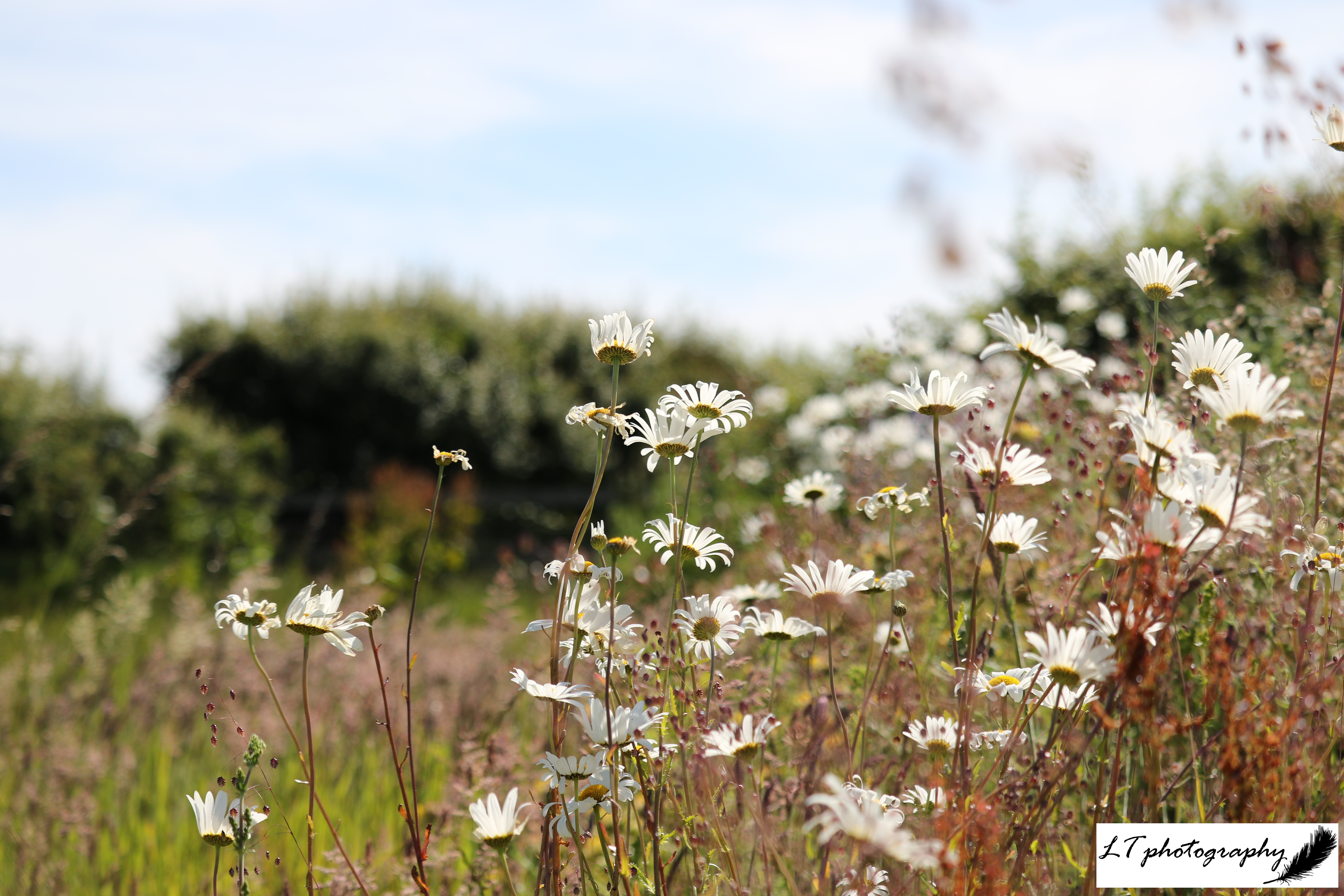
Plants flowering during spring 2024 occurred on average earlier, varying from 1 to 16 days. Following the same situation as with tree species, during spring 2025, the occurrence of plants flowering showed no true trend, with a 50:50 split between earlier or later. Primroses, cowslips, wood anemones, early purple orchids, yellow archangel, and oxeye daisies all first flowered 3-14 days earlier, whereas snowdrops, lesser celandines, daffodils, stitchwort, wild garlic, cuckooflowers, and bluebells all first flowered 5-21 days later. Like with the trees, no pattern was shown connected to month, and flowering this spring may instead also be due to fluctuating weather and temperature patterns.


Shrubs
During spring 2024, the majority of shrub events occurred earlier, ranging from 1 to 53 days. In spring 2025 though, there was more of a split. Of 18 recorded events, 10 were later than 2024, ranging from 1 to 29 days, 1 was the same day, and 7 were earlier than 2024, ranging from 4 to 20 days. Some species, such as blackthorn and elder, had all later events, but most species shared variation between budburst, leaves unfurling, and flowering. It is unsurprising that shrubs followed what was seen with other plant species though, being affected by the same factors, causing no discernable trends.


Insects
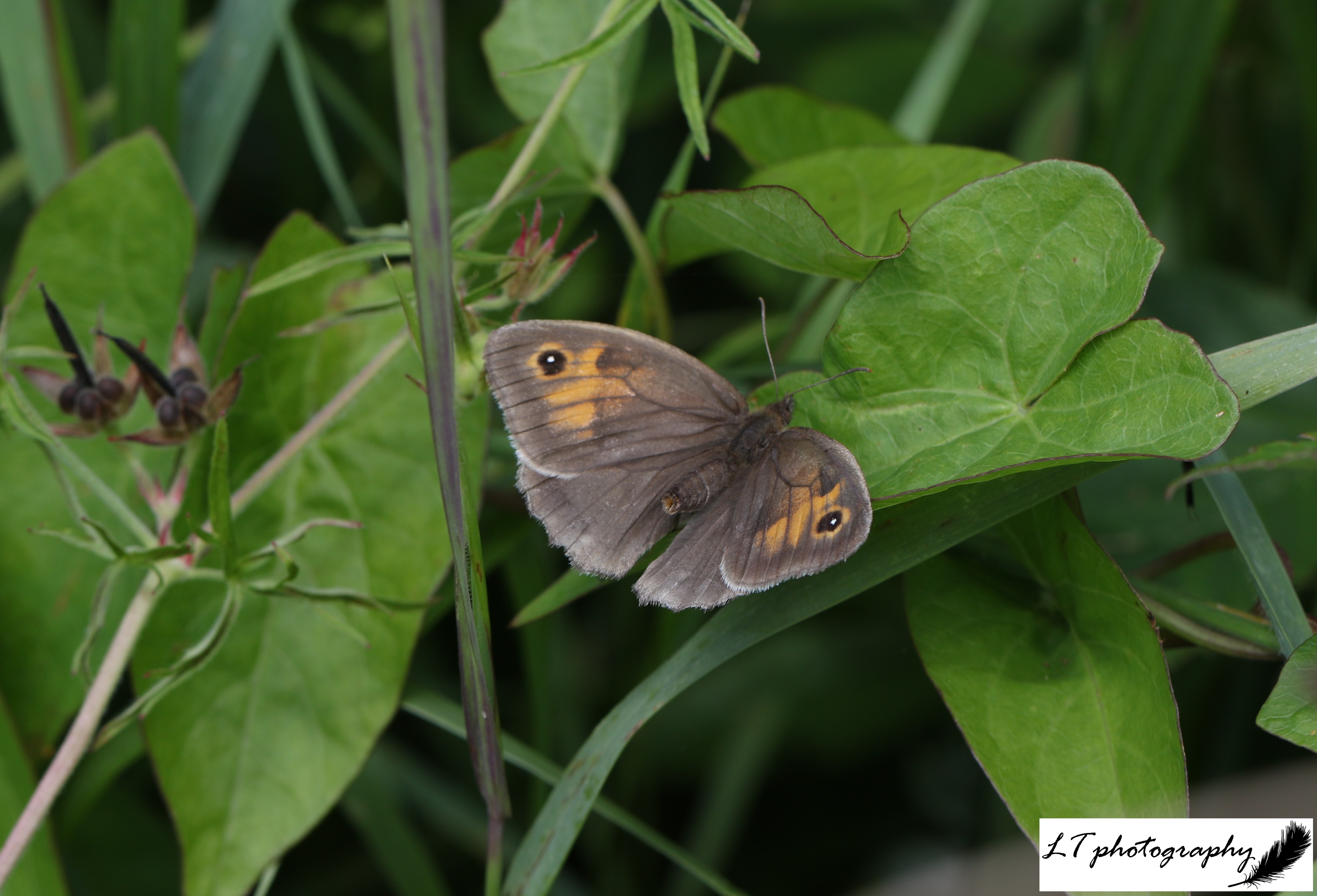
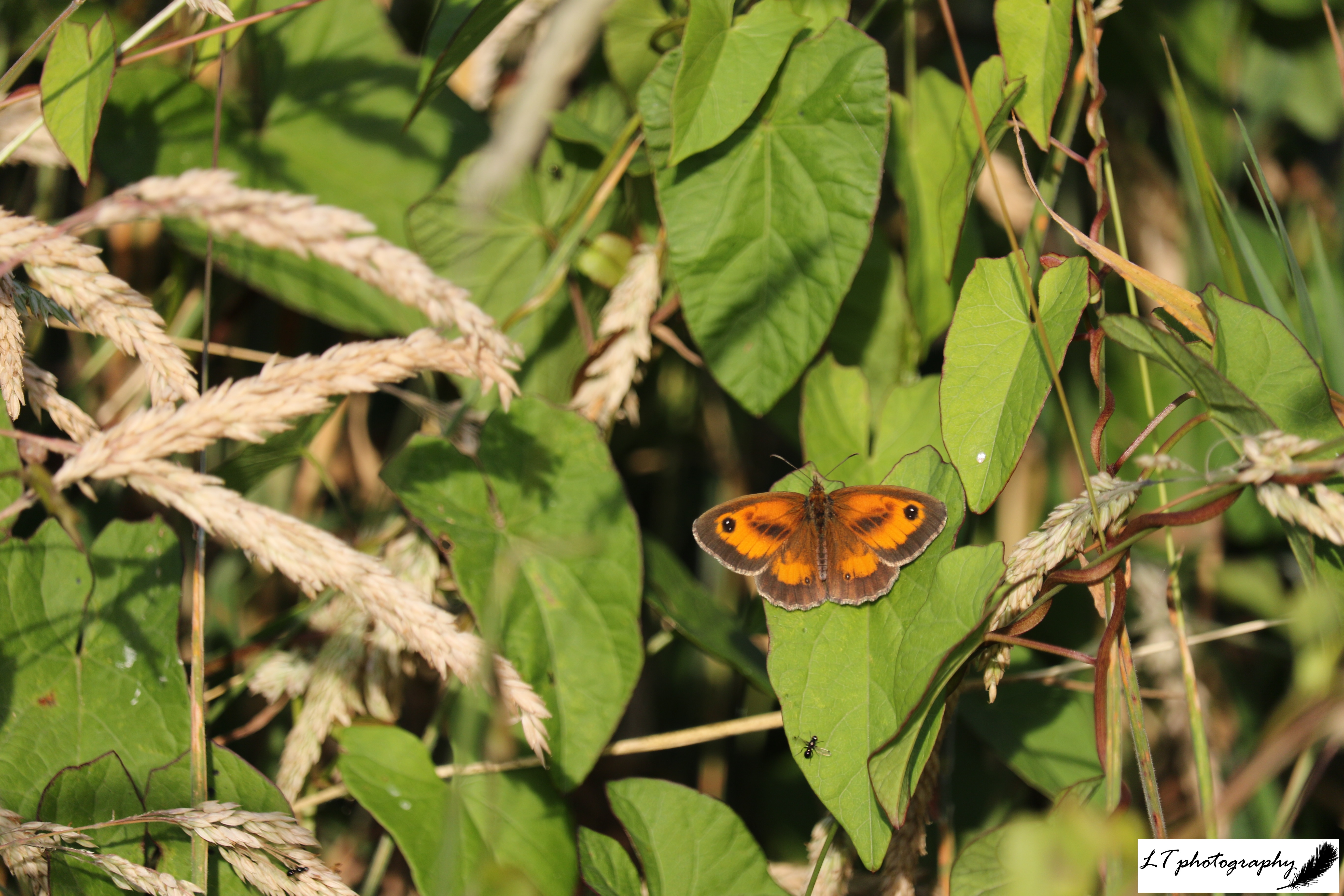
Of 10 species that had their first emergence date recorded during spring 2024, a 50:50 split was found for earlier and later dates. This year for the same 10 species though, there was a skew towards earlier emergences. For brimstone butterflies, buff-tailed bumblebees, 7-spotted ladybirds, peacock butterflies, small tortoiseshell butterflies, small white butterflies, and queen wasps, emergence ranged from 1-47 days earlier this spring. The exceptions were orange tip butterflies, red admiral butterflies, and speckled wood butterflies, emerging later by 4-32 days during April. Where plant species showed no great pattern between springs 2024 and 2025, these insect species recorded do show more earlier emergences, with on average warmer weather allowing this to occur.


Birds
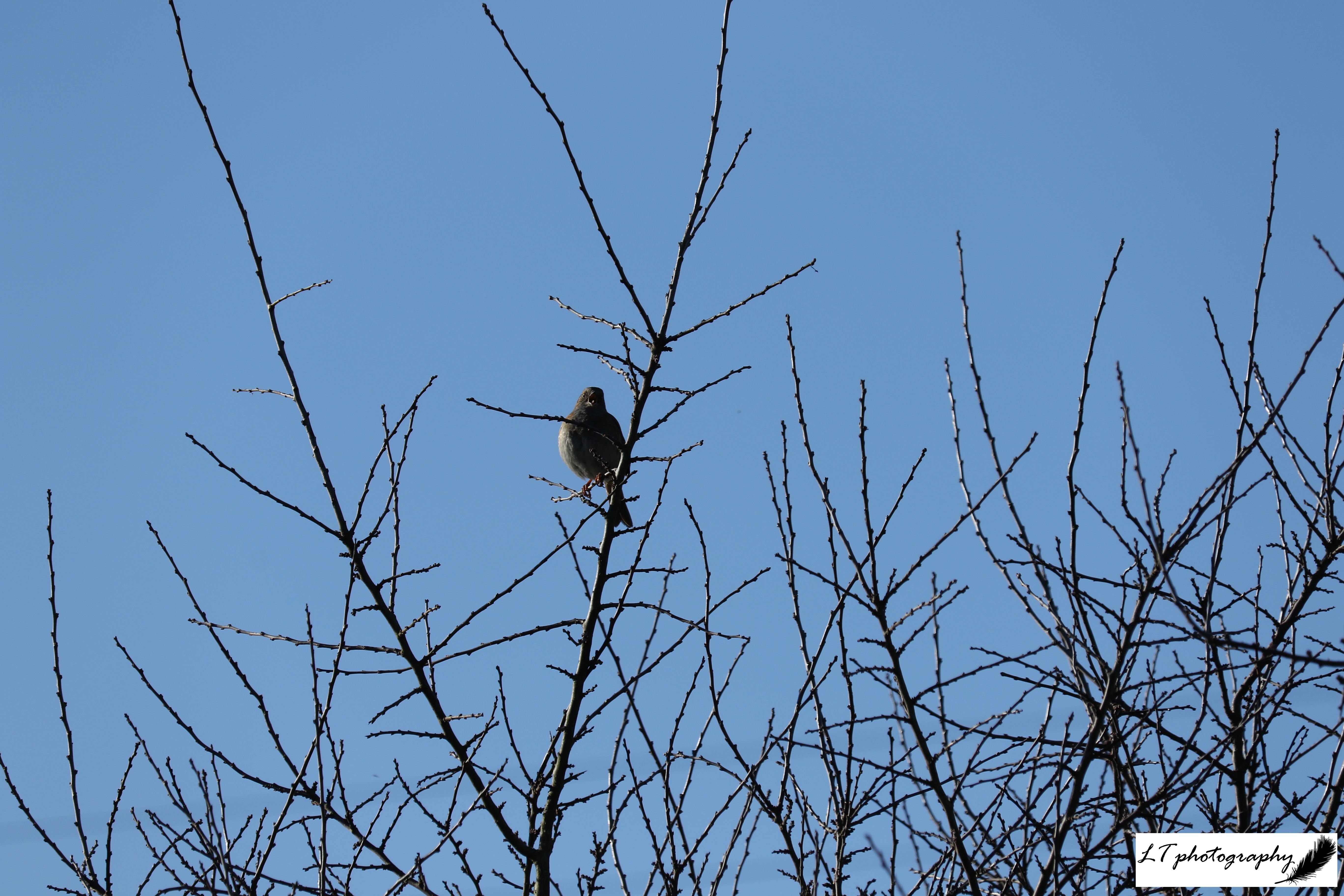
Over the last three years of recording bird events during spring, no clear trend was observed between years for the bird species that were recorded. For spring 2025 though, the events recorded were shown to have occurred on the same day as in 2024, or 1 to 26 days earlier. For example, cuckoos were heard earlier during April, and juvenile blackbirds were seen earlier, fledging during April. It is really interesting that where this year plant events were occurring all over the place compared to during previous years, bird species were responding earlier to spring conditions. This could be due to weather conditions being on average milder, whilst food sources were also made available earlier during spring this year.


Conclusion
When I first began writing this phenological report for my family’s Dorset farm this year, I began with the recorded plant species and was unable to find any observable trends between years and species, and within species. Though I was starting to feel that absence of trends was still important, things were looking more interesting when I turned my attention to recorded insect and bird species events. Both insect and bird species showed trends towards events occurring earlier this spring, which is more noticeable after a lack of trends over the last couple of years. These show that the season being on average warmer and sunnier this year did have an impact on animal species, even if more factors were involved in what was seen with recorded plant species.

Species List
- Alder (Tree) Alnus glutinosa
- Ash (Tree) Fraxinus excelsior
- Blackbird (Bird) Turdus merula
- Blackcap (Bird) Sylvia atricapilla
- Blackthorn (Shrub) Prunus spinosa
- Bluebell (Flowering Plant) Hyacinthoides non-scripta
- Brimstone butterfly (Insect) Gonepteryx rhamni
- Buff-tailed bumblebee (Insect) Bombus terrestris
- Chiffchaff (Bird) Phylloscopus collybita
- Common wasp (Insect) Vespula vulgaris
- Cowslip (Flowering Plant) Primula veris
- Cuckoo (Bird) Cuculus canorus
- Cuckooflower (Flowering Plant) Cardamine pratensis
- Daffodil (Flowering Plant) Narcissus spp.
- Dog rose (Shrub) Rosa canina
- Early purple orchid (Flowering Plant) Orchis mascula
- Elder (Shrub) Sambucus nigra
- English oak (Tree) Quercus robur
- Field maple (Tree) Acer campestre
- Greater stitchwort (Flowering Plant) Stellaria holostea
- Great-spotted woodpecker (Bird) Dendrocopos major
- Hawthorn (Shrub) Crataegus monogyna
- Hazel (Shrub) Crataegus monogyna
- Horse chestnut (Tree) Aesculus hippocastanum
- Lesser celandine (Flowering Plant) Ficaria verna
- Norway maple (Tree) Acer platanoides
- Orange-tip butterfly (Insect) Anthocharis cardamines
- Oxeye daisy (Flowering Plant) Leucanthemum vulgare
- Peacock butterfly (Insect) Aglais io
- Primrose (Flowering Plant) Primula vulgaris
- Lilac (Shrub) Syringa vulgaris
- Red admiral butterfly (Insect) Vanessa atalanta
- Rook (Bird) Corvus frugilegus
- Seven-spot ladybird (Insect) Coccinella septempunctata)
- Silver birch (Tree) Betula pendula
- Small tortoiseshell butterfly (Insect) Aglais urticae
- Small white butterfly
- Snowdrop (Flowering Plant) Galanthus spp.
- Song thrush (Bird) Turdus philomelos
- Speckled wood butterfly (Insect) Pararge aegeria
- Swallow (Bird) Hirundo rustica
- Sycamore (Tree) Acer pseudoplatanus
- Wild cherry (Tree) Prunus avium
- Wild garlic (Flowering Plant) Allium ursinum
- Wood anemone (Flowering Plant) Anemone nemorosa
- Yellow archangel (Flowering Plant) Lamium galeobdolon